Water Absorption and Specific Gravity
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Water Absorption
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing water absorption in aggregates. Can anyone tell me why this property is important for road construction?

I think it has to do with how much water the aggregate can hold?

Exactly! Lower water absorption means the aggregate is likely to be more durable. We aim for a maximum of 2% absorption. What might happen if it absorbs more water?

It could affect the strength of the pavement, right?

Correct! Excessive absorption can lead to weak mixes and reduced lifespan. Remember the acronym **WAM**: Water Absorption Matters!

Can we test the absorption in the lab?

Yes, there are specific tests we conduct to measure this. Let's move on to the next property.

So what's the significance of these tests in real-world applications?

Great question! They ensure that we select aggregates that enhance the pavement's durability and performance.

To recap, we learned that lower water absorption rates indicate better aggregate quality, which supports the longevity of road surfaces.
Exploring Specific Gravity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've covered water absorption, let's talk about specific gravity. How is it related to aggregates?

It's about how heavy the aggregate is compared to water, right?

Correct! Specific gravity typically ranges between 2.5 and 3.0 for road aggregates. Why do you think knowing this value is important?

It might help in calculating how much material we need for a project?

Exactly! Specific gravity helps determine the volume needed for proper mix design. Let’s use the mnemonic **GREAT**: Gravity Realizes Effective Aggregate Typology.

What would happen if the specific gravity is too low?

If aggregates have low specific gravity, they may not support the required loads, risking pavement failure. Remember, the properties of both water absorption and specific gravity collectively guide our aggregate selection and mix design.

So, can anyone summarize the importance of specific gravity?

It's crucial for determining the aggregate's suitability in construction and for mix calculations!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the significance of water absorption and specific gravity in road aggregates, noting that lower water absorption values indicate better performance, and typical specific gravity values range from 2.5 to 3.0. These properties are crucial for effective mix design and quality control in pavement construction.
Detailed
Water Absorption and Specific Gravity
Water absorption and specific gravity are vital physical properties of road aggregates that significantly affect their performance in construction.
- Water Absorption: This property measures the percentage of water an aggregate can absorb. Lower values (typically a maximum of 2%) indicate a more durable aggregate that performs better in road applications. High absorption rates can lead to excess water in the mix, affecting the strength and durability of the pavement.
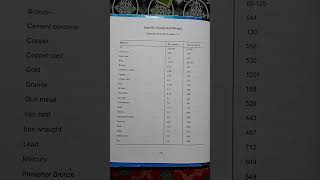
- Specific Gravity: This parameter refers to the density of the aggregate compared to water. For most road aggregates, specific gravity values generally range between 2.5 and 3.0. This property is essential for determining the quality and load-bearing capacity of pavement materials.
Together, these properties play a crucial role in mix design and quality control, influencing the longevity and performance of road surfaces under various traffic and environmental conditions.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Water Absorption
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Water Absorption: Lower absorption indicates better performance; max 2%.
Detailed Explanation
Water absorption refers to the ability of aggregate particles to soak up water. A lower percentage of water absorption is preferable as it suggests better quality and performance of the aggregates in concrete and asphalt mixtures. The maximum acceptable level of water absorption for road aggregates is set at 2%. This means that if aggregates can absorb less water than this threshold, they are considered to perform better in pavement construction.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge. A sponge that can absorb a small amount of water is more effective in holding and providing moisture than a sponge that can soak up a lot of water. Similarly, aggregates with low water absorption are more efficient because they maintain the integrity and strength of the paving material.
Specific Gravity
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Specific Gravity: Normally between 2.5 to 3.0 for road aggregates.
Detailed Explanation
Specific gravity is a measure of the density of a material compared to the density of water. For road aggregates, specific gravity usually falls between 2.5 and 3.0. This range indicates that aggregates are relatively dense, which contributes to the overall strength and stability of the pavement structure. Specific gravity considerations are essential for mix design, as they help engineers calculate the correct proportions of aggregates to achieve desired durability and performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using different types of rocks for a garden path. A heavier rock like granite will have a higher specific gravity compared to a lightweight pumice stone. In road construction, using aggregates with an appropriate specific gravity ensures that the pavement can support heavy vehicles and withstand wear and tear over time.
Importance of Water Absorption and Specific Gravity
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Importance: Affects the mix design and quality control.
Detailed Explanation
Both water absorption and specific gravity are crucial properties when designing concrete or asphalt mixes. They influence how much water is needed to achieve an appropriate workability and how well the aggregates will bond with the cement or bitumen. Understanding these properties helps in the quality control of materials, ensuring that the final pavement can handle the stress of traffic and environmental conditions effectively.
Examples & Analogies
When baking, the ratio of flour to water has significant effects on the final product. Too much water can make a cake soggy, while too little can make it dense and dry. Similarly, in road construction, the right balance of water based on the aggregates' absorption and specific gravity is vital to achieve a strong and durable pavement.
Key Concepts
-
Water Absorption: Lower values indicate better aggregate performance and durability.
-
Specific Gravity: Indicates the density of aggregates and is critical for mix calculations.
Examples & Applications
A tested aggregate with 1% water absorption is better suited for high-traffic areas compared to one with 4% absorption.
Aggregates with a specific gravity of 2.6 are typically acceptable for use in cement concrete pavements.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Water absorption's what we see, lower is better, you'll agree!
Stories
Imagine a sponge; it holds too much water and becomes heavy. Similarly, aggregates that absorb too much are like sponges that won't provide a solid foundation.
Memory Tools
Remember WASG: Water Absorption Stronger Gives great aggregates!
Acronyms
Use **GREAT** for Specific Gravity
Great Relevance for Effective Aggregate Typology.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Water Absorption
The percentage of water an aggregate can absorb, with lower values indicating better performance.
- Specific Gravity
The ratio of the density of an aggregate to the density of water, typically ranging from 2.5 to 3.0 for road aggregates.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
