Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding MCBs vs. Fuses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore Miniature Circuit Breakers, or MCBs, which are important safety devices. Can anyone tell me how MCBs are different from traditional fuses?

Fuses melt when there's too much current, right?

Exactly! Fuses provide a one-time protection by melting, while MCBs are resettable. So, if an MCB trips, what do you think you can do?

You can just turn it back on after fixing the issue?

Correct! This makes MCBs more convenient. Remember: MCB = Reset, Fuse = Replace. Let's keep that acronym in mind!

What kind of issues usually cause an MCB to trip?

Good question! The two main issues are overloads and short circuits. Remember, an overload occurs when too many devices are on one circuit, while a short circuit happens when live and neutral wires touch.

That means MCBs are really important for safety!

Absolutely! Safety first with MCBs! Let's review: MCBs reset, protect against overloads and shorts, and are crucial for household safety.
MCB Ratings and Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into MCB ratings. MCBs come in various current ratings. Can anybody tell me some ratings they may have seen?

I've seen ratings like 6A and 16A.

Very good! The rating indicates the maximum current the MCB can handle without tripping. Why do you think that is important?

So that it can handle the appliance's load without tripping accidentally?

Exactly! Choosing the right rating ensures the MCB is effective for specific circuits. For example, larger appliances need higher-rated MCBs.

Do MCBs come in types?

Yes, that's right! There are Type B, C, and D MCBs, designed for different uses, like lighting or industrial applications. Remember to choose wisely based on usage!

So it's not just about resetting but also choosing the proper rating and type?

Correct! Key takeaways: MCB ratings match circuit loads, and types vary by application. Great job, everyone!
Benefits and Limitations of MCBs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss the benefits of using MCBs. What do you think makes them better than fuses?

They can be reset!

And they're quicker to respond?

Yes! MCBs react faster during overloads, hence minimizing risks. What about limitations, if any?

Are they more expensive?

Good point! Initially, MCBs can be pricier than fuses, but they save money in the long run due to their lifespan and ease of use. Remember, upfront costs versus long-term benefits!

So they're generally better for homes?

Exactly! MCBs are more reliable and safer, thus making them ideal for home use. In summary: Benefits include reset capability and speed, while the price is a consideration.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
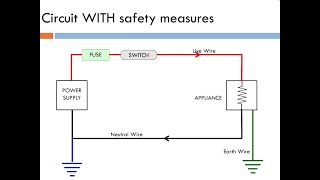
MCBs serve as essential safety devices in household electrical systems. They automatically trip and disconnect the power supply in the event of an overload or short circuit, making them more reliable and user-friendly than traditional fuses. Unlike fuses, MCBs can be reset manually without needing replacement.
Detailed
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
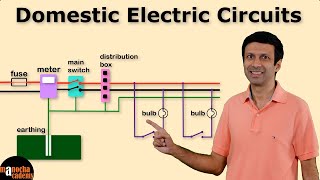
The Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is a crucial safety device used in household electrical circuits. Its primary function is to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. When there is a surge in current, either due to excessive load or a fault in the wiring, the MCB automatically disconnects the circuit, effectively preventing potential damage, electrical fires, or shocks. This tripping mechanism resets easily with a switch, unlike fuses, which require replacement once blown. MCBs come in various ratings, allowing them to be tailored to specific circuits, enhancing the overall safety and efficiency of electrical systems in a household.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is an MCB?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● An automatic switch that trips and disconnects supply in case of overload or short circuit.
Detailed Explanation
A Miniature Circuit Breaker, or MCB, is an automatic switch used in electrical systems to protect against overloads and short circuits. When the electrical current exceeds a certain level—usually due to excess load or a fault—the MCB 'trips,' which means it disconnects the electrical supply to prevent damage to the wiring and appliances.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the MCB like a lifeguard at a swimming pool. Just as a lifeguard watches for potential dangers and can evacuate the pool when it's unsafe, the MCB monitors the electrical current and shuts off the supply if it detects a problem, helping to keep the electrical system safe.
Resetting an MCB
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Can be reset manually without replacing any part.
Detailed Explanation
One of the advantages of an MCB is that after it trips due to an overload or short circuit, it can be reset manually. This means you don't need to replace any components or fuses. After addressing the issue that caused the MCB to trip, you can simply flip a switch to restore power, making it user-friendly and convenient.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine if a circuit breaker was like a light switch. When the light goes out (or the circuit gets overloaded), you don’t have to change the bulb (replace parts); you just need to flip the switch back on after fixing the problem. That’s how easy it is with an MCB!
Comparing MCBs with Fuses
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● More reliable and convenient than fuses.
Detailed Explanation
MCBs are considered more reliable and convenient than traditional fuses. Fuses melt and must be replaced after they blow, which can be inconvenient during an emergency. In contrast, MCBs reset with a switch and do not require replacement, making them a better option for modern electrical installations.
Examples & Analogies
You can compare MCBs to a modern smartphone charger that breaks if too much electricity flows through it. Instead of throwing it away, you can reset it quickly, unlike an older charger that might just melt away, requiring a trip to the store for a replacement. Similarly, MCBs save time and hassle because they can simply be reset.
Key Concepts
-
MCBs provide automatic disconnection during overload or short circuit.
-
MCBs can be reset manually, unlike fuses.
-
The right rating is essential for optimal protection against electrical faults.
Examples & Applications
MCBs are used in homes to protect circuits supplying lighting or high-power appliances like air conditioners.
In industrial settings, different types of MCBs are used for various electrical loads based on their ratings.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When wires are hot and current is flowin’, MCBs trip and that’s why they’re showin’.
Stories
Imagine a busy kitchen where a toaster overheats and draws too much power. The MCB senses the danger and trips, turning off the power, saving the kitchen from a fire.
Memory Tools
Remember: MCB = Manual comeback button. You reset it after an unwanted trip!
Acronyms
MCB
Miniature
Circuit
Breaker!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
An automatic switch that disconnects a circuit when it detects overload or short circuit conditions.
- Overload
A condition where the electrical load exceeds the safe capacity of a circuit.
- Short Circuit
A situation where an unintended connection allows current to flow directly between the live and neutral wires.
- Trip
The action of an MCB disconnecting the circuit in response to an overload or fault.
- Circuit Rating
The maximum current an MCB can handle without tripping.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
