Aggregate Proportions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Aggregate Proportions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, everyone! Today, we're going to delve into why aggregate proportions are crucial in High Performance Concrete. Can someone tell me why the right proportions matter?

I think it's because it affects the strength of the concrete?

Exactly! The right aggregate proportions influence not only strength but also durability and workability. For instance, if we use too much coarse aggregate, the concrete might not set properly. What else could happen?

Maybe it could become too dry and not mix well?

Right again! This points to the need for continuous grading, which helps the particles fit together well, minimizing voids. We often refer to this principle using the mnemonic 'GRAD'—Grading Reduces Aggregate Density. Can anyone remember what that stands for?

'Grading Reduces Aggregate Density'—it reminds us that well-graded aggregates lead to better density and performance!

Correct! This leads us to our next important topic.
Selecting Coarse Aggregates
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive deeper into selecting coarse aggregates. What are some qualities we should look for?

We need them to be of the right size and well-graded?

Exactly! Coarse aggregates should range from 10 to 20 mm, and ideally, they should have low water absorption and minimal harmful materials. Can anyone tell me how this would affect durability?

If they absorb too much water, it would affect the hydration process, right?

Yes! It's crucial for hydration and achieving the right strength. To help remember this, let's use the acronym 'WARM'—Water Absorption Reduces Mix performance. Can everyone repeat that? 'WARM'!

WARM!

Great! Let’s continue our discussion on fine aggregates next.
Fine Aggregate Proportions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Fine aggregates play a critical role too. Who can summarize their importance?

Fine aggregates help fill the gaps between coarse aggregates and improve workability.

That’s correct! They need to be proportioned to balance workability and packing density. What might happen if there’s too much fine aggregate?

It might make the mix too sticky or difficult to work with.

Exactly. So we need to maintain an optimal balance. A helpful memory tool is 'DAMP'—Diverse Aggregate Mix Proportioning! This reminds us that a variety of particle sizes in aggregates is crucial for optimal mix performance.

DAMP! I like that!

Perfect! Now, to wrap up today’s topic, can anyone recall what we learned about the importance of aggregate proportions?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Aggregate proportions are a critical aspect of High Performance Concrete mixture design, influencing its strength, durability, and workability. This section discusses the general guidelines for selecting coarse and fine aggregates, considering factors such as grading, specific gravity, and moisture content.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Aggregate proportions greatly impact the overall performance of High Performance Concrete (HPC), influencing its strength, durability, and workability. The section outlines the principles for determining the proportions of coarse and fine aggregates in the concrete mix:
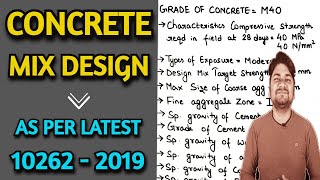
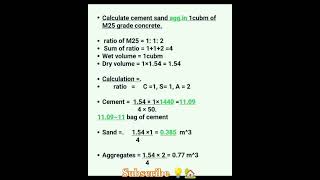
- Coarse Aggregates: Typically, coarse aggregates constitute 40-50% of the total volume of the concrete mix. Their size generally ranges from 10-20 mm, and they should be well-graded to minimize voids and maximize density.
- Key Considerations: Low water absorption and absence of deleterious materials are essential for achieving desired performance. The shape and texture of coarse aggregates significantly affect the mix's workability.
- Fine Aggregates: Fine aggregates are adjusted according to the desired workability and packing density. They should complement the coarse aggregates to fill voids while also improving the concrete's overall uniformity.
- Grading: Continuous grading helps minimize segregation and enhances the packing efficiency of the concrete by providing a variety of particle sizes.
- Moisture Content: It is crucial to evaluate the moisture content of aggregates prior to mixing. Aggregates can be either saturated surface dry (SSD) or completely dry, affecting the water-cement ratio calculations. Adequate adjustments must be made to ensure the desired workability and hydration during the curing process.
- Influence on Durability and Strength: Proper selection and proportioning of aggregates lead to improved mechanical and durability performances, making the concrete more resistant to environmental degradation, which is critical in applications like bridges and high-rise buildings.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Proportions of Coarse Aggregates
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Coarse aggregates: 40–50% of total volume.
Detailed Explanation
In designing high-performance concrete (HPC), the amount of coarse aggregates is determined to be between 40% to 50% of the total volume of the mix. This percentage is crucial as it helps achieve the desired strength and stability of the concrete. The coarse aggregates provide the bulk of the concrete volume, and their size and grading can influence the overall properties of the concrete.
Examples & Analogies
Think of concrete like a cake. The coarse aggregates are similar to the flour in the cake mix—too little and the cake won’t hold its shape, too much, and it becomes dense and hard to manage. Just like baking requires the right amount of flour for the perfect cake, HPC needs the right amount of coarse aggregates to achieve strength.
Proportions of Fine Aggregates
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Fine aggregates adjusted to maintain workability and packing density.
Detailed Explanation
Fine aggregates, which are smaller than coarse aggregates, play a critical role in adjusting the consistency or workability of the concrete mixture. Their proportions must be carefully controlled to ensure that the concrete flows easily during placement while still maintaining sufficient packing density, which helps in achieving high strength and durability. This adjustment typically involves increasing or decreasing fine aggregates based on the overall mixture requirements.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you’re making a smoothie. If you add too much ice (which is like coarse aggregates), you won’t have enough liquid (fine aggregates) to make it smooth and drinkable. The right balance between the two ingredients leads to a perfect smoothie, just like adjusting fine aggregates leads to a workable and durable concrete mix.
Key Concepts
-
Aggregate Proportions: The ratio of coarse and fine aggregates that affect the performance of concrete.
-
Continuous Grading: A process of selecting aggregate sizes to fill voids in the mix and enhance density.
-
Water Absorption: The measure of an aggregate's capacity to soak up water, impacting hydration and performance.
-
Packing Density: A crucial factor in determining the strength of the concrete based on how tightly aggregates are arranged.
Examples & Applications
In a typical HPC mix, the proportion of coarse aggregates might range from 40-50%, ensuring that the size and grading enhance concrete performance.
Using well-graded fine aggregates can significantly increase the packing density, allowing for a higher overall strength of the concrete.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For strong concrete, the size must be right, Coarse aggregates fit, and fine aggregates light.
Stories
Imagine a superhero named Aggregate, who fills gaps and makes concrete strong. Without him, the structure weakens and slowly crumbles over time.
Memory Tools
Use the acronym 'CAPS'—Coarse Aggregate Proportioning System—to remember the factors influencing aggregate selection.
Acronyms
Remember 'GRAD'—Grading Reduces Aggregate Density—to reinforce the importance of continuous grading.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Coarse Aggregates
Larger particles in concrete mixtures typically ranging from 10 mm to 20 mm.
- Fine Aggregates
Smaller particles in concrete mixtures, typically sand, which help fill voids between coarse aggregates.
- Continuous Grading
A method of selecting aggregate sizes to minimize voids and maximize the density of a concrete mix.
- Water Absorption
The ability of aggregate to absorb water, which can impact the hydration process and concrete performance.
- Packing Density
The measure of how densely aggregates are packed together in a mix, affecting strength and durability.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
