Types of Actuators
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Electric Actuators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are diving into electric actuators. Can anyone tell me what an electric actuator does?

Isn't it a device that converts electrical energy into motion?

Correct! Electric actuators, like stepper motors and servomotors, are crucial in providing precise control. They enable robotic arms to operate with high accuracy. Can anyone name an application for these?

They are used in robotic arms in manufacturing, right?

Exactly! They are perfect for applications where precision and repeatability are key. Remember the acronym 'PEAR'—Precision, Efficiency, Accuracy, and Repeatability—when thinking of electric actuators.

What’s the difference between a stepper motor and a servomotor?

Great question! Stepper motors divide a full rotation into equal parts, allowing precise positioning, while servomotors offer feedback to the controller, making them better for dynamic positions. Let's move on to hydraulic actuators.
Hydraulic Actuators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about hydraulic actuators. Who can tell me how they work?

They use pressurized fluids to generate force?

Exactly! They are known for creating high force outputs. Where do you think these are commonly used?

In construction machinery?

That's right! Hydraulic actuators are ideal for heavy lifting tasks. They can handle significant loads, making them invaluable in cranes and excavators. Let’s remember 'HUGE'—High Utility for Generating Energy—as a mnemonic for hydraulic actuators.

So, are they more powerful than electric actuators?

Yes, in terms of sheer force yes! But they are generally slower and are more complex in terms of maintenance. Lastly, let’s discuss pneumatic actuators.
Pneumatic Actuators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, we have pneumatic actuators. Who can explain their primary feature?

They use compressed air, right?

Correct! They are great for rapid and repetitive motion. What industries do you think utilize pneumatic actuators?

Manufacturing, I guess, like in pick-and-place systems?

Yes! That's a perfect example. They are generally less expensive and ideal for applications where speed is prioritized. Remember the mnemonic 'FAST'—Forces Air for Speed and Torque—in relation to pneumatic actuators. What do you think is the advantage of using pneumatics over hydraulics?

I think pneumatics are lighter and quicker?

Correct! They are more suitable for tasks requiring speed and less weight. In summary, we discussed electric, hydraulic, and pneumatic actuators today—each with its unique strengths.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Actuators play a crucial role in robotics by converting energy into motion. This section outlines three main types of actuators—electric, hydraulic, and pneumatic—highlighting their characteristics, uses, and suitable applications in robotic systems.
Detailed
Types of Actuators
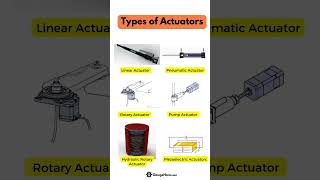
Actuators are essential components in robotic systems, responsible for converting various forms of energy into mechanical motion. This section discusses three primary types of actuators used in robotics:
- Electric Actuators: These include stepper motors and servomotors, which provide precise control of motion through electrical signals. They are suitable for applications requiring high accuracy and repeatability. Electric actuators are popular in applications like robotic arms for manufacturing and automation.
- Hydraulic Actuators: Utilizing pressurized fluid, hydraulic actuators are capable of producing high force outputs, making them ideal for heavy lifting and applications that require significant power. Commonly found in construction equipment, these actuators offer robustness in environments where heavy loads need to be manipulated.
- Pneumatic Actuators: Using compressed air, pneumatic actuators excel in applications requiring rapid and repetitive motion. They are commonly used in environments where speed and lightweight operations are necessary, such as pick-and-place systems in manufacturing. These actuators are typically less expensive compared to electric or hydraulic counterparts, especially where high-speed actions are prioritized.
Understanding these types of actuators is crucial for selecting the appropriate actuator type based on the specific application needs in robotics and automation.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Electric Actuators
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Electric Actuators: Stepper motors, servomotors for precision motion.
Detailed Explanation
Electric actuators are devices that convert electrical energy into precise motion. They typically use stepper motors or servomotors to achieve controlled and accurate movements. Stepper motors move in discrete steps, allowing for precise positioning, while servomotors provide continuous rotation with feedback control, making them ideal for applications requiring high precision.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a 3D printer that uses electric actuators to move the print head. Each small step the motor takes allows the printer to place material very accurately layer by layer, creating intricate designs with great detail.
Hydraulic Actuators
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Hydraulic Actuators: For high force applications like heavy lifting.
Detailed Explanation
Hydraulic actuators use pressurized fluid to create movement. They are capable of generating significant force and are commonly used in applications that involve heavy lifting and powerful movements. For instance, they can lift large construction equipment or heavy loads because fluid under pressure can exert a lot of force on a cylinder.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a hydraulic lift used in a garage. When you press a button, hydraulic fluid pushes against a piston, lifting a car into the air for repairs. This mechanism showcases the power and efficiency of hydraulic actuators in handling heavy weights.
Pneumatic Actuators
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Pneumatic Actuators: Use compressed air; good for fast and repetitive motion.
Detailed Explanation
Pneumatic actuators function using compressed air to produce motion. They are particularly effective for tasks requiring quick, repetitive movements, such as in assembly lines where products need to be moved or assembled rapidly. Because they operate at high speeds and can return to their original position quickly, pneumatic actuators are popular in many manufacturing environments.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a pneumatic drill used in construction. The compressed air inside the drill makes it powerful and fast, allowing it to drill through tough materials quickly. Similarly, pneumatic actuators work efficiently to perform repetitive tasks, making processes in manufacturing swift and effective.
Key Concepts
-
Electric Actuators: Essential for precise control and used in manufacturing robotics.
-
Hydraulic Actuators: Provide high force needed for heavy lifting in machinery.
-
Pneumatic Actuators: Utilize compressed air for fast movements in various applications.
Examples & Applications
Electric actuators are used in robotic arms to ensure high precision in tasks like welding.
Hydraulic actuators power heavy machinery such as excavators and bulldozers.
Pneumatic actuators are used in conveyor belts to ensure quick transport of materials in factories.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Electric motors are sure to delight, providing precision and motion just right.
Stories
Imagine a factory where robots move swiftly. Electric motors carefully paint the scene, hydraulic systems lift heavy goods, and pneumatic devices zoom around moving parts effortlessly, showcasing teamwork and efficiency.
Memory Tools
Remember 'EHP'—Electric for precise, Hydraulic for heavy, and Pneumatic for quick.
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'PEH' for the types of actuators
Precision (Electric)
Energy (Hydraulic)
and High-speed (Pneumatic).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Actuator
A device that converts energy into motion, essential in robotic systems.
- Electric Actuator
A type of actuator that uses electrical energy to produce controlled motion and precision.
- Hydraulic Actuator
An actuator that utilizes pressurized fluid to generate movement, ideal for high-force applications.
- Pneumatic Actuator
A device that uses compressed air to produce motion, suited for high-speed, repetitive tasks.
- Servo Motor
A motor that provides precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration.
- Stepper Motor
An electric motor that divides a full rotation into a series of equal steps for precision control.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
