Future Value (FV)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Future Value
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the concept of Future Value, often abbreviated as FV. Can anyone tell me what Future Value represents?

Is it how much my money will be worth in the future if I invest it?

Exactly! FV tells us how much current money will grow over time due to interest. Remember, there's a simple formula we can use: FV = PV × (1 + r)^n. What do you think the symbols stand for?

I think PV is present value, and r is the interest rate. But what about n?

Correct! n represents the number of periods or years the money is invested. To remember this, think of the acronym PV, r, n. Let’s keep this in mind for future calculations.

Can you give us an example to illustrate this?

Sure! If you invest ₹10,000 at an interest rate of 10% for 2 years, you can calculate FV. Let's do that together!
Applying the FV Formula
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

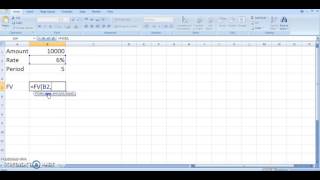
Let's calculate the Future Value of ₹10,000 at an interest rate of 10% for 2 years. Using the formula FV = 10,000 × (1 + 0.10)^2.

So, we first calculate (1 + 0.10) = 1.1, then raise it to the power of 2?

Exactly right! What does that give us?

That’s 1.1 × 1.1 = 1.21.

Great! Now, multiply that by the present value.

So, 10,000 × 1.21 = ₹12,100.

Well done! If you invest ₹10,000 today, it will grow to ₹12,100 in two years at a 10% interest rate.
Importance of FV in Financial Planning
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand how to calculate FV, why do you think it is important in financial planning?

It helps us see how our investments can grow over time!

Exactly! FV allows us to plan for future financial goals like retirement, buying a home, or funding education.

Can it help with comparing different investment options?

Absolutely! By calculating FV for different investments, you can make informed decisions about where to put your money.

It sounds like a really useful tool for making financial decisions!

Indeed it is! Knowing the potential growth of your investments provides clarity and direction in your financial strategy.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
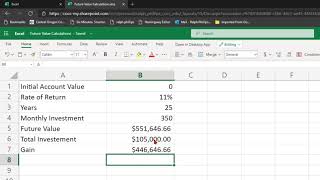
The Future Value (FV) is essential for understanding how investments grow over time due to interest earnings. It quantifies what a present amount of money will become in the future, taking into account the interest rate and compounding periods.
Detailed
Future Value (FV)
The concept of Future Value (FV) is a crucial component of the Time Value of Money (TVM) principle. FV represents the value of a sum of money at a specified date in the future, after accounting for interest accrued over that period. This concept highlights the potential of current money to generate earnings through investment.
The formula for calculating FV is given by:
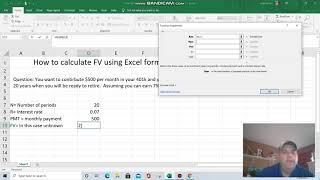
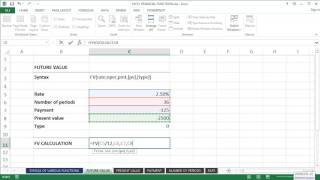
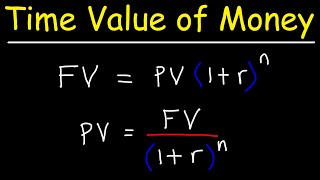
FV = PV × (1 + r)^n
Where:
- FV = future value
- PV = present value
- r = interest rate per period
- n = number of periods
Understanding FV helps individuals assess savings growth, investment returns, and financial planning for future goals. It emphasizes the importance of early investment to maximize returns over time.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Future Value (FV)
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The value of current money at a future date, given interest earnings.
Detailed Explanation
Future Value (FV) refers to how much money today will grow over time due to interest. It allows us to understand the potential worth of our current savings or investments at a set point in the future. Essentially, FV helps us anticipate how much our money can yield, allowing for better financial planning.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a plant (your money) that grows bigger (in terms of value) every week if you water it (apply interest). If you want to know how tall your plant will be after 2 months, you would be calculating its future value.
Future Value Formula
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
FV=PV ×(1 + r)^t
Detailed Explanation
The formula for calculating the Future Value (FV) is FV = PV × (1 + r)^t. Here, PV stands for Present Value or the initial amount of money, 'r' is the interest rate, and 't' is the time period in years. This formula shows that as time increases or as the interest rate increases, the future value of the investment also increases significantly. The (1 + r) part represents growth, and raising it to the power of 't' compounds that growth over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a snowball rolling down a hill. The longer it rolls (time) and the steeper the hill (interest), the bigger the snowball becomes. If you want to forecast how large the snowball will be in the future, you are calculating FV.
Example Calculation of FV
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example: If ₹10,000 is invested at 10% interest for 2 years:
FV=10,000 × (1 + 0.10)^2
Detailed Explanation
In this example, if you invest ₹10,000 at an interest rate of 10% for 2 years, you can plug those numbers into the FV formula. Perform the calculation as follows: First, add 1 and the interest rate (1 + 0.10 = 1.10). Then, raise this to the power of 2 (1.10^2 = 1.21). Finally, multiply this by the present value: 10,000 × 1.21 = ₹12,100. Thus, the Future Value is ₹12,100 after 2 years.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you planted a money tree with ₹10,000 worth of seeds that grows at a rate of 10% annually. After 2 years, your tree will not just yield the original amount, but it will bear more fruits (money), resulting in a total of ₹12,100.
Key Concepts
-
Future Value: Represents how much current money will grow over time due to interest.
-
Present Value: The current worth of a future sum of money.
-
Interest Rate: The percentage that determines how much money grows each period.
-
Compounding: The process of earning interest on both the initial principal and the accumulated interest.
Examples & Applications
If you invest ₹10,000 at 5% interest for 3 years, the FV would be ₹10,000 × (1 + 0.05)^3 = ₹11,576.25.
Investing ₹50,000 at 7% for 4 years yields: FV = ₹50,000 × (1 + 0.07)^4 = ₹65,201.43.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Future value, oh so bright, grows your cash way out of sight!
Stories
Imagine planting seeds (money), and each year they grow (interest) into a larger tree (future value) bearing fruit (wealth).
Memory Tools
Remember 'PV, r, n' – Present Value tells us where we start, interest shows how we grow, and n tells us how long we go.
Acronyms
FV
Future Value = 'Fund's Value rising' over time.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Future Value (FV)
The value of current money at a specific date in the future, taking into account interest earned.
- Present Value (PV)
The value of money currently, before interest is applied.
- Interest Rate (r)
The percentage at which money grows per period.
- Compounding Period (n)
The number of periods over which interest is calculated.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
