Household Circuits
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Household Circuits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, everyone! Today, we will explore household circuits. These circuits are vital because they distribute electricity safely in our homes. Can anyone tell me why safety is important in electrical systems?

To prevent fires and electrical shocks?

Exactly! Safety is paramount. We receive electrical supply via live and neutral wires. In India, this supply is at 220 V and 50 Hz. Remember the acronym 'L-N' for Live and Neutral. What can happen if these wires are mishandled?

You could get shocked or start a fire.

Good! Let's discuss what A.C. and D.C. currents are next.
A.C. and D.C. Current
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

A.C. stands for Alternating Current, which means it reverses direction. D.C. stands for Direct Current, where the flow is one direction only. Why do you think A.C. is preferred for household wiring?

Because it can be easily transformed and transmitted?

Correct! A.C. is more efficient for our domestic needs. Can you think of examples where we might use D.C.?

In batteries, like those in remote controls or flashlights!

Exactly! Now, let’s look at the main components of the household circuit.
Main Circuit of a House
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

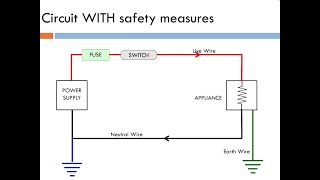
The main circuit in a house includes crucial elements. We have the main fuse to protect against overcurrent, the main switch to control the supply, and the energy meter to measure usage. Does anyone know the role of the distribution box?

It contains circuit breakers for different circuits?

Yes! The distribution box is where we manage our lighting and power circuits. It's important to remember that each type of circuit has a dedicated fuse or MCB for safety. Who can summarize the function of the earth wire?

It prevents electric shocks by grounding the appliances?

Perfectly said! Safety awareness is essential. Let’s move on to how we distribute electricity in our homes.
Distribution of Electricity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Electricity is usually divided into two types of circuits: the lighting circuit and the power circuit. Why do you think we separate them?

So we don’t overload the circuits with too many devices?

Exactly! Lighting circuits handle low-power devices, while power circuits are for high-power appliances. Each circuit has its own fuse or MCB for protection. Remember this separation when installing or using appliances!
Safety Precautions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss some safety precautions when using electricity at home. Anyone know a few?

Don’t use wet hands when touching switches or appliances!

Correct! Also, always use the right type of fuses or MCBs and do not overload sockets. Remember these tips by the acronym 'SAFE' - 'S' for Switches dry, 'A' for Appropriate fuses, 'F' for Fuse rating, and 'E' for Avoid overloads. Who can tell me the importance of earthing?

It keeps the appliance body at zero potential, so there’s no shock risk!

