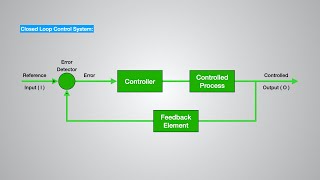
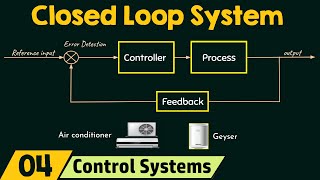
Closed-Loop (Feedback) Control Systems
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Closed-Loop Control Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing closed-loop control systems in robotics. Can anyone tell me what defines a closed-loop system?

Isn't it where the system uses feedback to adjust its operation?

Exactly! Closed-loop systems receive real-time data from sensors and use that information to adapt their actions. This is different from open-loop systems, which do not adjust based on feedback. Let's remember this difference with the acronym F.A.R. for Feedback, Adjust, and Real-time.

So, closed-loop systems are better for tasks that need precision?

Correct! They enhance accuracy by correcting errors as they happen, making them vital in many applications, especially in industrial settings.
Advantages of Closed-Loop Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone name some advantages of using closed-loop control systems?

They can adapt to changes in the environment, right?

Exactly! Their adaptability allows them to fine-tune operations in various conditions. Additionally, increased accuracy is another key advantage. Can anyone think of real-world applications where this is crucial?

In industrial robots, like those on assembly lines, they need high precision!

Great example! Using these systems ensures that robots can constantly correct their paths or actions to maintain high standards of performance.
Real-World Applications of Closed-Loop Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve into where we commonly see closed-loop control systems in action. What industries do you all think utilize this technology?

Maybe in manufacturing with robots on the production line?

Absolutely! Manufacturing is a primary sector for these systems. Robots on assembly lines rely on feedback to maintain precision. What about mobile robots, like drones? How might closed-loop systems help them?

They would need feedback to navigate around obstacles and adjust their flight paths!

Exactly! This responsiveness allows for safer navigation and operational efficiency. Remember, closed-loop systems are key players in both industrial and mobile applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section delves into the structure and advantages of closed-loop control systems in robotics, emphasizing their reliance on sensor feedback for real-time adjustments, leading to improved performance and accuracy. It distinguishes these systems from open-loop models and highlights their prevalent application in industrial and mobile robots.
Detailed
Closed-Loop (Feedback) Control Systems
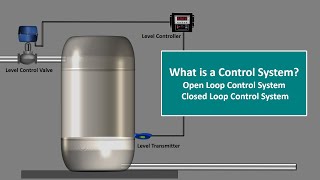
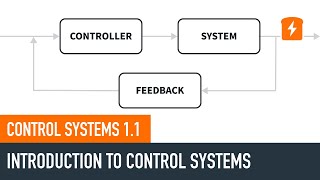
Closed-loop control systems, also known as feedback control systems, are integral to enhancing the functionality of robotics. Unlike open-loop systems, which operate without feedback, closed-loop systems actively utilize sensor data to adjust and refine the robot's performance in real-time. This capability allows for increased accuracy and the ability to adapt to changing conditions or environments, making closed-loop systems essential in complex applications requiring precise control.
Key Features of Closed-Loop Control Systems
- Real-Time Feedback: Sensors provide continuous data regarding the robot's state and environment, enabling the controller to make informed adjustments.
- Increased Accuracy: By correcting deviations and errors through feedback, these systems enhance the precision of the robot's actions.
- Adaptability: Closed-loop systems can respond dynamically to new stimuli or changes, ensuring optimal operational effectiveness in various situations.
Applications
Closed-loop control systems are commonly found in industrial robots (like those used in assembly lines) and mobile robots (such as drones), ensuring reliability and efficiency in performance. Their significance cannot be overstated, as they play a crucial role in realizing the potential of robots in automation and robotics.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Closed-Loop Control Systems
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Closed-Loop (Feedback) Control Systems
• Use sensors to provide real-time data to the controller.
• More accurate and adaptive to changes.
• Common in industrial and mobile robots.
Detailed Explanation
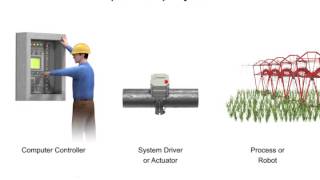
Closed-loop control systems integrate sensors that collect real-time data about the system's performance and conditions. This data is sent to the controller, which processes it to adjust the system's actions accordingly. By employing feedback from the environment, these systems can make corrections or changes to their operations based on real-time information. This adaptability leads to better precision in tasks and improved efficiency when compared to open-loop systems, which lack feedback.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine driving a car with a GPS system. The GPS continuously assesses your location and adjusts your route based on traffic conditions. If there's a traffic jam, it can reroute you to save time. Similarly, closed-loop systems use feedback to correct their course of action for optimal performance.
Advantages of Closed-Loop Systems
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• More accurate and adaptive to changes.
Detailed Explanation
One of the key advantages of closed-loop control systems is their ability to adapt to changing conditions. For example, in a robot performing assembly tasks, if a part is slightly misplaced, the system can correct its position using sensor feedback, rather than relying on pre-set instructions. This ability to adjust in real time significantly enhances the overall accuracy of tasks and minimizes errors.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a thermostat in your home heating system. It continuously checks the temperature and adjusts the heating output accordingly. If it gets colder, the thermostat increases the heating to maintain your desired temperature. This feedback loop ensures that your environment stays comfortable, just like how a closed-loop control system ensures optimal operation.
Applications of Closed-Loop Control Systems
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Common in industrial and mobile robots.
Detailed Explanation
Closed-loop control systems are widely used across various industries, particularly in robotics. In industrial settings, robots equipped with sensors can monitor their surroundings, detect obstacles, and adjust their tasks on-the-fly, ensuring efficient operation. In mobile robots, such as drones or autonomous vehicles, these systems allow for navigation and obstacle avoidance, making them valuable in applications like delivery and surveying.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a drone navigating through a forest. As the drone flies, it uses sensors to detect trees and avoid collisions. If it gets too close to a tree, the onboard closed-loop system can automatically alter its path to avoid it, similar to how a person would instinctively steer away from an obstacle while walking.
Key Concepts
-
Closed-Loop Control: Systems that utilize feedback to improve performance.
-
Feedback: The data collected by sensors that informs the controller about adjustments needed.
-
Accuracy: The importance of precise operations in robotics applications.
-
Adaptability: The ability of robots to adjust automatically to new conditions.
Examples & Applications
Industrial robots on assembly lines that adjust their speed and operations based on the tasks they're performing.
Drones that analyze real-time data about wind and obstacles to navigate accurately.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Feed the loop, make it tight, robot actions will be right.
Stories
Imagine a robot chef. It uses sensors to gauge temperature and adjust cooking time, making sure every dish is perfect each time.
Memory Tools
A.R.T. for Adaptability, Real-time Feedback, and Timely Adjustments.
Acronyms
F.A.R. - Feedback, Adjust, Real-time.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ClosedLoop Control System
A control system that uses sensor feedback to adjust actions in real-time for increased accuracy and adaptability.
- Feedback
Information obtained from sensors that is used to refine control actions.
- Accuracy
The degree to which a robot's actions conform to a desired outcome.
- Adaptability
The ability of a system to adjust its operations based on feedback from its environment.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
