Types of Sensors
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Proximity Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by discussing proximity sensors. They are essential in robotics as they can detect the presence or absence of objects without physical contact. Can anyone tell me how you think this might be useful?

Maybe for avoiding obstacles while moving?

Exactly! Proximity sensors prevent collisions by detecting nearby obstacles. They’re critical for mobile robots. Can anyone remember another application for these sensors?

I think they could be useful in security systems?

That's correct! They can be used to monitor entrances and ensure security. So, remember: Proximity Sensors = Collision Avoidance!
Infrared and Ultrasonic Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive into infrared and ultrasonic sensors. Who can explain how these work?

Infrared sensors detect heat or light, and ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to measure distance.

Good job! Infrared sensors are great for detecting objects based on heat, while ultrasonic sensors are perfect for measuring distances. Can you think of places where this technology might be used?

In robots that need to avoid hitting walls or in parking assist systems for cars?

Exactly! Both sensors are widely used in automotive applications and robotics. Remember: Infrared and Ultrasonic Sensors = Distance Measurement!
Gyroscopes and Accelerometers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's look at gyroscopes and accelerometers. What do you think these devices measure?

Gyroscopes measure rotation, while accelerometers measure how fast something is speeding up or slowing down.

Correct! Gyroscopes help in maintaining orientation, which is crucial for drones and robots. Accelerometers help determine speed in motion. Can anyone think of a practical application?

They must be used in smartphones for changing screen orientation?

Right again! They're also vital in gaming and navigation. Remember: Gyroscopes = Orientation; Accelerometers = Speed and Direction!
Vision Sensors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s discuss vision sensors. What functions do they perform?

They can capture images and help with recognizing objects and faces.

Absolutely! Vision sensors are essential for robotic vision tasks like object detection and navigation. What implications do you think this has for the future of robotics?

It means robots can interact more naturally with humans and environments!

Exactly! As vision sensors evolve, so do the possibilities for application. Remember: Vision Sensors = Image Capture and Recognition!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the different types of sensors integral to robotic systems, including proximity sensors, vision sensors, and motion detectors. Each sensor type serves unique purposes, enhancing the robot's interaction with its environment and enabling precise automation.
Detailed
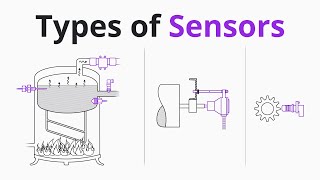
Types of Sensors
This section delves into the essential types of sensors utilized in robotics and automation, which play a pivotal role in enabling robots to interact with their environment effectively. Sensors are devices that detect changes or events in their surroundings and convert this information into signals that can be read and processed by control systems.
Key Types of Sensors:
- Proximity Sensors: These sensors detect the presence or absence of nearby objects without any physical contact. They are crucial for applications like obstacle detection in mobile robots.
- Infrared and Ultrasonic Sensors: Used for measuring distances and detecting obstacles, these sensors utilize different methods—infrared sensors work with light waves, while ultrasonic sensors use sound waves.
- Gyroscopes and Accelerometers: These sensors detect orientation and movement. Gyroscopes measure the rate of rotation around the robot's axes, while accelerometers measure the acceleration forces acting on the robot.
- Vision Sensors (Cameras): These sensors capture images and enable functions such as object recognition, face detection, and flaw detection in materials or components.
Understanding the functionalities and applications of these sensors is crucial for effective sensor integration in robotic systems, enabling precise control and automation.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Proximity Sensors
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Proximity Sensors: Detect presence or absence of objects.
Detailed Explanation
Proximity sensors are devices that can detect whether an object is nearby or far away, without needing to physically touch it. This is achieved through various technologies, such as infrared beams, magnetic fields, or capacitive sensing. For instance, when a person approaches a door with a proximity sensor, the sensor detects their presence and triggers the door to open automatically, allowing for hands-free entry.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a proximity sensor as a doorman who knows when someone is approaching the door. Instead of waiting for someone to knock, the doorman opens the door as soon as he sees the person getting close, making the entrance seamless for guests.
Infrared and Ultrasonic Sensors
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Infrared and Ultrasonic Sensors: Measure distances and detect obstacles.
Detailed Explanation
Infrared and ultrasonic sensors work by emitting waves and measuring the time it takes for the waves to bounce back after hitting an object. Infrared sensors use light waves, while ultrasonic sensors use sound waves. These sensors can determine how far away an object is based on the time delay of the reflected signals. They are commonly used in autonomous vehicles to avoid obstacles and help in navigation.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a bat using echolocation — it emits sounds that bounce off objects, allowing it to navigate in complete darkness. Similarly, ultrasonic sensors function like bats, helping robots identify how far away obstacles are in their paths.
Gyroscopes and Accelerometers
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Gyroscopes and Accelerometers: Detect orientation and movement.
Detailed Explanation
Gyroscopes are sensors that measure the rotation of an object, while accelerometers measure acceleration, which is the change in velocity. Together, they help determine an object's orientation in space and track its movement. This is particularly important in robotics, as it allows robots to maintain balance and navigate effectively, especially in dynamic environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to keep your balance on a bicycle. Gyroscopes act like your inner sense of balance, helping you understand when to lean or adjust to stay upright, while accelerometers help you feel how fast you're speeding up or slowing down. Both sensors work together to keep you steady as you ride.
Vision Sensors (Cameras)
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Vision Sensors (Cameras): For image capture, face/object recognition, and defect detection.
Detailed Explanation
Vision sensors, or cameras, are crucial in providing visual input to robots. They can capture images and process them to identify faces, recognize objects, or even detect defects in materials. Vision processing is essential in applications like quality control in manufacturing, where robots need to assess the quality of products accurately.
Examples & Analogies
Think of vision sensors as a pair of eyes for a robot. Just like our eyes help us see who is in front of us and identify whether something is broken or not, cameras equipped with advanced image processing allow robots to 'see' their environment, recognize important objects, and ensure everything is working correctly.
Key Concepts
-
Proximity Sensors: Detect objects without contact, preventing collisions.
-
Infrared Sensors: Measure distances through heat detection.
-
Ultrasonic Sensors: Use sound waves for distance measurement.
-
Gyroscopes: Measure rotation to maintain orientation.
-
Accelerometers: Measure acceleration to track movement and speed.
-
Vision Sensors: Capture images for recognizing and analyzing objects.
Examples & Applications
Robotic vacuum cleaners use proximity sensors to navigate around furniture.
Drones utilize ultrasonic sensors for altitude measurement and obstacle avoidance.
Gaming devices rely on accelerometers to track player movements for interactive gameplay.
Face recognition systems in security cameras use vision sensors to identify individuals.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For proximity, it's quite key, to detect what you cannot see!
Stories
The robot confidently moves thanks to its decision-making abilities, influenced by infrared sensors detecting nearby walls and ultrasonic sensors measuring the safe path.
Memory Tools
PIG V: Proximity, Infrared, Gyroscopes, Vision Sensors.
Acronyms
S.I.G.V. = Sensors in Robotics
Infrared
Gyroscope
Vision.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Proximity Sensors
Devices that detect the presence or absence of nearby objects without physical contact.
- Infrared Sensors
Sensors that detect heat or light to measure distances.
- Ultrasonic Sensors
Sensors that use sound waves to measure distances and detect obstacles.
- Gyroscopes
Devices that measure the rate of rotation around an axis.
- Accelerometers
Devices that measure acceleration forces acting on an object.
- Vision Sensors
Sensors that capture images for functions such as object and face recognition.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
