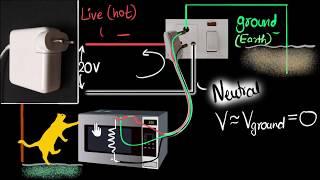
Live, Neutral and Earth Wires
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Live Wire
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by discussing the live wire. The live wire, marked by red or brown color, is crucial as it carries current to the appliance. Does anyone know why it's called the 'live' wire?

Is it because it provides power to the devices?

Exactly! It is 'live' as it is constantly providing electricity. Remember the acronym LEAD: 'Live, Electrocution, Current – Always Dangerous' to remind us of its hazards.

What happens if there’s a short circuit here?

Good question! A short circuit can lead to excessive current, heating up wires dangerously. We'll discuss these issues later.

So, what key point should you remember about the live wire?

That it carries current and can be dangerous!

Spot on! The live wire is essential, but also the most hazardous. Let's move to the neutral wire.
Role of the Neutral Wire
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore the neutral wire, which is colored black or blue. What is its primary purpose?

It returns the current back to the energy source.

Correct! It completes the circuit. Remember: 'Return for safety!' Can anyone explain what happens if the neutral wire fails?

It could cause a malfunction or possibly shock someone?

Great point! An open neutral can create dangerous situations. Why do you think the neutral wire is critical?

To make sure the circuits work efficiently!

Exactly! It prevents buildup of extra currents. Let's wrap this up with the earth wire.
Importance of the Earth Wire
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, we have the earth wire, identifiable by its green or yellow color. Why is this wire so important?

It prevents electrical shocks!

Right! The earth wire safely directs any excess current into the ground. Remember: 'Ground your safety!' How does this differ from the other wires?

It doesn't carry current during normal operation but only during faults.

Perfect! It's a critical safety measure. If all else fails and there's a fault, the earth wire protects us. What's the key takeaway about these wires?

The live wire provides power, the neutral wire returns it, and the earth wire keeps us safe!

Well summarized! Understanding these wires is crucial for anyone working with electricity.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Live, neutral, and earth wires are essential components of household electrical circuits. The live wire carries electrical current to appliances, while the neutral wire returns it. The earth wire serves as a safety mechanism, preventing electric shocks by redirecting excess current safely to the ground.
Detailed
Live, Neutral and Earth Wires
In household electrical systems, three main types of wires are critical for safe operation:
- Live Wire (L): This wire carries electrical current to the appliance. It is typically colored Red or Brown. The live wire is essential for the functioning of various household devices as it provides the necessary voltage.
- Neutral Wire (N): The neutral wire returns electrical current from the appliance back to the supply source. It is usually colored Black or Blue. The neutral wire helps complete the electrical circuit, ensuring that devices operate correctly without overloading the system.
- Earth Wire (E): The earth wire is a safety feature that connects the metal bodies of appliances to the ground. It is commonly colored Green/Yellow. The primary function of the earth wire is to prevent electric shocks by providing a safe path for excess current to flow into the ground, thus protecting users from the hazards of electrical faults.
Understanding the distinct roles and colors of these wires is crucial for both safety and proper installation practices in household circuits.
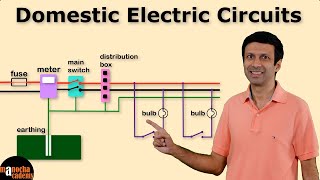
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Live Wire
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Live wire (L): Carries current to the appliance. Colour: Red/Brown
Detailed Explanation
The live wire, often colored red or brown, is the wire that delivers electrical current from the power source to the electrical appliance. It is important because it is where the voltage is present and drives electricity for the appliance's operation. The current flows into the appliance through this wire, allowing it to function.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the live wire as the main road that takes cars (electric current) from one city (the power supply) to another (the appliance). Just as cars need a road to travel on, electrical appliances need the live wire to receive power.
Neutral Wire
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Neutral wire (N): Returns current from the appliance. Colour: Black/Blue
Detailed Explanation
The neutral wire, typically colored black or blue, serves the purpose of returning current back to the electrical supply after it has passed through the appliance. It completes the electrical circuit, allowing the current to flow back and ensuring that the system is balanced and safe.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the neutral wire as a return path on a highway system. Once the cars (current) have delivered their goods (power) to a destination (the appliance), they need a way back home. The neutral wire provides that return route, ensuring the system can repeat the process again.
Earth Wire
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Earth wire (E): Connected to the metal body of appliances to prevent electric shocks. Colour: Green/Yellow
Detailed Explanation
The earth wire, which is often green or yellow, plays a critical role in safety. It is connected to the metal parts of electrical appliances and serves as a safety measure to redirect any stray electric current away from the appliance and into the ground. This prevents potential electric shocks to users and protects the appliance itself.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the earth wire as a safety net for acrobats. Just as the safety net catches an acrobat if they fall, the earth wire catches any misplaced electrical current, guiding it harmlessly into the ground instead of through a person.
Key Concepts
-
Live Wire (L): Carries current to devices.
-
Neutral Wire (N): Returns current from devices.
-
Earth Wire (E): Safety wire connecting appliances to the ground.
Examples & Applications
The live wire in a household circuit connects to the wall socket, supplying power to devices such as lamps and TVs.
The earth wire helps protect a washing machine operator by preventing electrical shock in case of a fault in the machine.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Live is red, neutral is blue, earth is yellow/green for safety too.
Stories
Once upon a time, in an electrical land, the Live Wire brought energy to all devices. The Neutral Wire helped return the currents, while the Earth Wire stood as a protector against dangers.
Memory Tools
Remember 'LNE' - Live, Neutral, Earth. The three essential wires for safety and power.
Acronyms
Think of 'L.N.E.' for Live (L), Neutral (N), Earth (E) - each has its critical purpose.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Live Wire
The wire that carries electrical current to an appliance, typically colored red or brown.
- Neutral Wire
The wire that returns electrical current from the appliance to the supply source, usually colored black or blue.
- Earth Wire
A safety wire connected to the ground, colored green/yellow, preventing electric shocks.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
