Role of Fuse and MCB
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Fuses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re discussing fuses. Can anyone tell me what a fuse does?

Isn't it something that protects electrical circuits?

Exactly! A fuse is a safety device that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a safe value. This prevents overheating. Remember, we can refer to it as the 'fire-stopper' of electrical devices.

How does it melt? What material is it made of?

Great question! Fuses are made from a thin wire that melts at a low temperature. Common ratings for fuses include 1A, 2A, 5A, and 15A, which are chosen based on the device’s power requirement.

So, it connects to the live wire? Why is that important?

Yes, always connect it to the live wire. This ensures that if there’s an overload, it will stop the flow of electricity, providing safety for the appliances. Remember: 'Fuse goes live!'

Let's remember what we discussed! Fuses protect circuits by melting when current is too high. Any questions?
Exploring MCBs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about Miniature Circuit Breakers or MCBs. Who can explain how they differ from fuses?

Are they like fuses but better?

Exactly! MCBs are automatic switches that trip to disconnect the supply during overload or short circuits. They can be reset easily, unlike fuses which need replacement.

What’s a short circuit?

A short circuit occurs when live and neutral wires touch, causing a surge of current. MCBs help protect against this by automatically disconnecting the supply. Think of them as 'resettable safety guards!'

Which one is better to use at home?

In most cases, MCBs are preferred because they offer more reliability, convenience, and safety compared to traditional fuses. They’re your go-to option for modern electrical safety!

Let's summarize: MCBs trip automatically and can be reset, making them more reliable than fuses. Any last questions?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Electric fuses and Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) play crucial roles in household electrical safety. Fuses are safety devices that melt to disconnect the circuit when excessive current flows, while MCBs are automatic switches that trip and can be reset after an overload or short circuit, making them more convenient than fuses.
Detailed
Role of Fuse and MCB
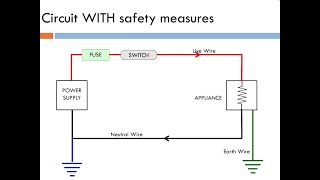
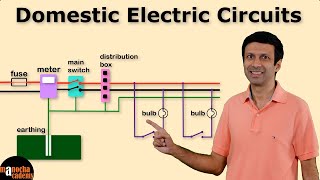
In household circuits, ensuring safety is paramount, especially concerning electrical devices and appliances. This is where the roles of fuses and Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) come into play.
Electric Fuse
An electric fuse is a safety device that melts when the electrical current exceeds a safe threshold, breaking the circuit and preventing potential hazards such as overheating and fires. Fuses are made from a thin wire which has a low melting point, and they come in various ratings like 1A, 2A, 5A, and 15A, ensuring that the electrical system is appropriately protected based on the power demands of devices. Fuses must always be connected to the live wire to function correctly.
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
Unlike traditional fuses, MCBs serve a similar purpose but are automatic switches that trip and disconnect the electrical supply when there’s an overload or short circuit. The key advantages of MCBs over fuses include their ability to be manually reset without needing a replacement, making them more reliable and ultimately more convenient for household use.
Understanding the difference between fuses and MCBs is crucial for maintaining a safe home environment and protecting electrical appliances from damage.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Electric Fuse
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● A fuse is a safety device that melts and breaks the circuit if current exceeds a safe value.
● Made of a thin wire of low melting point.
● Common rating: 1A, 2A, 5A, 15A
● Should always be connected to the live wire.
Detailed Explanation
A fuse is designed to protect electrical circuits from excessive current, which can cause overheating and potentially start a fire. When too much current flows through the fuse, the heat generated melts a thin wire inside the fuse, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This ensures that the rest of the electrical system remains safe. Common fuse ratings indicate the maximum current it can handle, such as 1A for low-power devices and up to 15A for high-power appliances. It is crucial that the fuse be connected to the live wire, as this is where the current enters the circuit.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a fuse like a safety valve on a pressure cooker. Just as the valve opens to release steam if it gets too hot, preventing an explosion, a fuse breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a safe level, preventing potential damage or fire.
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● An automatic switch that trips and disconnects supply in case of overload or short circuit.
● Can be reset manually without replacing any part.
● More reliable and convenient than fuses.
Detailed Explanation
An MCB serves a similar purpose to a fuse by providing a safety mechanism for electrical circuits. However, unlike fuses which must be replaced once they blow, MCBs can be reset with the flick of a switch after they have tripped due to overload or a short circuit. This makes MCBs more user-friendly and convenient, as the system can be quickly restored to normal operation without extra parts. MCBs are also designed to be more reliable, often providing faster and more precise protection compared to traditional fuses.
Examples & Analogies
Consider an MCB like a circuit breaker for a water supply. If too much pressure builds up in the pipes, the circuit breaker activates and stops the flow, preventing leaks or bursts. Just like you can reset a water circuit, restoring the supply when conditions are safe, you can quickly reset an MCB after ensuring the problem has been resolved.
Key Concepts
-
Electric Fuse: A device that protects circuits from overload by melting.
-
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB): An automatic switch that safely disconnects circuits during faults.
-
Overload Protection: Prevention against excessive current to protect electrical system.
-
Short Circuit: A dangerous condition caused by direct contact between live and neutral wires.
Examples & Applications
An electric fuse in a home circuit will blow when a hair dryer and an air conditioner are used simultaneously on the same circuit, preventing fire hazards.
An MCB will trip if a fault occurs in an electric heater, immediately cutting off the electricity supply.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
A fuse is the wire that melts away, keeps shocks and fires at bay!
Stories
Imagine a hero named 'Fuse' who melts away danger when currents are too high, saving the day without a sigh!
Memory Tools
FUSE: 'Fires Under Safety Exceeded' - remember that fuses protect against fire hazards.
Acronyms
MCB
'Manual Circuit Breaker' - clearly shows it can be reset manually!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electric Fuse
A safety device that melts to break the circuit when current exceeds a safe value.
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
An automatic switch that trips and disconnects supply in case of overload or short circuit.
- Overload
A condition where more current flows than the safe limit, potentially causing damage.
- Short Circuit
A fault condition where live and neutral wires touch, allowing excessive current to flow.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
