Main Circuit of a House
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Main Circuit Components
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the main components of a house's electrical circuit. Does anyone know what these components are?

I think there’s a fuse and a switch.

That's right! We have the main fuse to protect against overcurrent, the main switch for controlling the supply, an energy meter to track consumption, a distribution box for organizing circuits, and an earth wire for safety. Let's start with the fuse.

What exactly does the main fuse do?

Great question! The main fuse melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a certain limit. This helps prevent fire hazards. Can anyone think of why that's important?

Because it stops too much electricity from damaging the wiring or appliances.

Exactly! Protecting the wiring is critical for safety. Now, what about the main switch?
Understanding the Role of the Energy Meter
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the energy meter now. Who can tell me what this device does?

It measures how much electricity we use, right?

Correct! It measures electrical energy in kilowatt-hours or kWh, helping us track usage. Why might this be important?

It helps us manage our electricity bills!

Exactly! Monitoring usage can lead to energy savings. Now, let’s talk about the distribution box. What do you think it does?
Role and Importance of the Distribution Box and Earth Wire
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As mentioned, the distribution box organizes the circuits in your home. It contains circuit breakers for different functions, such as lighting and appliances. What might be the benefit of having these separate?

It makes it easier to manage which circuits are overloaded!

Exactly! This separation helps prevent electrical overloads and ensures safety. Now, let's explore the earth wire. Why do you think it's important?

It stops people from getting shocked when there's a fault.

That's absolutely right! The earth wire safely directs electrical faults into the ground, protecting you from electric shocks.
Safety and Maintenance of the Main Circuit
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, we know the components of the main circuit, what about safety? Why is regular maintenance of these components important?

To make sure everything works correctly and to prevent accidents!

Exactly! Regular checks can help identify issues before they become dangerous. What should we do if we notice something unusual?

We should call a professional electrician.

