Path, Paths, and Files (Java 7+)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to java.nio.file
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the `java.nio.file` package which was introduced in Java 7. It provides an improved way to handle files compared to the older `java.io.File` class. Why do you think we'd need that?

Maybe because it's more efficient?

Exactly! The `java.nio.file` package allows you to work with files more flexibly and efficiently. It handles paths as objects, which are easier to manipulate. Can anyone tell me what a 'Path' is in this context?

Is it like a string that points to a file?

That's a good start! A `Path` represents a file or directory location in a file system using a sequence of directory and file names. It's more than just a string, as it can include various methods to manipulate file paths.
Understanding Path and Files
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about the `Paths` class. This utility class helps you create `Path` instances. Can someone write an example of creating a Path object?

I think it would look something like this: `Path path = Paths.get("example.txt");`

Correct! Now, what about using the `Files` class to read from this file?

You could use `Files.readAllLines(path)` to get all lines from that file, right?

Spot on! `Files` is very helpful as it provides many methods for file operations. Let’s not forget to consider the encoding when reading text files; using UTF-8 is a good practice.
Practical Example with Practices Using Path and Files
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at a practical example. Who can tell me what happens when we attempt to read a file that does not exist?

It throws an exception, right?

Yes! Using methods from `Files` will throw an IOException if the file doesn't exist. So, it's essential to handle exceptions carefully in your code.

Should we always check if the file exists before trying to read it?

That's a safe approach! Let’s practice writing a code snippet where we check if a file exists before reading. Try this: `if (Files.exists(path)) { /* read file */ }`.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the java.nio.file package, which provides improved mechanisms for file handling using objects like Path and Files. It demonstrates how these classes replace the older File class, offering more robust functionalities like reading files with better encoding management.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The java.nio.file package, introduced in Java 7, enhances file handling capabilities significantly compared to the older java.io.File methods. This section provides an overview of key features such as Path and Files, which are crucial in managing file systems conveniently and efficiently.
Key Features:
- Path: This class represents a file system path as a sequence of directory and file names.
- Paths: This is a utility class used to obtain a
Pathobject for a specified URI or string representation of a file path. - Files: This class provides static methods to operate on files, such as reading, writing, and determining file attributes.
Example Implementation:
In this example, Paths.get() is used to convert a string path into a Path object, and Files.readAllLines() allows for reading all lines from a file simply, while specifying the character encoding to ensure proper text representation.
This modern approach simplifies file operations, making the code cleaner and more understandable while reducing the chances of errors common with older file handling methods.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Paths and Files
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The java.nio.file package improves file handling over java.io.File.
Detailed Explanation
The java.nio.file package was introduced to enhance file handling capabilities compared to the older java.io.File. Java NIO (New Input/Output) offers a more structured way to deal with files and paths, allowing developers to work with file systems more easily and efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the java.io.File as an old paper filing system where you have to physically open each file to check its contents. In contrast, the java.nio.file package acts like a modern digital filing system where you can quickly search for and access documents without needing to sift through every single file.
Reading a File Example
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
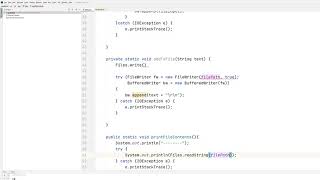
Example: Reading a File
Path path = Paths.get("example.txt");
List
Detailed Explanation
In the example provided, the Paths.get() method is used to create a path instance for the file named 'example.txt'. After that, the Files.readAllLines() method reads all lines from the file into a List of Strings. The encoding specified is UTF-8, which is a common character encoding that supports many characters from different languages, making it versatile for various types of text files.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a box full of letters (the file) in your attic. Using the Paths and Files classes is like having a digital scanner that can quickly read each letter and convert it into text on your computer. This saves you time compared to manually opening each letter to read it.
Key Concepts
-
Path: Represents file or directory location in a file system.
-
Paths: Utility class to create Path instances from strings.
-
Files: Contains methods for various operations on files.
Examples & Applications
Using Paths to create a path: Path path = Paths.get("example.txt");.
Reading a list of lines from a file: List<String> lines = Files.readAllLines(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Path in hand, Files at your command, reading and writing, oh so grand!
Stories
Imagine a traveler (Path) navigating through cities (files) with a guide (Files) who knows all the shortcuts to get there efficiently.
Memory Tools
Remember P-F-F: P for Path, F for Files, F for functionality!
Acronyms
P-F (Path & Files) helps organize, retrieve, and access data timely.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Path
An object that represents a file or directory path in a file system in the java.nio.file package.
- Paths
A utility class used to obtain Path instances from string representations or URIs.
- Files
A class that provides static methods to perform operations on files, such as reading, writing, and obtaining attributes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
