Java NIO.2 Enhancements (Java 7+)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
WatchService API
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the WatchService API in Java NIO.2, which allows us to monitor file system changes. Does anyone know why we might want to monitor file changes in a program?

Maybe to update the user interface when a file is added or removed?

Exactly! Applications can respond dynamically to changes. Now, can anyone tell me what kind of events we might monitor?

We could look for when files are created, modified, or deleted.

That's right! We use `StandardWatchEventKinds` to specify what types of events to listen for. Let's look at an example of how to implement this.

Here’s a code snippet showing how to set up a WatchService. Can anyone summarize what each line is doing?

The first line creates a watcher, then we register a directory to watch for file creation events.

Great job! So the application will be notified whenever a new file is created in the specified directory.

In summary, the WatchService API allows us to run applications that can respond to changes in the file system efficiently. Any questions?
Symbolic Links
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about symbolic links. Who can tell me what a symbolic link is?

It's like a shortcut to a file or directory, right?

Absolutely! And Java NIO.2 provides better support for working with these symbolic links. What do you think is crucial for developers when dealing with symbolic links?

I think it’s important to easily create and resolve them, so we don’t lose track of what they point to.

Exactly! Java’s `Files` class includes several methods for handling symbolic links seamlessly. Let’s consider how this improves our code's clarity and maintenance.

So, when we create or resolve symbolic links using Java’s APIs, we’re ensuring our applications are robust against file system changes. Any final thoughts?
Improved Exception Handling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We also have improved exception handling with NIO.2. Can anyone name a couple of the new exception types?

AccessDeniedException and NoSuchFileException.

Correct! These exceptions provide clearer context when things go wrong. Why is improved error information significant for developers?

It helps us diagnose issues faster and handle errors based on specific scenarios.

Exactly! Let’s look at how to use these exceptions effectively in our code.

In summary, with enhancements like improved exception handling, developers can create applications that respond intelligently to errors. Any final questions?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Java NIO.2 introduces several important enhancements, such as the WatchService API for monitoring file system events, improved handling of symbolic links, and more robust exception types to enhance error management in file operations. Together, these features improve the overall usability and performance of file operations in Java.
Detailed
Java NIO.2 Enhancements (Java 7+)
Java NIO.2, introduced in Java 7, expands the capabilities of the original NIO by providing several enhancements that simplify file handling and improve performance. Key features include:
WatchService API
The WatchService API allows developers to listen for file system events such as creation, modification, or deletion of files and directories, enabling the creation of responsive applications that can react to changes in real-time.
Example: Watching File Changes
Symbolic Links
Enhancements include better support for symbolic links, providing methods that facilitate their creation, resolution, and deletion.
Improved Exception Handling
The addition of specific exceptions like AccessDeniedException and NoSuchFileException allows developers to handle errors more gracefully and with more context.
Overall, NIO.2 significantly improves the flexibility and scalability of file handling in Java applications.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
WatchService API
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• WatchService API: Monitors file system events (like file creation, modification).
Detailed Explanation
The WatchService API is a new feature in the Java NIO.2 package that allows applications to listen for changes in the file system. This means that if a file is created, deleted, or modified, the application can be alerted and can respond accordingly. If you think of your computer's desktop, the WatchService API is like a notification system that informs you whenever a new file appears or an existing file is modified.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a security camera in your room (the WatchService). Whenever someone enters the room and puts a new item down (like a file being created), the camera captures that event and alerts you immediately. Similarly, the WatchService helps applications immediately know about file events in the file system.
Symbolic Links Support
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Symbolic Links: Better support.
Detailed Explanation
Symbolic links (also known as symlinks) are special types of files that point to another file or directory. With Java NIO.2, support for symbolic links has been enhanced, making it easier for developers to create and manage these shortcuts in the file system. This is especially useful for applications that require referencing files located in different directories without the need to duplicate them.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a symbolic link like a shortcut on your computer desk that points to a document stored in another folder. Instead of having the actual document in multiple places, the shortcut serves as a reference to where the document is located. This way, you can access it quickly without taking up extra space.
Improved Exception Handling
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Improved Exception Handling: e.g., AccessDeniedException, NoSuchFileException.
Detailed Explanation
Java NIO.2 includes enhanced exception handling capabilities, introducing specific exceptions such as AccessDeniedException and NoSuchFileException. These exceptions provide clearer indications of what went wrong during file operations. For instance, if an application tries to access a file that doesn't exist, it throws NoSuchFileException, allowing the developer to handle this specific case efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're trying to enter a building but find the doors locked (AccessDeniedException) or worse, you realize the building is no longer there (NoSuchFileException). Knowing exactly why you can't enter helps you decide your next steps—whether to unlock the door or go to a different building entirely.
Example: Watching File Changes
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
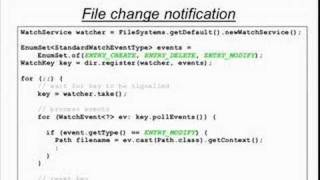
Example: Watching File Changes
WatchService watcher = FileSystems.getDefault().newWatchService();
Path dir = Paths.get("/some/dir");
dir.register(watcher, StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_CREATE);
WatchKey key = watcher.take();
for (WatchEvent<?> event : key.pollEvents()) {
System.out.println("New file: " + event.context());
}
Detailed Explanation
This example demonstrates how to set up a WatchService to monitor a specific directory for file creation events. When the directory is set up with a watcher, it registers for events like file creation. When you register the watcher and wait for events, it blocks the application until an event occurs. Once a new file is created in the directory being watched, the application prints out the name of the newly created file.
Examples & Analogies
Envision you have a doorbell that notifies you when someone enters your house. In this case, the WatchService is like that doorbell, alerting you when a new file steps into your monitored directory, allowing you to respond to it immediately, like welcoming a guest or preparing for their arrival!
Key Concepts
-
WatchService API: Enables monitoring of file system events.
-
Symbolic Links: Improved handling for easier file path management.
-
Improved Exception Handling: New exceptions provide context for better error handling.
Examples & Applications
Using WatchService to monitor a directory for new file creations.
Creating and resolving a symbolic link in Java using new NIO.2 methods.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When files change, see the WatchService arrange; it tells you fast, so you can act at last.
Stories
Imagine a library where every time a book is added or removed, the librarian receives an alert. This is similar to how the WatchService monitors changes in a file system.
Memory Tools
Remember 'W S S' for WatchService Signals: it watches for System changes.
Acronyms
S.L.E.D. for Symbolic Link Exception Definitions (System links, exceptions, denials).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- WatchService
An API that monitors file system events like creation and modification.
- Symbolic Link
A file that acts as a reference to another file or directory.
- AccessDeniedException
An exception thrown when an attempt to access a file or directory is denied.
- NoSuchFileException
An exception thrown when an attempt to access a file or directory that does not exist is made.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
