Power Rating of Appliances
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Power Ratings
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's discuss the power rating of appliances. Can someone tell me what a power rating generally indicates?

Is it how much electricity the appliance needs to work?

Exactly! The power rating indicates how much power, measured in watts, an appliance uses when in operation. This is crucial for energy management. Can anyone share an example of an appliance and its power rating?

I know a heater can use about 1500 watts!

Great example! Remember, more watts mean more energy consumption. What are some implications of using an appliance beyond its rated power?

It could be dangerous, right? Like causing a short circuit?

Exactly, overloading can lead to electrical fires. So always check the ratings!
Calculating Energy Consumption
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what power ratings are, let's learn how to calculate energy consumption using the formula E = P × t. Who can break that down for us?

E is energy, P is power, and t is time, right?

Right! If you ran a 1000 W appliance for 2 hours, how much energy would it consume?

E equals 1000 W times 2 hours, which is 2000 watt-hours or 2 kWh.

Perfect! This means if you ran that appliance for 2 hours, on your bill you'd see a cost for 2 kWh of energy. Why do we need to know this?

To budget our electricity costs better!

Exactly! Energy efficiency is key.
Safety with Power Ratings
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Safety is a major reason we pay attention to power ratings. What can happen if we ignore these ratings?

The wires might overheat, right?

That's right! Overheating can lead to fires. Can anyone think of other risks?

There could be electric shocks too!

True! Always using appliances according to their power ratings ensures safe operation. What should you check before plugging in an appliance?

The wattage it requires and if my circuit can handle it!

Great thoughts! Remember, safer practices create a happier home.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Every electrical appliance has a power rating, which indicates its power consumption in watts and the voltage it operates on. Understanding these ratings is vital for safe energy consumption and calculating energy usage over time.
Detailed
Power Rating of Appliances
Every electrical appliance in a household has a specific power rating, such as 1000 W or 230 V. This rating not only indicates the amount of electrical power that the appliance consumes but also the safe operating voltage. Properly understanding and applying this information is crucial for a few key reasons:
- Energy Consumption Calculation: The formula for calculating energy consumed over time is given as E = P × t, where E is the energy in kilowatt-hours (kWh), P is the power rating in watts, and t is the time in hours the appliance is used.
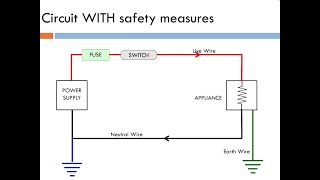
- Safety: Adhering to the power ratings helps ensure that appliances are not overused or overcurrent drawn, reducing the risk of electrical fires and other hazards.
- Efficiency: By understanding how much power appliances consume, consumers can make more informed decisions about energy use, leading to potential savings on bills and contributing to energy conservation efforts.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Power Rating
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Every electrical appliance has a power rating, e.g., 1000 W, 230 V.
Detailed Explanation
The power rating of an appliance indicates how much power it consumes when in operation. It's usually specified in watts (W) and volts (V). For example, an appliance with a power rating of 1000 W operates at a voltage of 230 V. This means it uses 1000 watts of electrical power when plugged in and working, and it is designed to work safely at a voltage of 230 volts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a power rating like the fuel consumption of a car. Just as a car's fuel efficiency tells you how much fuel it will use for a certain distance, the power rating tells you how much electricity an appliance will use during its operation. For instance, if you run a 1000 W microwave for an hour, it will consume the same amount of energy as a car that consumes a certain amount of fuel to drive for an equivalent time.
Importance of Power Rating
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Indicates the safe voltage and power consumption.
Detailed Explanation
The power rating is crucial because it informs consumers of the safe operating conditions for the appliance, including the voltage it requires and how much power it will consume. Knowing the power rating helps ensure that appliances are used correctly within their specified limits, which is essential for safety and efficiency. Using an appliance with the wrong voltage can damage it, while using too much power can lead to overheating and fire hazards.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're filling a cup with water. If you know the size of the cup (like knowing the power rating), you can determine how much water (electricity) you can safely pour in without overflowing (overloading). If you pour too much, like using more electricity than an appliance can handle, it could cause a mess or even damage the cup, just as it could harm the appliance.
Calculating Energy Consumption
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Helps in calculating energy consumed: E = P × t.
Detailed Explanation
The formula E = P × t allows us to calculate the energy consumed by an electrical appliance. In this formula, E stands for energy in kilowatt-hours (kWh), P is the power rating in kilowatts (kW), and t is the time in hours that the appliance operates. For instance, if a 1000 W (1 kW) microwave runs for 2 hours, it will consume 2 kWh of energy. This is important for understanding your electricity bill and the costs associated with running household appliances.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the analogy of a car trip. Just as the distance traveled (in miles) is a function of the speed (how fast you drive in miles per hour) and the time of travel, the energy used by an appliance is based on how much power it uses (in watts) and how long it runs. So, if a microwave is used for two hours, it's like saying you drove a certain distance at a steady speed for that time—each mile comes with its own fuel cost, and similarly, every kWh of energy consumed will show up in your electricity bill.
Key Concepts
-
Power Rating: Indicates how much power an appliance consumes in watts and guides safe usage.
-
Energy Consumption: Calculated using the formula E = P × t, important for understanding utility costs.
-
Safety Compliance: Following power ratings helps prevent hazards such as overheating and electric shocks.
Examples & Applications
A standard refrigerator might have a power rating of 200 W, which means it consumes 0.2 kWh if running for 1 hour.
An electric kettle with a power rating of 1500 W will consume 1.5 kWh if used for 1 hour.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Power high, consume you're sly; keep it low, avoid the woe.
Stories
A family used their heater for hours without checking its rating. One day, it overheated, causing a scare. They learned to check before they flip the switch!
Memory Tools
P-E-T: Power, Energy, Time - remember the order when calculating consumption!
Acronyms
PULSE - Power Understanding Leads to Safety and Efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Power Rating
The specified level of electrical power consumption of an appliance, measured in watts.
- Energy Consumption
The amount of electrical energy consumed over a specific period, often measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Watts (W)
A unit of power used to measure the rate of energy transfer.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