Exactly! You’ve all done great today. Always prioritize safety when working with electricity!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses household circuits, including the types of current used, main components of house wiring, distribution of electricity, and safety mechanisms like fuses and MCBs. It emphasizes the significance of proper earthing and the importance of using correctly rated electrical appliances.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Household Circuits
Household circuits consist of the electrical wiring setups that distribute electricity throughout homes, ensuring safe and efficient usage. The main electrical supply enters homes through live and neutral wires at a standard voltage of 220 V and a frequency of 50 Hz in India.
Key Components
The essential components of a household circuit include:
- Main Fuse: Protects wiring from overcurrent.
- Main Switch: Controls electricity supply.
- Energy Meter: Measures energy consumption in kWh.
- Distribution Box: Hosts circuit breakers for various circuits (lighting and power).
- Earth Wire: Ensures safety against electric shocks.
Types of Current
Household circuits primarily use Alternating Current (A.C.) which reverses direction periodically, suitable for domestic appliances, unlike Direct Current (D.C.) which flows in one direction, mainly used in batteries.
Circuit Distribution
Electricity is divided between:
- Lighting Circuits: For low-power devices (e.g., bulbs and fans).
- Power Circuits: For high-power appliances (e.g., geysers, microwaves).
Each circuit is safeguarded by a dedicated fuse or Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB).
Safety Measures
Safety is crucial; components include:
- Earthing: Provides a safe path for current and prevents shocks, especially for metal appliances.
- Fuses and MCBs: Protect against overloads and short circuits.
Understanding these components is vital for ensuring safety and proper functionality in household electricity usage.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Household Circuits
Chapter 1 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Household circuits refer to the electrical wiring system used in homes to distribute electricity safely and efficiently.
● The main supply to a house is received from the electric supply station via live (L) and neutral (N) wires.
● In India, the voltage of mains electricity is 220 V, and the frequency is 50 Hz.
Detailed Explanation
The introduction sets the stage for understanding household circuits. These circuits form the backbone of electrical systems in homes, ensuring that electricity is distributed in a safe manner. The household receives electricity from an external source through two primary wires: the live wire, which carries electricity to appliances, and the neutral wire, which returns electricity to the source. It's important to note that in India, the standard voltage is 220 volts, and the frequency is 50 hertz, which are crucial for electrical appliances to function correctly.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a water supply system in a house: the live wire is akin to the pipe bringing clean water in, while the neutral wire acts like the pipe carrying used water out. Just as maintaining correct pressure is essential for water flow, keeping the voltage and frequency stable ensures electrical appliances operate smoothly.
Alternating Current (A.C.) and Direct Current (D.C.)
Chapter 2 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Alternating Current (A.C.): Current that reverses direction periodically. Used in household supply.
● Direct Current (D.C.): Current flows in one direction only. Used in batteries, cells.
● A.C. is more suitable for domestic wiring because it can be easily transmitted and transformed.
Detailed Explanation
There are two types of electric current: A.C. and D.C. Alternating current (A.C.) periodically changes direction, allowing it to be easily transmitted over long distances, which is why it's used in household supplies. On the other hand, direct current (D.C.) flows in one direction, ideal for batteries. A.C. also allows for the voltage to be transformed, making it more practical for different appliances in a household.
Examples & Analogies
Think of A.C. like a river that flows and changes course, carrying water to different areas efficiently. D.C., on the other hand, is like a straight pipe delivering water to a single household, ensuring it gets there consistently, but not allowing for easy adjustments or long-distance delivery.
Main Circuit of a House
Chapter 3 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Consists of:
○ Main fuse: Protects the entire wiring from overcurrent.
○ Main switch: Controls the supply to the house.
○ Energy meter: Measures electrical energy consumed (in kWh).
○ Distribution box: Contains circuit breakers for different circuits (lighting, power).
○ Earth wire: For safety from electric shocks.
Detailed Explanation
The main circuit is composed of several critical components. The main fuse protects against overcurrent by breaking the connection when the current exceeds safe levels. The main switch can turn all power off to the house, serving as a central control point. The energy meter tracks electricity usage, helping households monitor their consumption. The distribution box is where multiple circuits branch out, ensuring that different parts of the house, like lights and power outlets, can be controlled independently. Finally, the earth wire provides safety, allowing any leakage current to safely dissipate into the ground, preventing shocks.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the main circuit as the heart of your home’s electrical system. Just like the heart circulates blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients while keeping everything running smoothly, the main circuit ensures electricity flows to where it's needed, with the fuse and switches acting as guardians to prevent any problems.
Distribution of Electricity in a House
Chapter 4 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Supply is divided into two circuits:
○ Lighting circuit: For bulbs, fans, tube lights, etc. (Low power)
○ Power circuit: For high-power appliances like geysers, ACs, microwaves.
● Each circuit has a separate fuse or MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker).
