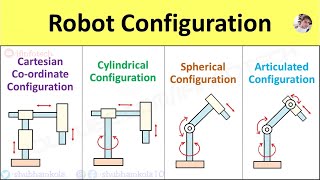
Interface Types
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Teach Pendants
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In today's session, we will start off by discussing teach pendants. Can anyone tell me what a teach pendant is?

Isn't it a handheld device used to control robots manually?

Exactly, Student_1! Teach pendants are crucial for programming and controlling robots. They allow operators to guide the robot's movements directly. This direct manipulation is useful for programming complex tasks. Who can think of a situation where a teach pendant might be particularly helpful?

Maybe during the initial setup of a robot on a construction site?

That's right! During setup and troubleshooting, they provide a practical way to interface with the robot. Remember, the acronym 'T.P.' can help you remember 'Teach Pendant'!

What kind of programming can you do with them?

Good question, Student_3! They allow manual control for tasks and can help in creating and storing waypoints for automated paths. To sum up, teach pendants offer both flexibility and control in robotic applications.
Gesture and Voice Interfaces
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's dive into gesture and voice interfaces. Why do you think these methods of interaction are beneficial?

They make it easier for people to communicate their needs without complicated controls.

That's correct! They promote a more natural interaction. For example, instead of pressing multiple buttons, you can simply wave a hand or give a voice command to instruct the robot. This could reduce the learning curve for new operators. Can anyone share an example of where this might be applied?

In a construction site, if a worker is busy, they could just say 'lift' to make a robot perform a lifting task.

Exactly! A practical scenario indeed. Always remember, these interfaces help increase safety since the operator can maintain visual contact with the task while giving commands. In short, intuitive interfaces can enhance operational efficiency!
Augmented Reality Interfaces
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's discuss augmented reality interfaces. What do you think is the primary benefit of using AR for interacting with robots?

It provides real-time data and visuals, right?

Correct! AR can overlay useful operational commands or data onto the real world, allowing for an improved understanding of what the robot is doing. Can anyone think of how this would be useful in civil engineering?

Maybe for inspecting structures? If I could see data about stress or strain over the building I'm inspecting through AR, that would be super helpful.

Absolutely! That way, operators can make informed decisions on the spot. Remember, AR improves not just interaction but also situational awareness. To summarize, using AR interfaces enhances our ability to control and understand robotic systems on-site.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, key interface types for effective human-robot interaction are discussed. Teach pendants, gesture and voice interfaces, and augmented reality (AR) interfaces facilitate intuitive commands and enhance operational efficiency. Understanding these interfaces is crucial for deploying robots in civil engineering applications safely and effectively.
Detailed
Interface Types in Human-Robot Interaction
In the growing field of robotics, especially within civil engineering, the interface between humans and robots is essential for successful operation and collaboration. This section outlines three primary types of interfaces:
- Teach Pendants: These are handheld devices that allow operators to program and control robots manually. They provide an intuitive way to direct robotic behavior and can be used for troubleshooting and testing.
- Gesture and Voice Interfaces: These interfaces enable natural and intuitive interaction between human operators and robots. Using gestures or voice commands significantly enhances the ease of communication, making robot operations smoother and more human-friendly.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Interfaces: AR interfaces allow operators to visualize the robotic systems’ state through wearable devices. This real-time access to data or instructions helps improve decision-making and operational efficiency.
Understanding these interfaces is crucial for leveraging robotics effectively in civil engineering projects, promoting safer and more efficient working conditions.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Teach Pendants
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Teach Pendants: Handheld devices to manually program and control robots.
Detailed Explanation
Teach Pendants are like remote controls used to operate robots. They allow an operator to input commands directly into the robot. This programming can involve using buttons or a screen on the Teach Pendant to enter movement commands or other instructions. By using this device, an operator can guide the robot through its tasks manually, giving them direct control over its operations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using a remote control car. Just like you have buttons to move it forward or backward, a Teach Pendant allows you to control a robot’s movements precisely. If you want the robot to pick up an object, you tell it where to go and when to move, similar to how you navigate your toy car.
Gesture/Voice Interfaces
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Gesture/Voice Interfaces: Allow natural interaction between human operators and robots.
Detailed Explanation
Gesture and voice interfaces utilize technology to interpret human actions and commands. Gesture interfaces can recognize movements, such as waving a hand to signal the robot to start or stop. Voice interfaces enable operators to issue commands verbally, making interaction more intuitive. This hands-free approach allows for efficient communication with robots, especially in situations where manual input is inconvenient or impossible.
Examples & Analogies
Think of smart home assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Home. When you say, 'Turn on the lights,' the assistant understands your command and acts on it. Similarly, robots with gesture or voice interfaces can understand human commands, making them easier to use in everyday tasks.
Augmented Reality (AR) Interfaces
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Augmented Reality (AR) Interfaces: Operators view real-time data or instructions through wearable devices.
Detailed Explanation
Augmented Reality interfaces enhance a user’s interaction with robots by overlaying digital information onto the real world. Using AR glasses or screens, operators can see data such as robot status, location, and instructions while having a visual connection to the physical environment. This real-time feedback helps operators make informed decisions quickly and accurately.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine wearing a pair of smart glasses that display navigation paths while you’re walking through a city. Just as you would see directions on the glasses without looking at a map, AR interfaces allow robot operators to receive information and instructions right in their line of sight, seamlessly integrating digital data with the physical environment.
Key Concepts
-
Teach Pendants: Handheld devices for manual programming and control of robots.
-
Gesture and Voice Interfaces: Intuitive interaction methods that use body movements or spoken commands.
-
Augmented Reality Interfaces: Systems that provide real-time data and visual overlays to enhance operator awareness.
Examples & Applications
A construction worker uses a teach pendant to program a robotic arm for specific tasks like placing concrete.
An operator gives voice commands to direct a cleaning robot in a warehouse.
Using AR glasses, a technician inspects a bridge while visualizing stress data on the structure.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When you want your robot to glow, speak a command or let your hands show.
Stories
Imagine a robotic assistant at a construction site, who understands your gestures and voice, allowing you to focus on inspecting buildings while it carries the load.
Memory Tools
T.G.A. - Teach Gestures and Augmented reality are the interfaces in robotics.
Acronyms
R.A.G.E - Remember Augmented, Gesture, and Enhanced interaction for robotics.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Teach Pendant
A handheld device used for programming and controlling robotic movements manually.
- Gesture Interface
A control method that allows users to interact with robots using hand or body movements.
- Voice Interface
A control method allowing users to communicate with robots using spoken commands.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Interface
An interface that overlays digital information onto the real-world view, enhancing situational awareness.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
