Applications in Earthquake Engineering
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Dynamic Analysis of Buildings
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss how Multi-Degree-of-Freedom systems are essential for dynamic analysis of buildings. Can anyone tell me why a single-degree-of-freedom model might not be sufficient?

Because buildings have multiple floors and structural components that can move independently?

Exactly! MDOF systems account for each floor as an independent degree of freedom, which allows for a more accurate depiction of a building's response to ground motions.

What kind of analysis do we actually perform on these MDOF systems?

Great question! We perform dynamic analyses like modal response spectrum analysis and time-history analysis to understand how these structures behave during earthquakes.

What’s the difference between those two methods?

Modal response spectrum analysis uses pre-calculated spectra to estimate peak responses, while time-history analysis simulates the actual ground motion for more detailed results.

So, both methods are important in ensuring buildings can withstand earthquakes?

Exactly! It's about choosing the right tool for our needs. To summarize, MDOF systems help us analyze buildings in a way that accounts for their complexity during seismic events.
Seismic Design Methodologies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into how MDOF systems influence seismic design. What role do you think they play?

They help us predict how buildings will respond to earthquakes?

Yes, they do! By simulating dynamic responses, we can optimize our designs. Can anyone name a specific analysis method used in seismic designs?

Is it the modal response spectrum analysis?

That's correct! This method allows us to gauge the maximum expected responses for each mode. What do you think about time-history analysis? How does it differ?

It probably involves using actual earthquake records?

Exactly! Time-history analysis provides detailed information by simulating how a building reacts under specific seismic events. Remember, the goal of these analyses is to ensure structural safety.
Retrofit Design with Base Isolation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss retrofitting techniques, particularly base isolation. Does anyone know why we use base isolation in earthquake-prone areas?

To reduce the forces transferred to the building during an earthquake?

Correct! Base isolation decouples the structure from ground motion. What effect does that have on the design?

It helps minimize structural damage?

Precisely! The MDOF system is modified to include this isolation. How do you think we model this in our analysis?

Do we add an additional degree of freedom for the base movement?

Exactly! This change allows us to accurately capture the dynamics of the entire system. Remember, effective retrofitting can significantly enhance the resilience of a building.
Bridge Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s look at bridge analysis using MDOF systems. Why might bridge structures pose unique challenges during seismic events?

They're often long and can have irregular shapes?

Exactly! The dynamic characteristics differ from buildings. What impact does this have on analysis?

It must make predicting their response in an earthquake more complex.

Correct again! MDOF systems allow us to account for these complexities. Can anyone think of a specific method we would use for bridge analysis?

Would it be similar to modal analysis for buildings?

Yes! We use similar techniques, but tailored to the specific geometries of bridge structures. Always remember, each structure has its unique behaviors we must consider.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The application of MDOF systems in earthquake engineering is significant as it aids in dynamic analysis of structures such as multi-storey buildings and bridges. Key topics include seismic design methodologies, retrofitting strategies with isolation systems, and the considerations for unique structural challenges, all crucial for enhancing structural resilience against earthquakes.
Detailed
Applications in Earthquake Engineering
MDOF systems are integral to earthquake engineering, employed in multiple critical areas to ensure that structures can withstand seismic events. This section highlights the following applications:
Dynamic Analysis of Buildings
MDOF systems facilitate the dynamic analysis of multi-storey frame or shear models, enabling engineers to predict how buildings respond during earthquakes.
Seismic Design
MDOF systems are essential in seismic design, where modal response spectrum analysis and time-history analysis methods are utilized to estimate how structures will react under seismic loads.
Retrofit Design
The evaluation of the impact of base isolation and damping devices relies on MDOF models. These systems are key to developing strategies that enhance the resilience of existing structures against seismic activity.
Bridge Analysis
MDOF systems are also used in the analysis of long-span and irregular bridge structures, which pose unique challenges during seismic events. These analyses ensure that dynamic effects such as lateral loads are effectively taken into account.
Understanding these applications not only improves the safety and performance of buildings and bridges during earthquakes but also enhances the overall resilience of urban environments.
Youtube Videos
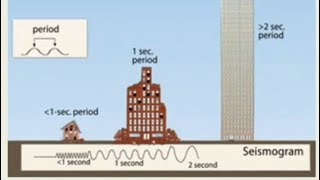









