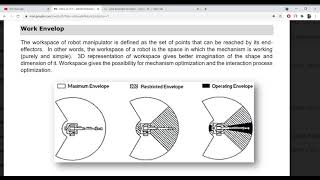
Work Envelope
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Work Envelope
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore the concept of the work envelope in robotics. Can anyone tell me what they think it might refer to?

Is it related to the area where a robot can work?

Exactly! The work envelope is the 3D space within which a robot can operate. It's crucial for selecting the right robot for specific tasks.

So, how does the robot's design affect this work envelope?

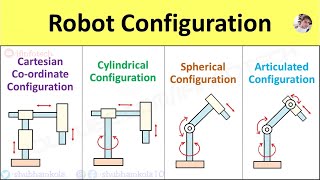
Good question! The design, type of joints, and range of motion all influence the size and shape of the work envelope. For instance, Cartesian robots have rectangular envelopes.

What about other types of robots?

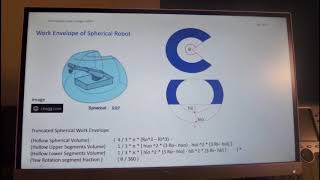
Articulated robots have spherical or irregular work envelopes. Understanding these differences helps us choose the right robot for tasks like concrete pouring.

In summary, knowing a robot's work envelope is essential in assessing its suitability for construction tasks.
Applications Based on Work Envelope
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into how the work envelope impacts construction tasks. Why do you think understanding this concept is vital?

It probably helps ensure the robot can actually reach the areas where it needs to perform tasks.

Correct! For example, in concrete pouring, the robot must maintain a certain reach to cover the area effectively without running into obstacles.

How does a robot's work envelope affect its efficiency?

An appropriate work envelope ensures that the robot can move freely, thereby increasing efficiency and minimizing errors. If the envelope is too small, it may not reach necessary points.

So, if we have a project with tight spaces, we need a robot with a smaller or more flexible work envelope?

Exactly! Selecting a robot with the right work envelope tailored to project specifications can greatly enhance productivity.

To recap, understanding a robot's work envelope is essential for its effective application in construction tasks.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Understanding the work envelope is vital for selecting the appropriate robot for construction tasks, as it outlines the operational capabilities based on structure and joint type. Different robot types possess unique work envelopes influencing their effectiveness in specific tasks.
Detailed
Work Envelope
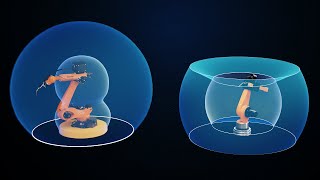
The Work Envelope refers to the three-dimensional space within which a robot can effectively operate, heavily influenced by the robot's design, type of joints, and its range of motion. This concept is critical for effective selection and application of robotic systems, particularly in construction tasks such as concrete pouring and material placement, where precise movement is crucial.
Types of Work Envelopes
- Cartesian Robots: Feature a rectangular work envelope, allowing movement along the x, y, and z axes in straight lines.
- Articulated Robots: Possess spherical or irregular work envelopes, offering more versatile movement but with potentially more complex spatial navigation.
Understanding and calculating the work envelope is essential for ensuring the selected robotic system can meet the physical demands of specific tasks. Selecting a robot with an appropriate work envelope aligns with project requirements and operational efficiency.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Work Envelope
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Work Envelope is the 3D space within which a robot can operate. It depends on the robot’s structure, type of joints, and range of motion.
Detailed Explanation
The Work Envelope refers to the specific three-dimensional area where a robot can function and perform tasks. This area is influenced by various factors, including the robot's physical build, the kind of joints it has, and how far those joints can move. Understanding the Work Envelope is crucial for determining how a robot can be used effectively in different applications.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a human being limited by their arm reach. If someone has a long reach, they can easily grab items from further away, whereas someone with a short reach may struggle to do the same. Similarly, a robot's Work Envelope defines its ability to reach out and interact with its environment.
Types of Robots and Their Work Envelopes
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Cartesian Robots have rectangular work envelopes.
• Articulated Robots have spherical or irregular work envelopes.
Detailed Explanation
Different types of robots have distinct Work Envelopes. For instance, Cartesian robots, which typically move along straight axes, have a rectangular Work Envelope, allowing them to operate effectively within a defined length and width. In contrast, articulated robots, like robotic arms, often have a more complex, spherical, or even irregular Work Envelope due to their multi-joint structures, allowing for more flexibility in their movements.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a robotic arm modeled after a human's arm. A Cartesian robot would be like a simple machine moving straight up and down along a straight line, like an elevator moving between floors. An articulated robot, however, resembles a person who can wave their hand in various angles and curves, allowing more intricate movements to access different areas.
Importance of Understanding Work Envelope
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding the work envelope is essential for selecting robots in construction tasks such as concrete pouring or material placement.
Detailed Explanation
Grasping the concept of the Work Envelope is vital when choosing the right robot for specific tasks in construction. For example, if a robot is required to pour concrete in particular locations, its Work Envelope must encompass those areas without any obstructions. Failure to understand this could result in selecting a robot that cannot reach all necessary spots, leading to inefficiencies or incomplete tasks.
Examples & Analogies
When picking tools for a job, like painting a room, you would need to ensure that your paintbrush can reach every corner and nook. If a brush is too short or the handle too thick, you won't be able to paint effectively. Similarly, ensuring that a robot's Work Envelope matches the job requirements ensures that it can complete tasks efficiently and accurately.
Key Concepts
-
Work Envelope: The 3D space in which a robot operates effectively.
-
Cartesian Robots: Robots characterized by linear movement in rectangular work envelops.
-
Articulated Robots: Robots with versatile movement and irregular work envelops, suitable for complex tasks.
Examples & Applications
In a construction site, a Cartesian robot may use its rectangular work envelope to pour concrete evenly across a base.
An articulated robot might operate in high places with a spherical work envelope to conduct inspections and repairs in hard-to-reach areas.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a robot's space, it can twist and turn,/ Select the right type, for smooth tasks to earn.
Stories
Imagine a robot named Rosie who couldn't reach her tools. She learned that her joints and design shaped her work envelope, allowing her to move freely or get stuck like in a narrow tunnel.
Memory Tools
For selecting robots: 'Joints Make Space' (JMS) - remember the joints affect the robot's operational space.
Acronyms
W.E.R.K (Work Envelope Research and Knowledge) helps us remember to investigate a robot's workspace effectively.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Work Envelope
The 3D operational space within which a robot can operate, influenced by its structure and joint type.
- Cartesian Robot
A robot with a rectangular work envelope that moves in straight lines along x, y, and z axes.
- Articulated Robot
A robot with a work envelope that can be spherical or irregular, allowing for versatile movements.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
