Distribution of Electricity in a House
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Circuits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to talk about how electricity is distributed in a house. Can anyone tell me what a circuit is?

A circuit is a path for electricity to flow, right?

Exactly! There are two main circuits in a house: the lighting circuit and the power circuit.

What’s the difference between them?

Great question! The lighting circuit is for lower power devices like bulbs and fans, while the power circuit is for high-power appliances.

So, how do they stay safe?

Each circuit has a fuse or MCB. These protect the circuits from overloads.

Why do we need two separate circuits?

To prevent high-power devices from affecting the safety of the lighting circuit. It keeps our home safe and functional!
Importance of Fuses and MCBs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive into fuses and MCBs. Why do you think they are important?

They prevent too much current from going through, which can be dangerous.

Exactly! If too much current flows, it can cause overheating or even fires. Can anyone think of a scenario where this might happen?

What if several high-power appliances run on one circuit?

Yes, that is called overloading. Fuses and MCBs disconnect power when they detect this issue, keeping us safe.

So, how do we reset an MCB if it trips?

You can reset an MCB without replacing it, which is very convenient.
Summary and Recap
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s summarize what we've learned today about electricity distribution in a house. Can someone name the two circuits?

The lighting circuit and the power circuit!

Correct! And why do we need separate fuses or MCBs for each circuit?

To protect against overload and ensure safety!

Exactly! Great job, everyone. Any final questions?

Can we have more examples of devices in each circuit?

Sure! Lighting circuit includes bulbs and fans, while power circuit includes geysers and microwaves.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
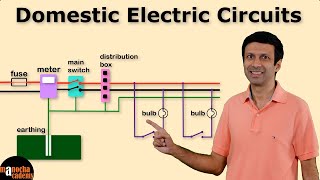
Electricity distribution in a house is managed through two primary circuits. The lighting circuit primarily powers lower wattage devices like bulbs and fans, while the power circuit caters to high-power appliances such as geysers and microwaves, with protective devices like fuses or MCBs for safety.
Detailed
Distribution of Electricity in a House
In this section, we explore how electricity is effectively allocated throughout a home through two distinct circuits: the lighting circuit and the power circuit. The lighting circuit is responsible for illuminating spaces using bulbs, fans, and tube lights, typically operating at lower power levels. Conversely, the power circuit is designed for higher power consumption, providing energy to appliances such as geysers, air conditioners, and microwaves.
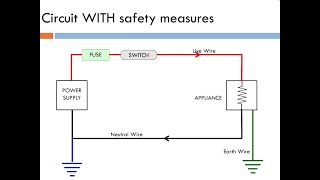
To ensure safety and protect the household electrical system, each of these circuits is equipped with its own fuse or miniature circuit breaker (MCB). These devices serve as critical components in preventing overloads and potential hazards by interrupting the electrical flow in case of faults or long-term underperformance.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Circuits Division
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Supply is divided into two circuits:
○ Lighting circuit: For bulbs, fans, tube lights, etc. (Low power)
○ Power circuit: For high-power appliances like geysers, ACs, microwaves.
Detailed Explanation
In a typical household, the electricity supply is subdivided into two different types of circuits. The first is the lighting circuit, which powers lower power-consuming devices such as light bulbs, ceiling fans, and tube lights. These devices do not require a significant amount of current to operate. The second is the power circuit, which supplies electricity to high-power appliances such as geysers, air conditioners (ACs), and microwaves. These appliances draw more current, thus requiring a dedicated circuit to ensure they operate safely and efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a busy highway (power circuit) that supports large trucks transporting heavy goods, like geysers and ACs, while a side road (lighting circuit) caters to smaller vehicles like cars and bicycles, representing your light bulbs and fans. Just like the highway needs to be wider to accommodate larger vehicles, the power circuit has to be designed to handle higher electricity loads.
Fuses and MCBs
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Each circuit has a separate fuse or MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker).
Detailed Explanation
To ensure the safety and functionality of each circuit in a house, each one is protected by its own fuse or Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB). Fuses are safety devices that will melt and break the circuit if there is an overcurrent, preventing potential damage. Similarly, MCBs automatically turn off the electricity supply in case of an overload or short circuit, and they can be easily reset without needing replacement. This segregation helps in isolating issues and maintaining the overall safety of the electrical system.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a fuse or MCB as a guardian for each room in a house party. If one room gets too noisy (overload), the guardian (fuse or MCB) steps in and quiets it down (cuts off power), ensuring the rest of the house remains unaffected and the party continues smoothly.
Key Concepts
-
Lighting Circuit: Used for low power devices.
-
Power Circuit: Used for high power devices.
-
Fuse: Melts to break circuit in case of overload.
-
MCB: Automatically trips to protect circuits.
Examples & Applications
A ceiling fan connected to the lighting circuit provides home illumination.
A microwave oven operates on the power circuit due to its high energy consumption.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the house where power flows, Lighting circuits keep it low, Power circuits work with might, Heating, cooling, shining bright.
Stories
Once in a small house, there were two friends, Lighty, who loved to keep things bright, and Power, who powered the kitchen each night. They each had their own special circuit to ensure everything ran just right, kept safe with their fuses, ready to trip at the slightest fright.
Memory Tools
Fuses Protect Power: Fuses prevent overloads; Power circuit is for high power appliances.
Acronyms
F.M.L.P. (Fuses protect against Malfunctions, Lighting for low, Power for high.)
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Lighting Circuit
A circuit designed for low power appliances like bulbs and fans.
- Power Circuit
A circuit intended for high power appliances such as geysers and microwaves.
- Fuse
A safety device that melts and breaks the circuit if current exceeds a set value.
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
An automatic switch that trips and disconnects the supply in case of overload or short circuit.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