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Dynamic Analysis of Buildings
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
MDOF systems are used in:
- Dynamic analysis of buildings: Multi-storey frame or shear models
Detailed Explanation
MDOF systems are crucial for conducting dynamic analyses of buildings, which allows engineers to understand how multi-storey structures respond to forces such as earthquakes. In this context, multi-storey frame or shear models represent the entire building's response to ground motion. By modeling the building as an MDOF system, engineers are able to evaluate how each part of the structure moves relative to one another under dynamic loads, as opposed to using a simpler SDOF (single-degree-of-freedom) model that overlooks complex interactions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a multi-storey building as a concert where each floor represents a different musical instrument. If there's a sudden loud sound (like an earthquake), each instrument may respond differently based on its construction and placement. Using MDOF is like ensuring every instrument plays in harmony, allowing the engineers to create a well-structured performance (or building) that stands strong during the 'loud sound'.
Seismic Design Techniques
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Seismic design: Modal response spectrum analysis, time history analysis
Detailed Explanation
Seismic design is a critical area in earthquake engineering, focusing on creating structures that can withstand seismic forces without significant damage. Engineers utilize techniques such as modal response spectrum analysis and time history analysis to predict how structures will behave during earthquakes. Modal response spectrum analysis uses a spectrum that relates the maximum responses of structures to different natural frequencies, enabling engineers to quickly assess performance against seismic demands. Time history analysis, on the other hand, involves simulating the actual ground motion over time to assess how the structure will respond to varying forces throughout the earthquake event.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine preparing for a dance competition with unpredictable music. Modal response spectrum analysis is like rehearsing to different music genres to see what style fits best for each dancer's movements, while time history analysis is akin to practicing to the actual music the day of the competition to adapt the performance in real-time. This combination allows dancers (structures) to be ready for any rhythm (earthquake).
Retrofit Design Considerations
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Retrofit design: Evaluating impact of base isolation, damping devices
Detailed Explanation
Retrofit design involves upgrading existing structures to improve their performance during seismic events. One common method is the incorporation of base isolation systems, which allow a building's foundation to move independently of ground motion, significantly reducing forces transmitted to the structure. Damping devices, such as tuned mass dampers, can also be installed to absorb and dissipate seismic energy. Evaluating the effectiveness of these systems is vital for ensuring safety and resilience of older buildings that may not have been designed to current seismic standards.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a vintage car that you want to keep driving safely on modern roads. Base isolation is like adding better shock absorbers that allow the car to handle bumps smoothly, while damping devices are similar to installing an advanced braking system that prevents the car from bouncing back harshly when stopping. Together, these upgrades extend the car's life and enhance safety, just as retrofitting older buildings does in seismic areas.
Bridge Analysis in Seismic Context
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Bridge analysis: Long-span and irregular bridge structures
Detailed Explanation
Bridge analysis under seismic loading is another application of MDOF systems. Long-span and irregular bridge structures pose unique challenges due to their size and geometric configurations. MDOF models help engineers assess how these complex structures respond to vertical and lateral seismic forces. By analyzing the dynamic behavior of bridges, engineers can identify critical points that may require reinforcement or additional flexibility to withstand earthquakes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a large, intricate spider web (the bridge) stretched across a distance. During an earthquake, if the web vibrates, certain parts may stretch and twist differently. Analyzing the web with MDOF models enables the caretaker (engineer's team) to determine which strands (components) need reinforcement to prevent tearing, ensuring the integrity of the entire web structure under stress.
Key Concepts
-
MDOF Systems: A modeling approach that allows for complex interactions in structural responses during seismic events.
-
Dynamic Analysis: Critical for predicting how structures will respond to earthquake loads.
-
Base Isolation: A retrofitting technique that helps protect buildings from seismic forces by decoupling them from ground motion.
Examples & Applications
An MDOF system is used in analyzing a multi-storey building to predict its response to an earthquake, ensuring safety.
Base isolation techniques prevent seismic energy from affecting the upper structure, reducing the risk of damage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a quake, keep the structure straight, With MDOF, it can respond just great!
Stories
Imagine a tall building swaying in a dance with earthquake waves. MDOF helps it glide and stay in tune, avoiding collapse.
Memory Tools
To remember MDOF benefits, think 'D-B-R' for Dynamic response, Balance, and Resilience.
Acronyms
B.I. for Base Isolation
Better Impact.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- MDOF
Multi-Degree-of-Freedom system, a model that captures more than one degree of freedom for accurate dynamic analysis.
- Seismic Design
The process of designing structures to withstand seismic forces from earthquakes.
- Dynamic Analysis
A method used to determine the response of structures under dynamic loads, such as seismic activity.
- Base Isolation
A technique that decouples a structure from ground motion using isolators.
- Modal Response Spectrum Analysis
An analysis technique that estimates the maximum responses of structures from seismic loads.
- TimeHistory Analysis
A method that simulates a structure’s response to actual earthquake records.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
