Components Influencing TVM
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Principal
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by discussing the principal amount. Can anyone tell me what principal means in finance?

Is it the original amount of money that is invested or borrowed?

Exactly! The principal (P) is the base amount. It's crucial because all interest calculations are based on this amount. Remember: 'P is for Principal.' How can the principal impact your investment returns?

Larger principal amounts generally lead to more interest earned, right?

Right! The more you start with, the more you can earn through interest. Let's keep exploring!
Exploring Interest Rates
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next up is the interest rate. What do you think it signifies?

It's the percentage of the principal that you earn or pay for using the money, right?

Correct! Interest rates (r or i) directly influence how much your money grows or costs you. A simple way to remember this is 'I is for Interest.' Why could a higher interest rate be beneficial?

It helps in earning more money on our investments!

Exactly! And remember, the rates can vary based on many economic factors. Important to keep updated!
The Importance of Time Period
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s talk about time. How does the time period (t or n) factor into TVM?

Longer time periods lead to more interest being accumulated, right?

Exactly! The more time your money has to grow, the more returns you'll see. We can remember this as 'T is for Time.' Why might short-term investments be less advantageous?

They earn less interest over time compared to long-term ones.

That's correct! Time is a powerful tool in finance. Let's keep building our understanding!
Understanding Compounding Frequency
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss compounding frequency. What does this mean?

It's how often interest gets added to the principal, like monthly or annually, right?

Exactly! The more frequently the interest compounds, the more your investment grows due to interest on interest. Remember, 'F is for Frequency.' Can someone explain why compounding more frequently is advantageous?

More frequent compounding means more total interest earned over time.

Exactly! Understanding these fundamentals arms you with the tools to make more informed financial decisions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
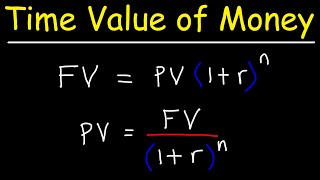
In understanding the Time Value of Money (TVM), several components play a critical role: the principal amount, the interest rate, the duration of the investment or loan, and how often interest is compounded. These elements interact to determine the future or present value of money, making them essential in financial decision-making.
Detailed
Components Influencing Time Value of Money (TVM)
The Time Value of Money (TVM) is a pivotal concept in finance that asserts the value of money changes over time due to interest and other factors. This section explores four primary components that influence the TVM:
-
Principal (P):
The principal is the original sum of money that is invested or borrowed. It serves as the baseline amount upon which interest calculations are made. -
Interest Rate (r or i):
The interest rate is the percentage at which the principal amount earns interest over a specified period. It reflects the growth rate of the investment or the cost of borrowing. -
Time Period (t or n):
This indicates the duration for which the money is invested or loaned. A longer time period generally results in a higher amount due to the effect of compounding interest. -
Frequency of Compounding:
This refers to how often the accrued interest is added to the principal. Frequent compounding (e.g., monthly) results in a higher return compared to annual compounding, due to interest being calculated on an increasing principal amount.
Significance:
Understanding these components helps in comprehending how to evaluate investments, make financing decisions, and plan for financial goals, making these foundational concepts for anyone working in finance or management.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Principal (P)
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Principal (P) – The original amount of money invested or borrowed.
Detailed Explanation
The principal is the initial amount of money that a borrower or investor puts in or borrows. This is the starting point for any calculations regarding the time value of money. When you invest, you begin with a principal amount, and understanding this base amount is crucial as all interest calculations will stem from it.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you lend a friend ₹5,000 with the expectation that they will pay you back later. That ₹5,000 is your principal. In terms of investment, if you deposit ₹10,000 in a savings account, that amount is your principal that will earn interest over time.
Interest Rate (r or i)
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Interest rate (r or i) – The rate at which money grows over time.
Detailed Explanation
The interest rate is essentially the cost of borrowing or the return on investment. It is usually expressed as a percentage and informs you how much your money will earn over a specified period. A higher interest rate generally means greater earnings or costs, depending on whether you are investing or borrowing.
Examples & Analogies
Think of interest rates like the growth rate of a plant. If a plant gets enough sunlight and water, it grows quickly (high interest rate). If it receives little care, it barely grows (low interest rate). Just as plants need certain conditions to thrive, your money needs a favorable interest rate to grow significantly.
Time Period (t or n)
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Time period (t or n) – The duration for which money is invested or borrowed.
Detailed Explanation
The time period refers to the length of time money is held in an investment or loan. The longer the time money is invested or borrowed, the more interest can accumulate, significantly affecting the future value of the investment or the total repayment amount of the loan.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a garden that you plant. If you tend to it for a long time, you'll reap a greater harvest than if you just planted it for a few weeks. Similarly, the longer your money is invested, the larger the amount due to compounding interest.
Frequency of Compounding
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Frequency of compounding – How often interest is calculated (annually, semi-annually, monthly).
Detailed Explanation
The frequency of compounding determines how often interest is added to the principal balance of an investment or loan. More frequent compounding leads to more interest being earned or paid because interest will start earning interest. This can significantly impact the overall returns or payments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine filling a bottle with water. If you add water only once a year, the bottle fills slowly. However, if you add water every month, the bottle fills much quicker. Similarly, with more frequent compounding (like monthly), your investment grows faster as interest is calculated and added frequently.
Key Concepts
-
Principal (P): The original amount of money invested or borrowed.
-
Interest Rate (r or i): The growth percentage of the principal over time.
-
Time Period (t or n): The duration for which the money is invested/borrowed.
-
Compounding Frequency: Frequency at which interest is added to the principal.
Examples & Applications
If a principal of ₹10,000 is invested at an interest rate of 5% for 2 years with annual compounding, the final amount will be greater than simply ₹10,000 due to interest accrued.
In a scenario where the principal is ₹10,000, an interest rate of 10%, and interest compounds monthly, the future value will be significantly higher compared to annual compounding.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To find how money grows on tree, remember Principal, Interest, Time, and Frequency.
Stories
Once upon a time, a small amount of money named Principal wanted to grow. With the help of Interest, Time, and the magic of Frequency, it multiplied and flourished!
Memory Tools
P-I-T-F -> Principal, Interest, Time, Frequency.
Acronyms
PITF - Remember PITF when thinking of money growth.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Principal
The original amount of money invested or borrowed.
- Interest Rate
The percentage at which the principal amount grows over time.
- Time Period
The duration for which money is invested or borrowed.
- Compounding Frequency
How often interest is calculated and added to the principal.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
