Serialization
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Serialization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning class! Today, we're diving into serialization in Java. Who can tell me what serialization means?

Isn't it about saving an object's state or something?

Exactly, Student_1! Serialization allows us to convert an object into a byte stream so we can save it to a file or send it over a network. Does anyone know what the main interface we must implement is?

Is it the Serializable interface?

That's correct, Student_2! Only classes that implement the Serializable interface can be serialized. This ensures the object can be properly converted. Let’s recall this as 'S' for Serialization, 'S' for Serializable.

What happens if a class does not implement that interface?

Good question! If you try to serialize an object of a class that doesn't implement Serializable, you'll get a NotSerializableException. So, remember: 'serialize only with Serializable!'

To summarize, serialization is the process of converting an object into a byte stream, and it requires the Serializable interface. We'll look at some code examples next.
Implementing Serialization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now see how serialization is implemented in code. Can someone tell me how we write an object to a file?

You would use ObjectOutputStream, right?

"Correct, Student_4! Here's an example:
Deserialization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we’ve serialized an object, who knows how we can get that object back from the file?

We would use ObjectInputStream?

"Correct! The process of retrieving the object is known as deserialization. Here's a snippet:
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section covers the concept of serialization, its purpose in Java programming for preserving an object's state, and provides a simple code example to illustrate its application. Serialization is essential for various tasks, including object persistence and remote communication.
Detailed
Serialization in Java
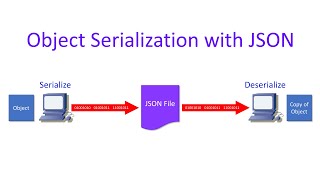
Serialization is a crucial concept in Java that allows programmers to save the state of an object as a byte stream, facilitating the storage of these objects to files or transmission over a network. This process involves the ObjectOutputStream class, which converts an object's data into a format that can be easily written to a file or sent over a network. When an object is serialized, its class must implement the Serializable interface, indicating that its instances can be serialized and deserialized.
Key Points
- Definition: Serialization is the conversion of an object into a byte stream to save its state.
- Purpose: It allows for object persistence and remote communication between applications.
- Implementation: The process typically uses
ObjectOutputStreamto perform the actual serialization, for example:
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.ser"));
out.writeObject(someObject);
out.close();
- Serializable Interface: Any class whose objects are to be serialized must implement this interface.
Understanding serialization is integral to effectively managing data flows in Java applications, especially when involving storage and communication.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Serialization
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Serialization allows saving the state of an object.
Detailed Explanation
Serialization is a process in Java that enables the conversion of an object into a byte stream. This is vital for saving the object's state, especially when you need to store it in a file or send it over a network. When an object is serialized, its entire state, including its attributes, is captured so it can be reconstructed later. This allows for persistent storage or transmission of complex data structures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of serialization as taking a snapshot of a family photo. Just as you capture the image of your family at a moment in time, serialization captures the state of an object at a specific moment, allowing you to recreate that exact scene later. When you deserialize (the reverse process), it's like printing out that photo at home, enabling you to see your family just as they were in the snapshot.
Writing Serialized Objects to a File
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.ser")); out.writeObject(someObject); out.close();
Detailed Explanation
To serialize an object in Java, we use an instance of the ObjectOutputStream class. This class is initialized with FileOutputStream, indicating that we want to write the serialized data to a file. The writeObject method is then called with the object we want to serialize as an argument. After writing the object, it's essential to close the output stream to release system resources and ensure all data is flushed to the file. The file "data.ser" will now contain the serialized representation of someObject which can later be read back into a program.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine mailing a beautifully wrapped gift (the serialized object) to a friend. You put the gift into a box (the file stream), seal it, and address it (using ObjectOutputStream). Once it's ready, you drop it in the mail (calling writeObject) and close the package (using out.close()). Your friend can then open the package and see the gift just as you intended!
Key Concepts
-
Serialization: The process of converting an object into a byte stream.
-
Serializable: An interface that designates whether a class can be serialized.
-
ObjectOutputStream: A class used to serialize objects.
-
Deserialization: The reverse of serialization, where a byte stream is converted back into an object.
Examples & Applications
Saving the state of a user object to a file for later retrieval.
Transmitting an object over the network for remote procedure calls.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Serialize, oh so wise, save that state before sunrise.
Stories
Once there was a gardener named Serializable Sam. He had a magical bucket that could store seeds, and beneath the sun, he'd save their essence to replant in the future.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SOS' for serialization - Save Object State.
Acronyms
S for Save, O for Object, S for State.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Serialization
The process of converting an object into a byte stream for storage or transmission.
- ObjectOutputStream
A class that enables writing objects to an output stream in a serialized form.
- Serializable
An interface that must be implemented by classes whose objects need to be serialized.
- Deserialization
The reverse process of serialization, retrieving an object from a byte stream.
- NotSerializableException
An exception thrown when an attempt is made to serialize an object that does not implement the Serializable interface.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
