Simple Interest (SI)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Simple Interest
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will discuss Simple Interest, which is very important for short-term financial decisions. The formula to calculate Simple Interest is SI = (P × r × t) / 100. Can anyone tell me what each letter in the formula stands for?

I think P stands for the principal amount, right?

Correct, P is indeed the principal amount. What about r?

r is the interest rate.

Exactly! And t represents the time period in years. Why do you think we multiply these variables together?

To find out how much interest we earn over that time, I guess?

Right! Remember, Simple Interest is only calculated on the principal. This means it's crucial for shorter terms. Who can give me an example of when you might use Simple Interest?

When taking a personal loan that needs to be paid back in a short time?

Absolutely! Let’s summarize: SI is calculated only on the principal amount using the specified formula. This simplicity makes it vital for short-term financial decisions.
Calculating Simple Interest
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's do a calculation to make sure we understand how to apply the formula for Simple Interest. If you invest ₹10,000 at an interest rate of 5% for 3 years, what is the Simple Interest?

Using the formula: SI = (10,000 × 5 × 3) / 100, right?

Exactly! What do you get when you calculate it?

So, that would be ₹1,500 of Simple Interest.

Great job! Now, why is it important to know how to calculate SI?

It helps with making informed decisions about loans or investments, and comparing different options!

Exactly! Knowing how to calculate Simple Interest empowers you to make better financial choices.
Real-life Applications of Simple Interest
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss where you might encounter Simple Interest in real life. Can anyone think of an example?

Maybe in a savings account where you earn interest but don't have to wait long!

Exactly! Savings accounts often use Simple Interest for short terms. What other examples can you think of?

Short-term loans or payday loans?

Correct! Understanding SI can help you avoid high-interest loans and save money. It's essential to assess the total cost. Can someone conclude the lesson for today?

Simple Interest is calculated only on the principal and is useful for short-term loans and investments.

Excellent summary! Remember this concept; it's foundational for your financial literacy.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Simple Interest (SI) is calculated using the formula SI = (P × r × t) / 100, where P is the principal amount, r is the interest rate, and t is the time period. SI is commonly used in short-term loans and deposits, making it crucial for basic financial literacy.
Detailed
Simple Interest (SI)
Simple Interest is a vital financial concept primarily used in calculating the interest on loans or deposits within a specified short period. The calculation for Simple Interest is straightforward, represented by the formula:
$$
SI = \frac{P \times r \times t}{100}
$$
where:
- P = Principal amount (the initial sum of money)
- r = Annual interest rate (percentage)
- t = Time period (in years)
Unlike Compound Interest, where interest is calculated on the principal and accumulated interest, Simple Interest is computed solely on the original principal. This distinction makes SI particularly useful for short-term financial decisions, such as loans that require clarity on basic interest calculations. Understanding SI is crucial for students and professionals alike, especially in tech and financial fields, making it a foundational aspect of financial literacy.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Simple Interest Formula
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The formula for calculating Simple Interest (SI) is:
SI = \( \frac{P \times r \times t}{100} \)
Where:
- SI = Simple Interest
- P = Principal amount
- r = Rate of interest (as a percentage)
- t = Time period (in years)
Detailed Explanation
The formula for Simple Interest (SI) allows you to calculate the interest earned or paid on a principal over a set period of time at a specific interest rate. To use this formula, you need to know three variables: the principal amount (the initial sum of money), the interest rate per period (expressed as a percentage), and the time the money is invested or borrowed (in years). By multiplying these three variables and dividing by 100, you can obtain the total interest.
Examples & Analogies
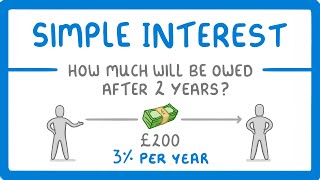
Imagine you lend ₹10,000 to a friend for 2 years at an interest rate of 5% per year. Using the Simple Interest formula:
SI = (10,000 × 5 × 2) / 100 = ₹1,000.
This means after 2 years, your friend owes you the original ₹10,000 plus ₹1,000 in interest, totaling ₹11,000.
Characteristics of Simple Interest
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Simple Interest is calculated on the initial principal only. It is typically used in short-term loans or deposits.
Detailed Explanation
The key feature of Simple Interest is that it is calculated solely on the initial amount of money, or principal, without taking into account any previously accumulated interest. This makes SI straightforward, especially for short-term loans or investments, as the same interest calculation applies every year for the duration of the loan or deposit.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a bank offering a savings account that pays Simple Interest. If you deposit ₹5,000 at an interest rate of 4% for 3 years, the bank calculates interest only on the ₹5,000 each year. After 3 years, you will earn:
SI = (5,000 × 4 × 3) / 100 = ₹600.
You will receive ₹5,600 in total at the end of 3 years, as the interest is not compounded.
Applications of Simple Interest
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Simple Interest is commonly used for short-term loans or deposits such as personal loans, car loans, or short-term savings accounts.
Detailed Explanation
Simple Interest is often preferred for situations where the borrowing or investment period is relatively brief. This includes personal loans, auto loans, and certain savings accounts where the simplicity of calculating interest quickly is advantageous. Borrowers benefit by knowing their exact payment obligations, while lenders can easily predict earnings on their loans.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you take out a personal loan of ₹15,000 for 1 year at a 6% interest rate. The interest calculation would be:
SI = (15,000 × 6 × 1) / 100 = ₹900.
At the end of the year, you would owe ₹15,900, making it easy for both you and the lender to understand the repayment amount without complex calculations.
Key Concepts
-
Simple Interest Formula: SI = (P × r × t) / 100
-
Interest is calculated only on the principal.
-
Used primarily in short-term loans and deposits.
Examples & Applications
If ₹5,000 is invested at an interest rate of 4% for 2 years, SI = (5000 × 4 × 2) / 100 = ₹400.
For a loan of ₹15,000 at 6% for 5 years, SI = (15000 × 6 × 5) / 100 = ₹4,500.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Simple Interest is very clear, it’s fixed and it’s near. On the principal it’s based, adding years, it’s not displaced!
Stories
Imagine Sarah borrowed ₹10,000 for her startup at 6%. She calculated her simple interest yearly, knowing she'd pay it back in 2 years. Each year, she simply added ₹600 to her plan, keeping it straightforward!
Memory Tools
Remember SI = P × r × t / 100, where 'SI' = Simple Interest, 'P' = Principal, 'r' = rate, 't' = time.
Acronyms
Use 'PIT' to recall Simple Interest
'P' for Principal
'I' for Interest
and 'T' for Time.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Principal (P)
The initial amount of money invested or borrowed.
- Interest Rate (r)
The percentage at which interest is calculated for a financial asset or liability.
- Time Period (t)
The duration for which the money is invested or borrowed, usually measured in years.
- Simple Interest (SI)
Interest calculated on the principal amount only, without compounding.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
