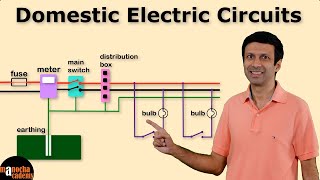
Safety Devices in Household Wiring
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Fuse
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll start with one of the primary safety devices used in household wiring: the fuse. Can anyone explain what a fuse does?

Isn't it like a safety switch that melts if too much current goes through?

Exactly! A fuse melts to break the circuit when excessive current flows. This prevents overheating and possible fires. Remember, we often call this device a 'current limiter.'

What's that thing made of?

Good question! Fuses are typically made of a thin piece of wire with a low melting point. For instance, common ratings are 1A, 5A, or 15A, depending on the circuit requirements. Can anyone think of where a fuse might commonly be found?

In our home electric panels, right?

Yes, precisely! They’re found in our homes to protect entire circuits. To help you remember, think of the acronym 'S.A.F.E'—S for Safety, A for Always replace it when blown, F for Fuse limits current, and E for Emergency prevention.

That's a great way to remember it!

Exactly! The key takeaway here is that fuses are essential for safeguarding your household from electrical hazards.
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move on to the Miniature Circuit Breaker or MCB. What distinguishes MCBs from fuses?

I think MCBs can be reset while fuses need to be replaced?

That's correct! MCBs automatically break the circuit when excessive current is detected, and you can reset them by simply switching them back on, making them more convenient.

Does that mean MCBs are safer than fuses?

Yes, in many cases! Since they can be reset, it minimizes downtime after a trip. Remember, MCBs are there to protect both your appliances and your safety from overloads or short circuits.

Are MCBs more expensive than fuses?

Generally, yes. But considering their advantages in reliability and safety, they are often worth the investment. As a memory aid, think of 'C.R.I.S.P.'—C for Circuit protection, R for Reset, I for Instant trip, S for Safety, P for Prevents damage.

I’ll remember that one!

Fantastic! MCBs play a significant role in modern electrical systems.
Earth Wire and Safety
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve into the earth wire now. Who can tell me its main purpose?

Isn't it to prevent electric shock?

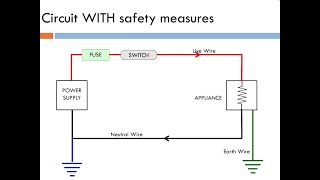
Correct! The earth wire provides a safe path for fault current to flow into the ground, which prevents shocks if there's an insulation failure. It's crucial for any metal-bodied appliances.

How does it connect to the ground?

Good question! It connects to a rod driven into the ground, which dissipates electrical energy safely. Remember, you can think of the earth wire as a 'safety umbrella'—it shields you from harmful currents.

So it's really important for safety.

Absolutely! Using appliances with proper earthing is critical. And don't forget, remember 'G.E.N.'—G for Grounding, E for Earth wire, N for Neutralize shocks.

Got it!

Excellent! Always prioritize safety in handling electrical devices.
Double Insulation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss double insulation. What do you think this means?

Could it be two layers of insulation around electrical components?

Yes, that's spot on! Double insulation means there are two insulating layers to prevent accidental contact with live parts, especially in appliances with metal bodies. This is essential in reducing electrical shock risk.

Are all appliances double insulated?

Not all, but many modern appliances are designed this way. Look for the 'double insulation' symbol on the product. To help remember this, think of 'D.I.D.'—D for Double, I for Insulation, D for Defense against shocks.

So is double insulated equipment better?

Yes! It’s one of the best safety features for domestic appliances, ensuring added protection. Always opt for them when possible.

This has been really informative!

