Future Value (FV) and Present Value (PV)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Future Value (FV)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss Future Value, often abbreviated as FV. FV is a method to calculate how much money you will have in the future based on present investments. Does anyone know the formula for calculating FV?

Is it FV = PV × (1 + r)^t?

Exactly! Great job, Student_1! In this formula, PV stands for Present Value, and 'r' represents the interest rate. Why do you think understanding FV is important in finance?

It helps in planning investments and knowing what to expect from savings in the future.

Correct! FV helps us make informed decisions about our finances by estimating the growth of our investments over time using interest rates.

So, if I invested ₹10,000 at an interest rate of 10% for two years, how much would that be?

Great question! Applying the formula, FV = 10,000 × (1 + 0.10)^2, which equals about ₹12,100. It shows how compounding interest can add up!

Does that mean the earlier we invest the more we earn?

Exactly, Student_4! The sooner you invest, the more interest you accrue, which is a key principle in finance.
Understanding Present Value (PV)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've discussed FV, let's move on to Present Value, or PV. Who can explain what PV means?

PV is the current worth of a future amount of money.

Exactly right! The formula for PV is PV = FV / (1 + r)^t. It helps us determine how much future cash flows are worth today. Why is this important?

It allows us to compare the value of money we will receive in the future against today’s money.

Precisely! PV helps in evaluating how an investment will perform against inflation and risk factors.

So if I have ₹12,100 coming in two years at a 10% interest rate, what's its present value?

Using our formula: PV = 12,100 / (1 + 0.10)^2, your PV would be approximately ₹10,000.

That makes sense! We know that amount today is worth the same as that future sum.

Exactly, Student_4! This critical understanding of present and future value aids in making wise financial choices.
Applications of FV and PV
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss how we can apply FV and PV in everyday financial decisions. Can anyone share an example?

Maybe in investment planning, like savings accounts or retirement funds?

Absolutely, Student_3! These calculations help predict how much money you will have when retiring, for instance.

What about loans? How do they fit into this?

Great thought! When taking out a loan, understanding PV helps you gauge how much to borrow and how interest will affect the total repayment over time.

And it can assist businesses in evaluating project investments, right?

Exactly! FV and PV can help in determining the viability of investment opportunities, presenting a clearer picture of profitability.

So, mastering FV and PV gives us a huge advantage in finance?

Definitely! It provides a solid foundation for understanding financial principles and making savvy investment decisions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section explains the concepts of future value and present value, providing formulas to compute each, along with their significance in assessing the worth of money over time. It emphasizes the relationship between present and future money, highlighting how understanding these concepts can impact financial decision-making.
Detailed
Future Value (FV) and Present Value (PV)
The concepts of future value (FV) and present value (PV) are essential in finance for determining the worth of money at different points in time.
Future Value (FV)
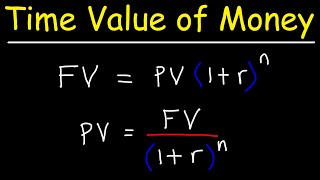
Future Value refers to the value of money at a specific date in the future, based on an assumed rate of interest. The formula to calculate FV is:
FV = PV × (1 + r)^t
Where:
- PV = Present Value
- r = annual interest rate
- t = number of years
This formula highlights how money today can grow given that it earns interest over time.
Present Value (PV)
Present Value, on the other hand, is the current worth of a future sum of money given a specified rate of return. The formula for PV is:
PV = FV / (1 + r)^t
This formula illustrates how much a future amount of money is worth today, allowing for evaluation of potential investments or expenses.
Significance
Understanding FV and PV is crucial for various financial analyses, enabling individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about investments, loans, and budgeting. Grasping these concepts forms the foundation for more complex financial tools and strategies.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Future Value (FV)
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The value of current money at a future date, given interest earnings.
- Formula:
FV = PV × (1 + r)^t
Detailed Explanation
Future Value (FV) represents how much an amount of money today will grow over a specified period at a particular interest rate. The formula for calculating FV is FV = PV × (1 + r)^t, where PV is the Present Value, r is the interest rate, and t is the time in years. This formula helps in understanding how investments increase over time due to interest earnings.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have ₹10,000 that you want to invest. If you invest it in a savings account that earns 10% interest per year, after one year, you'll have ₹11,000 (₹10,000 + ₹1,000 interest). If you leave it for two years, you will have approximately ₹12,100. This growth illustrates how money can work for you over time.
Present Value (PV)
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The current worth of money to be received in the future.
- Formula:
PV = FV / (1 + r)^t
Detailed Explanation
Present Value (PV) allows us to determine how much a future sum of money is worth today. Using the formula PV = FV / (1 + r)^t, we can calculate PV by dividing the future value (FV) by the compound growth factor (1 + r)^t. This concept is crucial in finance because it helps in assessing how much future cash flows are worth in today's terms.
Examples & Analogies
Suppose someone promises to give you ₹12,100 two years from now, and the interest rate is 10%. To find out how much that promise is worth today, you would calculate PV = 12,100 / (1 + 0.10)^2, which would show you the amount you would be indifferent to receiving now versus later. This helps in making informed decisions about accepting future payments.
Example Calculation
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example:
If ₹10,000 is invested at 10% interest for 2 years:
- FV = 10,000 × (1 + 0.10)^2
Detailed Explanation
In this example, we are calculating the future value of an investment of ₹10,000 at an interest rate of 10% over a period of 2 years. Plugging these values into the FV formula gives us FV = 10,000 × (1 + 0.10)^2 = 10,000 × 1.21 = ₹12,100. This calculation shows that, after two years, your investment would grow to ₹12,100 due to interest accumulation.
Examples & Analogies
This is like planting a tree that grows taller and provides shade over time. The ₹10,000 is the tree you plant today, and the interest is like the tree growing taller each year, providing you with 'shade' or benefits in the form of money in the future.
Key Concepts
-
Future Value (FV): The projected value of a current investment at a specified future date.
-
Present Value (PV): The current worth of a future sum adjusted for interest rates.
-
Formulas: FV = PV × (1 + r)^t and PV = FV / (1 + r)^t.
-
Importance: Both concepts are critical for making informed financial decisions regarding investments, loans, and budgeting.
Examples & Applications
If ₹10,000 is invested at a 10% interest rate for 2 years, the future value would be ₹12,100 using the FV formula.
If you expect to receive ₹12,100 in 2 years and the interest rate is 10%, the present value today is approximately ₹10,000 using the PV formula.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Money today grows in the play, future value will pave the way!
Stories
Imagine a seed (PV) planted today that grows into a tree (FV) with fruits in the future, nurturing one’s finances.
Memory Tools
Fruits Grow Fast (FV = PV × (1 + r)^t) - Demonstrating how investments grow with time and interest.
Acronyms
FAV (Future Amount Value) reminds us of FV.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Future Value (FV)
The worth of an investment at a future date based on its present value and interest rate.
- Present Value (PV)
The current worth of a future sum of money, discounted at a specific interest rate.
- Principal (P)
The original sum of money invested or borrowed.
- Interest Rate (r or i)
The percentage at which interest is paid on the principal.
- Compounding
The process where interest earned is added to the principal for future interest calculations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