Detailed Explanation
Electricity in a house is distributed into two main circuits: the lighting circuit, which powers low-energy devices like bulbs and fans, and the power circuit, which supplies energy to high-power appliances like geysers and air conditioners. Each circuit is equipped with its own protection—either a fuse or a miniature circuit breaker (MCB)—which will cut off the power if there is an overload, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the two circuits as different roadways: the lighting circuit is like a quaint street lined with houses, designed for local traffic with smaller vehicles, while the power circuit resembles a highway built for larger trucks delivering heavy goods. Each road serves a different purpose but must remain safe to traffic.
Live, Neutral and Earth Wires
Chapter 5 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Live wire (L): Carries current to the appliance. Colour: Red/Brown
● Neutral wire (N): Returns current from the appliance. Colour: Black/Blue
● Earth wire (E): Connected to the metal body of appliances to prevent electric shocks. Colour: Green/Yellow
Detailed Explanation
The electrical system in a home consists of three main types of wires. The live wire, typically red or brown, brings electricity to appliances, enabling them to function. The neutral wire, identified by black or blue, returns the current back after it has passed through the appliance. Finally, the earth wire, which is colored green or yellow, is a safety feature connected to the metal parts of appliances to prevent electrical shocks by grounding any stray electricity.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the live wire as a water supply pipe delivering water into a sink (the appliance), the neutral wire as the drainage pipe taking the leftover water away, and the earth wire as a safety valve ensuring that if something goes wrong, excess water doesn’t flood the surroundings, but instead streams harmlessly away.
Need for Earthing
Chapter 6 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Earthing provides a low-resistance path for current to flow safely into the ground in case of insulation failure.
● Prevents electric shock by keeping appliance body at zero potential.
● Especially important for metal-bodied appliances.
Detailed Explanation
Earthing is a crucial safety feature in electrical wiring. It creates a direct pathway for electrical currents to flow into the ground, which is particularly important in cases of insulation failure where live wires could become exposed. By doing this, it prevents appliances, particularly those with metal casings, from carrying dangerous voltage levels, effectively minimizing the risk of electric shock to users.
Examples & Analogies
Think of earthing like a safety net under a high-wire performer. Just as the net catches anyone who might fall and keeps them safe, earthing ensures that in the event of an electrical fault, any excess current is safely redirected away, protecting the users from harm.
Short Circuit and Overloading
Chapter 7 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Short Circuit
● Happens when live and neutral wires touch directly, allowing large current to flow.
● Can cause overheating and fire.
Overloading
● Occurs when too many high-power appliances are used on a single circuit.
● Increases current beyond safe limit, causing wires to heat.
Detailed Explanation
Short circuits and overloads are two common electrical problems. A short circuit occurs when the live and neutral wires directly touch each other, creating an unintended path for electricity that can lead to excessive current flow, overheating, and potentially fires. Overloading happens when too many high-power devices are connected to a single circuit, increasing the current beyond the safe limit, which can also cause overheating and damage to wiring.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a garden hose: if you accidentally puncture it and the water rushes out uncontrollably, that's akin to a short circuit. Conversely, if too many hoses are connected to the same faucet, unable to handle the pressure, you might find one bursting—that's similar to an overload.
Role of Fuse and MCB
Chapter 8 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Electric Fuse
● A fuse is a safety device that melts and breaks the circuit if current exceeds a safe value.
● Made of a thin wire of low melting point.
● Common rating: 1A, 2A, 5A, 15A
● Should always be connected to the live wire.
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
● An automatic switch that trips and disconnects supply in case of overload or short circuit.
● Can be reset manually without replacing any part.
● More reliable and convenient than fuses.
Detailed Explanation
Fuses and MCBs are essential safety devices in household wiring. A fuse works by melting when the current exceeds a predetermined value, thus breaking the circuit to prevent damage. The ratings (e.g., 1A, 2A, 5A) indicate the current threshold. Fuses connect to the live wire only. On the other hand, an MCB acts as an automatic switch that trips to cut power during an overload or short circuit event. One advantage of MCBs is that they can be reset without needing replacement, making them more efficient for modern homes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a fuse as a firecracker: once it blows, it stops any danger but needs replacing. An MCB is like a circuit breaker in a home; it’s more advanced and can be turned back on with a flick of a switch instead of needing to be replaced, making it more user-friendly.
Precautions in Using Electricity at Home
Chapter 9 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Do not touch switches or appliances with wet hands.
● Always use properly rated fuses or MCBs.
● Do not overload sockets.
● Ensure all appliances are properly earthed.
● Turn off main switch during repairs.
Detailed Explanation
Safety precautions are critical for using electricity safely at home. Users should avoid touching electrical switches or appliances with wet hands to prevent shocks. It's essential to use fuses or MCBs that match the appliance ratings to prevent overloads. Overloading sockets can increase the risk of fires, so it’s crucial to distribute power usage correctly. Proper earthing of appliances also guards against electrical shocks. Lastly, turning off the main switch during repairs avoids accidental injuries.