Right again! Always prioritize safety and avoid trying to fix complex electrical issues on your own. To summarize, the main circuit components work together to ensure our electrical system functions safely and efficiently.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section details the components that make up the main circuit of a house, including the main fuse for overcurrent protection, the main switch for controlling power supply, the energy meter for measuring electricity consumption, a distribution box with circuit breakers for various circuits, and an earth wire for safety against electric shocks. Each component plays a crucial role in household electrical systems.
Detailed
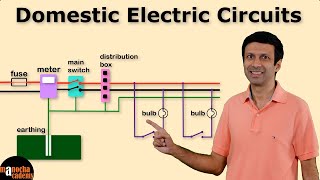
Main Circuit of a House
The main circuit of a house is crucial in managing the electrical system safely and efficiently. It includes several key components:
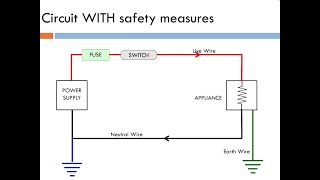
- Main Fuse: This is a safety device that protects the household wiring from overcurrent, preventing potential fires or damage due to excess current flow.
- Main Switch: This switch controls the overall supply of electricity to the house, allowing users to turn off all electrical power when necessary—for instance, during maintenance or emergencies.
- Energy Meter: Installed to measure the electrical energy consumed (usually in kilowatt-hours), which helps in tracking electricity usage and expenses.
- Distribution Box: This box houses circuit breakers that manage different circuits within the home, typically separating lighting circuits from power circuits. Each circuit has its protective device to ensure safety.
- Earth Wire: Essential for safety, the earth wire provides a path for electrical faults to safely dissipate into the ground, protecting users from electric shocks.
Understanding these components is vital for anyone managing household electrical systems.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Main Fuse
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Main fuse: Protects the entire wiring from overcurrent.
Detailed Explanation
The main fuse is an essential safety device in the electrical circuit of a house. Its primary role is to protect the electrical wiring of the house from damage due to overcurrent. Overcurrent can occur if too much electricity flows through the wires, which could happen during a fault in the wiring or if too many appliances are used simultaneously. When overcurrent is detected, the fuse melts, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity to prevent overheating and potential fires.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the main fuse as a firefighter for your home’s electrical system. Just like a firefighter puts out fires to protect buildings and people, the main fuse stops the current from flowing too much and causing damage. If the current gets too high (like a fire getting out of control), the fuse melts quickly to keep everything safe.
Main Switch
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Main switch: Controls the supply to the house.
Detailed Explanation
The main switch is a device that controls the electricity supply to all circuits within a house. It allows the user to turn off all electricity at once for safety reasons, such as during maintenance or emergencies. When the main switch is turned off, it disconnects the house from the electrical supply, preventing any current from flowing through the system.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the main switch as the master control panel in a video game. Just like you can pause the game completely to prevent any actions from happening, turning off the main switch pauses the electricity flowing in your house, giving you complete control and safety.
Energy Meter
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Energy meter: Measures electrical energy consumed (in kWh).
Detailed Explanation
The energy meter is an important device that tracks the amount of electrical energy consumed in the home over time, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This device provides consumers with information on their energy usage, allowing them to monitor performance and make adjustments to save electricity or reduce costs. Utility companies use this data to bill customers for their energy usage.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the energy meter like a scoreboard in a sports game. Just as a scoreboard tracks the progress and performance of the teams during the game, the energy meter keeps track of how much electricity you use in your house, helping you stay aware of your consumption and possibly helping you save money.
Distribution Box
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Distribution box: Contains circuit breakers for different circuits (lighting, power).
Detailed Explanation
The distribution box is a critical component of the electrical system in a household. It houses circuit breakers, which are devices that automatically shut off power to a circuit in case of a fault, such as a short circuit or overload. This helps prevent wiring damage and reduces the risk of electrical fires. The distribution box allows the electrical supply to be split into various circuits—for example, one for lighting and another for power outlets—ensuring that each area can be managed safely and efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the distribution box like a traffic intersection in a city. Just as traffic lights control the flow of cars at busy intersections to prevent crashes and manage traffic smoothly, the distribution box controls the flow of electricity throughout your home, directing it safely to different areas based on their needs.
Earth Wire
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Earth wire: For safety from electric shocks.
Detailed Explanation
The earth wire is a safety feature of the electrical system that provides a pathway for electricity to flow safely into the ground in case of a fault or malfunction. It prevents electric shocks by ensuring that in the event of a short circuit or insulation failure, the excess electricity does not pass through a person who may touch the appliance. The earth wire is usually connected to the metal casing of tools and appliances, grounding them and keeping them safe for use.
Examples & Analogies
You can imagine the earth wire as a safety net for trapeze artists. Just as the net catches a performer if they fall during a stunt, the earth wire provides a safe escape route for stray electricity, ensuring that it doesn’t harm anyone using the electrical appliances in your home.
Key Concepts
-
Main Fuse: This component protects the wiring from overcurrent.
-
Main Switch: Controls the overall electrical supply to the house.
-
Energy Meter: Measures electricity consumption in kWh.
-
Distribution Box: Organizes different household circuits.
-
Earth Wire: Provides safety from electric shocks.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: The main fuse melts and breaks the circuit during a power surge to prevent further damage.
Example 2: An energy meter shows that a family's monthly electricity consumption is 300 kWh.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
The fuse protects, the switch controls, the meter tracks our power rolls.
Stories
Once upon a time in a house of wires, the main fuse defended against electrical fires, the switch brought light, the meter kept count, while the earth wire ensured safety on every front.
Memory Tools
FAME: Fuse, Ampere (current), Meter, Earth–all key components of the electrical circuit.
Acronyms
M-FED
Main Fuse
Main Switch
Energy meter
Distribution box – remember the main components!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Main Fuse
A safety device that protects the electrical system from overcurrent.
- Main Switch
A switch that controls the overall supply of electricity to the house.
- Energy Meter
A device that measures the electrical energy consumed in kilowatt-hours.
- Distribution Box
A box that houses circuit breakers for various electrical circuits in a home.
- Earth Wire
A wire that connects electrical appliances to the ground, providing safety against electric shocks.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