I'm glad to hear that! Remember these key safety concepts for better electrical practices.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Fuses and Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) are crucial safety devices that prevent excessive current and protect against overloads and short circuits. The earth wire ensures safety from electric shocks, while double insulation provides added protection against accidental contact with live parts.
Detailed
Safety Devices in Household Wiring
In this section, we explore the essential safety devices that safeguard household wiring systems against electrical hazards. The main devices include:
1. Fuse: A fuse is designed to prevent excessive current by melting when it exceeds a particular safe threshold, hence breaking the circuit. It is typically made from thin wire with a low melting point.
2. Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB): An MCB is an automatic switch that breaks the circuit when it detects an overload or a short circuit, providing a more convenient alternative to traditional fuses since it can be reset without needing replacement.
3. Earth Wire: The earth wire is a safety feature that prevents electric shock by directing any leakage current away from a person and into the ground.
4. Double Insulation: Double insulation refers to a technique where appliances are designed with an insulating layer both internally and externally, reducing the risk of accidental contact with live components.
These devices play a vital role in ensuring safety in household electrical systems and significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Fuse
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Fuse: Prevents excessive current by melting.
Detailed Explanation
A fuse is a safety device that helps to protect electrical circuits from excessive current. When the current in a circuit exceeds the fuse's rated capacity, the wire inside the fuse heats up and melts. This breaking of the circuit stops the flow of electricity, preventing potential damage to electrical appliances or wiring from overheating.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of a fuse like a safety valve in a pressure cooker. Just as the valve releases steam to prevent the cooker from exploding under too much pressure, a fuse breaks the circuit to prevent damage from too much electrical current.
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● MCB: Automatically breaks circuit on overload/short circuit.
Detailed Explanation
An MCB is a modern safety device that automatically switches off electrical circuits when it detects an overload or a short circuit. Unlike fuses, MCBs can be reset after tripping without the need for replacement. They work faster than fuses and provide a more reliable method of protecting home wiring systems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine an MCB as a smart traffic light. If there is too much traffic, the light changes to red to prevent accidents and ensure safety. Similarly, an MCB switches off the circuit to prevent overheating or damage when there's too much electrical load.
Earth Wire
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Earth wire: Prevents electric shock.
Detailed Explanation
The earth wire is a crucial safety feature in household wiring. Its primary function is to prevent electric shock. It provides a safe path for electrical current to flow into the ground in case of a fault or short circuit, ensuring that exposed metal parts of appliances do not become live with electricity, which can lead to serious electric shocks.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the earth wire like a safety net for acrobats. Just as the net catches the acrobat if they fall, the earth wire ensures that any stray current is safely directed away, protecting people from getting shocked.
Double Insulation
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Double insulation: Prevents contact with live parts.
Detailed Explanation
Double insulation refers to a safety design feature intended to prevent electrical shock. It is achieved by using two layers of insulating material to shield the live components of an appliance or electrical device. This means that even if the outer layer were to be damaged, the inner layer would still prevent any electrical contact, greatly enhancing user safety.
Examples & Analogies
Think of double insulation as wearing two pairs of socks on a cold day. If the outer sock gets wet, the inner sock still keeps your feet dry. Similarly, double insulation protects users by ensuring there's always a layer of safety, even if one layer is compromised.
Key Concepts
-
Fuse: A device that protects against excessive current by melting.
-
MCB: An automatic switch that trips during overloads or short circuits.
-
Earth wire: A wire that protects people from electric shocks by connecting to the ground.
-
Double insulation: A design feature that includes two insulating layers to enhance safety.
Examples & Applications
A fuse in a lamp that blows when the current exceeds 5A, preventing damage.
An MCB that trips when a faulty appliance tries to draw too much current, ensuring safety.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Fuses melt, when current swells, protecting home from danger spells.
Stories
Once in a house, the appliances were buzzing, but when the current surged, the fuse melted. The house was safe, thanks to its clever design!
Memory Tools
Remember D.E.C.S. for safety devices: D for Double Insulation, E for Earth Wire, C for Circuit Breaker, S for Safety Fuse.
Acronyms
S.A.F.E for Fuse
for Safety
for Always replace it
for Fuse limits current
for Emergency prevention.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Fuse
A safety device that melts to break an electrical circuit when excessive current flows.
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
An automatic switch that disconnects the circuit in case of an overload or short circuit.
- Earth wire
A safety wire connected to the ground, preventing electric shocks.
- Double Insulation
A technique where appliances have two layers of insulation to prevent contact with live parts.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
