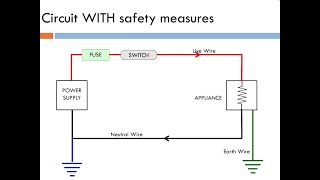
Electric Fuse
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Electric Fuse
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore electric fuses. Can anyone tell me what a fuse is?

Isn't it a device that helps stop electrical overloads?

Exactly! A fuse melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a certain safe level. This prevents overheating and potential fires.

How does it know when to melt?

Great question! It is made of a thin wire that melts at a specific temperature when too much current passes through it.
Fuse Ratings
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into fuse ratings. Fuses come in different ratings like 1A, 2A, and 5A. Who can help me understand what this means?

So, does the number refer to how much current it can handle?

Correct! It indicates the maximum current the fuse can carry before it blows. Choosing the right rating is crucial for safety.

What happens if we use a fuse rated too high?

If a fuse is rated too high, it may not blow during an overload, which can be dangerous.
Connection of Fuse to Live Wire
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about how we connect the fuse in a circuit. Which wire do we connect it to?

It should be connected to the live wire, right?

Exactly! Connecting it to the live wire ensures that the current is interrupted during an overload, protecting the entire circuit.

Can you remind us why it’s not connected to the neutral wire?

If the fuse were connected to the neutral wire and it blew, the current could still be flowing through the live wire, which isn’t safe.
Importance of Fuses for Safety
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think fuses are so important in our homes?

They help prevent fires and protect appliances!

Yes! By breaking the circuit during overloads, fuses protect both our appliances and our homes from electrical hazards.

Could we have a situation where a fuse doesn't work?

Certainly! If the fuse is corroded or if the wrong type is used, it may not function correctly, highlighting the need for regular checks on electrical systems.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The electric fuse plays a crucial role in household circuits by melting and breaking the circuit in case of excessive current. This section discusses how fuses are constructed, their ratings, and their significance in maintaining electrical safety.
Detailed
Electric Fuse
An electric fuse is a critical safety device used in household circuits to protect against excessive current that can result in overheating and potential fires. A fuse consists of a thin wire made of a low melting point metal. When the current exceeds a predetermined safe level, this wire melts, effectively breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity.
Construction and Ratings
Fuses are available in various ratings such as 1A, 2A, 5A, and 15A, indicating their capacity to carry current. Proper selection of the fuse rating is essential to ensure optimal protection without frequent interruptions in supply due to unnecessary fuse blowing.
Wiring Considerations
It is important that the fuse is connected to the live wire to effectively protect the circuit. Understanding these aspects of fuses enhances electrical safety within household circuits.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Electric Fuse
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● A fuse is a safety device that melts and breaks the circuit if current exceeds a safe value.
Detailed Explanation
A fuse is an important safety component in electrical circuits. Its main purpose is to protect the circuit from excessive current, which can lead to overheating and potential fires. When the current flowing through the fuse exceeds its rated capacity, the fuse's conductor melts, interrupting the flow of electricity and breaking the circuit.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of a fuse like a safety valve in a pressure cooker. Just as a safety valve releases steam if the pressure gets too high, a fuse prevents too much electricity from flowing through the circuit by 'blowing' or melting when the current is too high.
Construction of a Fuse
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Made of a thin wire of low melting point.
Detailed Explanation
The fuse is constructed from a thin wire that has a low melting point. This is crucial because, under normal circumstances, the wire conducts electricity safely. However, when the current exceeds safe levels, the wire heats up and melts quickly, which breaks the circuit and stops the flow of electricity. This design ensures that the fuse reacts quickly to dangerous electrical situations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making a paper airplane with delicate paper. If too much weight is added (analogous to excessive current), the paper will tear (like the fuse melting), ensuring that the airplane doesn't fly dangerously.
Common Ratings of Fuses
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Common rating: 1A, 2A, 5A, 15A.
Detailed Explanation
Fuses come in various ratings to match the requirements of different electrical circuits and appliances. The ratings refer to the maximum current, measured in Amperes (A), that the fuse can handle safely. For example, a 1A fuse is designed for low power applications, while a 15A fuse can protect higher power devices. It's essential to choose the correct fuse rating to prevent damage to devices and ensure safety.
Examples & Analogies
Think of fuses like the weight limit on a bridge. If the weight of vehicles exceeds the limit, the bridge could collapse, similar to how an overloaded circuit can cause a fuse to blow. Using the right fuse rating is like following the weight limit rules to keep everything safe.
Connection of Fuse to Circuit
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Should always be connected to the live wire.
Detailed Explanation
Fuses should always be installed in the live wire of an electrical circuit. This is because the live wire carries the electrical supply to the appliance. By connecting the fuse here, it can effectively cut off the electricity supply if the current exceeds safe levels. This placement is essential for safety, as it prevents any current from reaching the appliance when the fuse has blown.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a fuse like a traffic light that controls the flow of cars (electricity). If a traffic light is broken at the intersection (like a blown fuse), it ensures that no cars can pass (no electricity reaches the appliance), preventing accidents.
Key Concepts
-
Electric Fuse: A safety device that prevents fires by breaking the circuit during overloads.
-
Fuse Ratings: Indicate the maximum current a fuse can handle before it melts.
-
Connection to Live Wire: Ensures that the fuse operates correctly to protect the circuit.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: A standard household fuse rated at 5A protects household lighting circuits from overload.
Example 2: A 15A fuse might be used for power circuits serving high-demand appliances like refrigerators.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Fuses break the current flow, / Protect our homes, and help us grow.
Stories
Imagine a brave little fuse standing guard, ready to melt and protect every time the currents ran too far.
Memory Tools
Remember 'FUSE' as Follow Up for Safety in Electricity.
Acronyms
FUSE - 'Fighting Unwanted Surges in Electricity.'
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electric Fuse
A safety device that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a safe level.
- Current Rating
The maximum current that a fuse can allow before it melts.
- Live Wire
The wire that carries current to the appliance.
- Overload
Excessive demand on the electrical circuit, leading to high current.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
