Types of Data in GIS
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Spatial Data
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss spatial data. Can anyone tell me what spatial data refers to? It relates to the location and shape of geographic features.

Is spatial data just maps?

Great question! Spatial data encompasses more than just maps. It includes two main types: vector and raster data. Vector data represents features as points, lines, and polygons. For example, a city park can be a polygon shape on a map.

And what's raster data then?

Raster data is composed of pixels and is used primarily for images, like satellite images. Think of it like a grid where each square holds a specific value, representing information like temperature or elevation.

So, vector is like detailed, precise shapes, and raster is about broad information?

Exactly! To remember this distinction, you can think of 'Vectors Vertex' vs 'Raster Raster.' This helps differentiate that vector is about specific shapes while raster covers the broader image.

In summary, spatial data is crucial for understanding and interpreting the geographic information in GIS.
Exploring Attribute Data
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift focus to attribute data. Who can explain what attribute data is?

Isn’t it the data that gives information about spatial features?

Correct! Attribute data provides additional details about a spatial feature. For example, a road could be associated with attributes such as its name, width, and the material it's made of.

So it’s kind of like a profile for each feature?

Precisely, Student_4! Just think of each spatial feature having a 'data card'. To remember this, imagine 'A for Attributes, A for Additional info.' This will help you connect the concept.

In summary, attribute data enriches our understanding and allows for deeper analysis of spatial data.
Integrating Spatial and Attribute Data
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss how spatial and attribute data work together in GIS. How do you think these two types of data interact?

They must complement each other to give a full picture of an area?

Exactly! When you combine spatial data with attribute data, you can perform complex analyses. For instance, analyzing road conditions using both the spatial paths (lines) and their attributes (like width or material).

So GIS helps us gather insights effectively by analyzing both types of data?

Yes! A good way to remember their relationship is to think of 'Spatial tells where, Attribute tells more.' This can help you solidify their roles in GIS.

In conclusion, understanding both spatial and attribute data is fundamental for leveraging GIS in a meaningful way.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section elaborates on spatial data types, which include vector and raster data, and attribute data that provides additional information about spatial features. Understanding these data types is essential for effective GIS analysis and applications.
Detailed
Types of Data in GIS
Spatial Data
GIS primarily utilizes two main types of spatial data, which are instrumental in mapping and analyzing geographic features:
- Vector Data: This type represents features using geometric shapes—points (e.g., locations of schools), lines (e.g., roads), and polygons (e.g., administrative boundaries). Vector data is essential for precise representations of discrete features on a map.
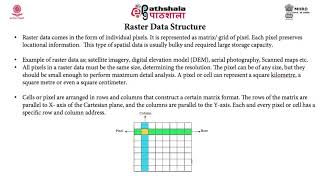
- Raster Data: Unlike vector data, raster data is organized in a grid format, where each cell in the grid has a value representing information such as color, elevation, or temperature. Raster data is widely used for aerial and satellite imagery, as well as environmental modeling.
Attribute Data
Attribute data refers to non-spatial information associated with spatial features. For instance, a road can be represented spatially (as a line) with attributes like:
- Name
- Width
- Material type
- Maintenance schedule
Understanding both spatial and attribute data is crucial for effectively utilizing GIS in various applications, including urban planning, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure management.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Spatial Data
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Spatial data refers to the location and shape of geographic features.
- Vector Data: Represents features as points, lines, and polygons (e.g., roads, boundaries).
- Raster Data: Represents data in grid format (e.g., satellite images, elevation models).
Detailed Explanation
Spatial data is essential in GIS because it describes where things are located and how they are shaped in the real world. This data can be categorized into two main types. The first type, vector data, uses geometric shapes to represent spatial features. Points could represent specific locations like a well or bus stop, lines could depict roads or rivers, and polygons can show areas such as parks or national borders. The second type, raster data, is made up of a grid of cells, where each cell contains a value, such as temperature or elevation. This format is often used for images taken from satellites, allowing us to analyze patterns and changes in the Earth's surface.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are creating a treasure map. The locations of hidden treasures are marked with points (vector data), and the paths connecting these treasures are drawn as lines. Now, to understand the landscape better, you take a picture of the terrain with a drone; that photo represents raster data, showing colors and textures of the ground that help you visualize the area.
Attribute Data
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These are non-spatial data associated with spatial features. For example, a road (spatial feature) may have attributes like name, width, material type, and maintenance schedule.
Detailed Explanation
While spatial data tells us where features are located, attribute data provides additional information about those features. Every spatial element, such as a road or a tree, can have various attributes detailing its properties. For instance, for a road, attributes could include its name, the material it is made from (like asphalt or gravel), the width of the road, and even details on its maintenance schedule. This data helps users understand not just where things are but also the characteristics and status of these features.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a school library. The location of each book on the shelf is like spatial data, telling you where to find it. However, information about the book—such as its title, author, genre, and whether it's available or checked out—represents the attribute data. Both types of data are essential for effectively using the library’s resources.
Key Concepts
-
Spatial Data: Refers to the location and shape of geographic features, crucial for mapping.
-
Vector Data: Represents features as geometric shapes, essential for precise location depiction.
-
Raster Data: Composed of pixels, suitable for representing continuous data and images.
-
Attribute Data: Offers non-spatial insights, enriching the understanding of spatial data.
Examples & Applications
An example of vector data is a city map that shows roads as lines and parks as polygons.
An example of raster data is a satellite image of a landscape, showing terrain elevations in a grid pattern.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Vector shows the line, Raster captures space, Together they intertwine.
Stories
Imagine a city map where roads are drawn like lines on paper, while pictures of the city skyline are presented in boxes filled with color; that's how vector and raster bring a city to life!
Memory Tools
Think 'V for Vivid shapes of vector, R for Rows of raster' to remember the types of spatial data.
Acronyms
Remember the acronym 'VR'—Vector is for representation, Raster is for real images.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Spatial Data
Data that represents the location and shape of geographic features.
- Vector Data
A type of spatial data that represents features by points, lines, and polygons.
- Raster Data
A type of spatial data represented in a grid format, typically used for images and continuous data.
- Attribute Data
Non-spatial data that provides additional information about spatial features.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
