Introduction to Household Circuits
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Household Circuits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will discuss household circuits. Can anyone tell me what they understand by 'household circuits'?

I think it’s about how electricity is distributed in our homes.

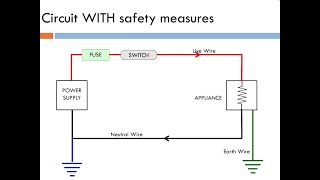
Exactly! Household circuits are the wiring systems used in homes to distribute electricity safely. They include live and neutral wires.

What voltage does our electricity use?

In India, we use 220 V with a frequency of 50 Hz. This knowledge is important for understanding how our appliances function.

Why is it important to know this?

Well, recognizing the voltage helps us select appliances suitable for our electrical systems, preventing damages and ensuring safety.

So it really affects how we use electricity at home?

Absolutely! Understanding these basics enhances our safety while using electrical devices. Let's summarize the key points: Household circuits distribute electricity via live and neutral wires, with 220 V and 50 Hz standards in India.
Importance of Live and Neutral Wires
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive deeper into the components. Who can tell me the function of live and neutral wires?

I believe the live wire carries the current to the device?

Correct! The live wire carries current to the appliance, while the neutral wire brings it back. Imagine L=Live and N=Return – both are crucial for completing the circuit.

What happens if the live and neutral wires touch?

That can create a short circuit, which is dangerous as it allows excessive current to flow and may result in overheating or fire.

So having them insulated is really important?

Precisely! Proper insulation can prevent such hazardous situations. Let’s recap: The live wire carries current to the appliance, while the neutral wire returns it, both essential in ensuring circuit completion.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces household circuits, explaining the role of live and neutral wires in electrical distribution, the standard voltage and frequency in India, and the significance of these circuits in ensuring effective and safe electricity usage in homes.
Detailed
Introduction to Household Circuits
Household circuits encompass the electrical wiring systems found in homes, designed to distribute electricity safely and efficiently. The primary source of electrical supply to residential properties is from electric supply stations, transmitted through live (L) and neutral (N) wires. In India, the standard voltage for mains electricity is 220 V, and the frequency is 50 Hz, which establishes the framework for domestic energy consumption. Understanding these circuits is crucial as they provide a foundation for addressing various electrical aspects, including safety precautions and maintenance.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What Are Household Circuits?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Household circuits refer to the electrical wiring system used in homes to distribute electricity safely and efficiently.
Detailed Explanation
Household circuits are the essential wiring systems found in our homes, designed specifically to carry and manage electricity. The main purpose of these circuits is to ensure that electrical energy is delivered safely and efficiently to various appliances and fixtures in a house. They consist of a network of wires, switches, and other components that safely route electricity from the main supply to the places it is needed.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of household circuits like a city's road system. Just as roads connect various areas of the city and allow cars to travel safely to their destinations, household circuits connect the main electricity supply to various parts of our homes, enabling our devices to function properly.
Main Supply of Electricity
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● The main supply to a house is received from the electric supply station via live (L) and neutral (N) wires.
Detailed Explanation
The main supply of electricity to a house comes from an external source, typically an electric supply station. This supply enters the house through two primary wires: the live wire, which carries the current to the appliances, and the neutral wire, which returns the current back to the supply. This system ensures that electrical current flows safely and effectively, allowing appliances to function as intended.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a water supply system where pipes bring water to your home. The live wire is like the pipe that brings fresh water in (the current to power your devices), while the neutral wire is like the pipe that takes used water away (returning the current). Both are needed for the system to work efficiently.
Voltage and Frequency Specifications
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● In India, the voltage of mains electricity is 220 V, and the frequency is 50 Hz.
Detailed Explanation
Electrical systems operate under specific voltage and frequency specifications. In India, the mains electricity voltage is standardized at 220 Volts, which is the electrical pressure pushing the current through the wires. The frequency of 50 Hertz (Hz) indicates how many times the current changes direction in a second, which is common in household electricity. These specifications are crucial as they determine how appliances are designed to operate safely and efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of voltage as the speed limit on a road. Just as vehicles must adhere to specific speed limits for safety, electrical appliances are built to operate within certain voltage limits to function correctly and avoid damage.
Key Concepts
-
Household Circuits: Systems that distribute electricity in homes.
-
Live Wire: Carries current to devices.
-
Neutral Wire: Returns current from devices.
-
Voltage: Measure of electrical potential difference.
-
Frequency: Cycles per second in AC supply.
Examples & Applications
In a typical home, the lighting fixtures and outlets are connected through household circuits, designed to function with 220 V mains electricity.
Using a multimeter, one can measure the voltage across live and neutral wires to ensure they meet the standards.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Live wires give, neutral wires take, Circuit flows for safety's sake.
Stories
In a cozy little house, the live wire excitedly carried energy to each room. The neutral wire patiently returned it home, ensuring everything stayed safe.
Memory Tools
L for Live (carries), N for Neutral (returns) – remember L-N for circuit flow.
Acronyms
HCS
Household Circuit Safety – Always check wires
use proper voltage.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Household Circuits
The electrical wiring system used in homes to distribute electricity.
- Live Wire (L)
The wire that carries current to an appliance.
- Neutral Wire (N)
The wire that returns current from the appliance.
- Voltage
The electric potential difference, measured in volts.
- Frequency
The number of cycles per second in an AC supply, measured in hertz (Hz).
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
