Optimization of Particle Packing
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Particle Packing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today we're going to discuss the optimization of particle packing in High Performance Concrete. Can anyone tell me why particle packing is important?

I think it's important because it affects the density of the concrete?

Exactly! Optimizing particle packing helps achieve a denser concrete mix. By filling voids with finer materials like silica fume, we can improve durability. This can be remembered as the ‘FILL’ – Filling Invalid Least Loosely!

So, if we fill those voids, does it also help reduce permeability?

Yes, reducing porosity leads to lower permeability, which is essential for HPC. Great question!
Materials for Optimization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into the materials used for optimizing particle packing. What kinds of materials do you think we could use?

Maybe fine aggregates like sand?

Correct! Fine aggregates are crucial. We also use supplementary materials like silica fume and fly ash. Remember the acronym 'SAFE' – Silica, Aggregates, Fly ash, for effective packing!

How do we know if we're using the right amount?

Great follow-up! We perform trial mixes to adjust the materials and ensure optimal packing and performance.
Testing for Optimization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Testing is key! How can we check if our particle packing is effective?

Maybe by looking at the density and porosity after mixing?

Exactly! Density tests and permeability tests are essential. Think of the mnemonic 'D-PAP' – Density, Porosity, Adjustments, and Performance.

What if the tests show we're not meeting standards?

Good point! We would need to modify the mix based on test results. Continuous evaluation is vital in HPC!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Optimizing particle packing involves using fine materials to fill voids between larger particles, enhancing density and reducing porosity. This principle is critical in achieving the high performance characteristics desired in HPC and requires careful consideration of material selection.
Detailed
Optimization of Particle Packing in HPC
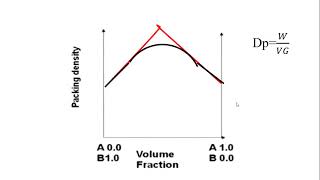
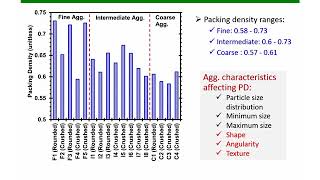
Optimization of particle packing is a crucial principle in the proportioning of High Performance Concrete (HPC). The goal is to fill the voids between larger aggregate particles using finer materials, such as silica fume and fly ash, to achieve a denser concrete matrix. This approach not only enhances the overall density but also significantly reduces porosity, which is essential for increasing the durability and longevity of concrete structures.
In this section, we explore several factors that contribute to effective particle packing, including material selection, the use of chemical admixtures, and methods for testing and adjusting the mixture to ensure optimal performance. By implementing principles of particle packing, we can minimize the voids in the concrete mix, resulting in a more robust and resilient structure capable of withstanding various environmental stresses.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Use of Fine Materials
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Use of fine materials (silica fume, fly ash, etc.) to fill voids between cement grains.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, the focus is on using fine materials like silica fume and fly ash in the concrete mixture. These fine materials have tiny particles that can fit into the spaces or voids between larger cement grains. By maximizing the use of these fine materials, the overall density of the concrete can be improved. This means that there are fewer empty spaces within the concrete, leading to stronger and more durable concrete.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a box of different sized marbles. If you fill the larger spaces with medium-sized marbles and then top it off with small marbles, the box becomes much more packed and there is less empty space. Similarly, adding fine materials like silica fume to the concrete mix fills in the gaps between larger particles, ensuring a tighter, more robust structure.
Improvement of Density
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Improves density and reduces porosity.
Detailed Explanation
This point highlights that by utilizing fine materials to optimize the packing of concrete particles, the density of the final concrete mix increases. Higher density is beneficial because it translates into reduced porosity. Lower porosity means that the concrete has fewer voids or spaces that could be filled with harmful substances like water or chemicals, which can weaken the concrete over time. Thus, improving density through fine material packing leads to a stronger, more durable concrete.
Examples & Analogies
Think of density like packing a suitcase. If you want to fit as much as possible, you’d fill it with smaller items between the larger ones, which lets you use all available space efficiently. Just like that, optimizing particle packing in concrete ensures that every bit of space is used effectively, producing stronger concrete.
Key Concepts
-
Optimization of Particle Packing: Improving density and reducing porosity for better concrete performance.
-
Fine Materials: Using fine aggregates and supplementary materials to fill voids.
Examples & Applications
Using silica fume as a filler in concrete mixtures to improve strength and reduce permeability.
Testing various combinations of aggregate sizes to find the most effective packing arrangement.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For concrete so strong, keep packing tight and long.
Stories
Imagine packing a suitcase. To fit everything, you add smaller items between larger ones. That's how we optimize concrete!
Memory Tools
FILL: Filling Invalid Least Loosely (to remember the goal of packing).
Acronyms
SAFE
Silica
Aggregates
Fly ash for effective packing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Particle Packing
The arrangement of particles in a material design, crucial for defining the density and porosity.
- Silica Fume
A byproduct of silicon metal production that enhances strength and durability in concrete when used in small amounts.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