Examples & Analogies
Using electricity without precautions is like driving a car without wearing a seatbelt. Just as seatbelts protect you from injury during accidents, these safety practices protect you from electrical hazards.
Power Rating of Appliances
Chapter 10 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Every electrical appliance has a power rating, e.g., 1000 W, 230 V.
● Indicates the safe voltage and power consumption.
● Helps in calculating energy consumed: E = P × t
Detailed Explanation
Every electrical appliance comes with a ratings label indicating its power (in watts) and voltage requirements. For example, a 1000 W appliance operates safely at 230 V. Understanding these ratings is crucial as they guide consumers in selecting appliances that fit their electricity supply and help calculate energy consumption using the formula E = P × t, where E is energy in kilowatt-hours, P is power in kilowatts, and t is time in hours.
Examples & Analogies
Think of power ratings like nutrition labels on food: they inform you about what you're getting. By knowing how many watts an appliance uses, you can manage your ‘electricity diet’ just like you would manage your caloric intake.
Three-Pin Plug and Socket
Chapter 11 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Three-pin plug has:
○ Live pin (thin)
○ Neutral pin (thin)
○ Earth pin (thick and longest)
● Earth pin connects first for safety.
● Ensures metal body is earthed before live connection is established.
Detailed Explanation
The three-pin plug design enhances safety. It includes a live pin and a neutral pin, both thin, and a thicker, longer earth pin. This design guarantees that the earth connection is established first, which is crucial in preventing electric shocks. This setup ensures that if there is a fault and the appliance's body becomes live, the current will travel through the earth pin to the ground, eliminating the risk of shock to the user.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a three-pin plug like a safety clamp for a heavy object. As long as it’s secured properly, it ensures that everything is stable, just like how the earth pin secures the appliance and protects users from hazards.
Colour Coding in Wiring
Chapter 12 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Wire Type Function Colour (Standard)
Live Carries current Red or Brown (Phase)
Neutral Return path for current Black or Blue
Earth Safety grounding Green/Yellow
Detailed Explanation
Color coding of wires plays a vital role in identifying their function, which helps prevent accidents. The live wire, which delivers energy, is colored red or brown, while the neutral wire, responsible for returning current, is black or blue. The earth wire, crucial for safety, is colored green or yellow. These standards help electricians and users identify wires quickly and correctly, minimizing the risk of errors during installations or repairs.
Examples & Analogies
Think of color coding like a traffic signal: just as colors instruct drivers when to go and stop, colored wires signal electricians on how to properly connect the circuits and ensure safe operation.
Safety Devices in Household Wiring
Chapter 13 of 13
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Fuse: Prevents excessive current by melting.
● MCB: Automatically breaks circuit on overload/short circuit.
● Earth wire: Prevents electric shock.
● Double insulation: Prevents contact with live parts.
Detailed Explanation
Safety devices are essential components of household wiring. Fuses act as fail-safes, melting to break the circuit when excessive current flows, while MCBs automatically interrupt the supply during overloads or short circuits, protecting against potential hazards. The earth wire helps prevent electric shock by grounding excess current. Additionally, double insulation of appliances prevents users from coming into contact with live parts, providing extra layers of safety.
Examples & Analogies
Think of safety devices like a robust defense system for your home: just as security measures protect your home from intruders, these devices protect you from electrical dangers, ensuring your living space remains secure and risk-free.
Key Concepts
-
Household Circuits: Wiring systems used in homes for distributing electricity.
-
A.C. vs. D.C.: Alternating Current used in homes; Direct Current used in batteries.
-
Main Circuit Components: Main fuse, main switch, energy meter, distribution box, and earth wire.
-
Electrical Circuits Distribution: Separation into lighting and power circuits for efficiency.
-
Safety Mechanisms: Importance of earthing, fuses, and circuit breakers to prevent electrical hazards.
Examples & Applications
Example of A.C.: Electricity that powers lights, fans, and appliances in homes.
Example of D.C.: Batteries used in remote controls, flashlights, and mobile phones.
Example of a fuse: A 5A fuse in a circuit protecting low-power appliances like light bulbs.
Example of MCB: An MCB that trips when a high-power microwave is turned on with other devices running.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When wires collide, a short you will find; keep them apart to keep safety in mind!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a cozy home, a brave fuse protected the appliances from a greedy current trying to surge over its limits, ensuring safety through coordination.
Memory Tools
Remember 'E-L-S' for household circuit safety: Earth wires for grounding, Live wires for power, Switches for control.
Acronyms
Use 'SAFE' for Electrical Safety
- Switches dry
- Appropriate fuses
- Fuse rating
- Avoid overloads.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Alternating Current (A.C.)
Current that reverses direction periodically, used for household supply.
- Direct Current (D.C.)
Current that flows in one direction, typically used in batteries.
- Main Fuse
A protective device that breaks the circuit if overcurrent occurs.
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
An automatic device that disconnects electricity in case of overload or short circuit.
- Earthing
A safety mechanism that provides a low-resistance path for fault current to ground.
- Distribution Box
Contains circuit breakers for various circuits for separate control and protection.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
