Present Value of an Annuity (PVA)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Annuities
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the concept of annuities. Can anyone tell me what an annuity is?

Isn't an annuity a series of equal payments made over time?

Exactly! An annuity is defined as a series of equal payments made at regular intervals. Now, there are different types of annuities, but we'll focus on the Present Value of an Annuity (PVA) today.

Can you explain why PVA is important in finance?

Sure! PVA helps determine the current worth of future cash flows, which is essential for making investment decisions. Remember, money available today is worth more than the same amount in the future because of earning potential.
PVA Formula
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move on to the formula for PVA. It is PVA = PMT × [(1 - (1 + r)^(-n)) / r]. What do you think each component represents?

PMT must be the payment amount, right?

Correct! And r is the interest rate per period, while n is the total number of payment periods. Together, they will help us calculate the present worth of those future payments.

Could you provide an example?

Sure! If you expect to receive ₹1,000 annually for 5 years at an interest rate of 5%, you could use this formula to determine its value today.
Application of PVA
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

PVA has multiple applications in finance. Can anyone think of an example where understanding PVA would be beneficial?

Maybe when planning for retirement? Knowing how much you need to save now could help.

Exactly! Whether you're saving for retirement or looking to invest in real estate, determining the present value of your expected cash flows helps you make better financial decisions.

What if the interest rate changes? Wouldn't that impact the PVA calculation?

Yes! Changes in the interest rate can significantly affect the present value. It's crucial to stay informed about financial trends.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
PVA is calculated using the formula PVA = PMT × (1 - (1 + r)^(-n)) / r, where PMT is the payment per period, r is the interest rate, and n is the number of periods. Understanding PVA is essential for evaluating long-term financial obligations and investments.
Detailed
Present Value of an Annuity (PVA)
The Present Value of an Annuity (PVA) represents the total value today of a series of cash flows that will occur in the future, given a specific interest rate. It is a critical financial concept, particularly in areas like loan amortization, retirement planning, and capital budgeting. The formula to calculate the PVA is as follows:
PVA = PMT × [(1 - (1 + r)^(-n)) / r]
Where:
- PMT = periodic payment
- r = interest rate per period
- n = total number of payment periods
Understanding PVA helps individuals and corporations make informed decisions regarding cash flows and investments, allowing for thorough financial analysis and planning.
Youtube Videos









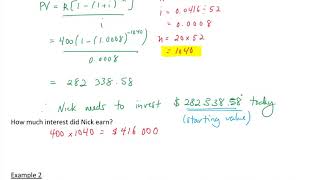
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Present Value of an Annuity
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
PV A = PMT × ¿
Detailed Explanation
The formula for the Present Value of an Annuity (PVA) expresses how to calculate the current worth of a series of equal periodic payments (PMT) that will be received or paid in the future. Essentially, it's about determining how much those future payments are worth right now, considering a specific interest rate.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you plan to receive ₹10,000 every year for the next five years from a family trust. You want to understand how much that series of payments is worth today if the interest rate is 5%. The PVA formula helps you convert those future payments into a single lump sum today. This is similar to knowing what it feels like to have a certain monetary value right now rather than waiting for it in parts over the years.
Identifying Components of the PVA Formula
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Where:
- PMT = periodic payment
- r = interest rate
- n = number of periods
Detailed Explanation
In the PVA formula, there are specific components you need to be aware of: the 'PMT' refers to the amount paid or received in each period, 'r' is the interest rate at which the money is expected to grow or discount back to the present, and 'n' denotes the total number of payment periods. Understanding these variables is key to accurately calculating the present value.
Examples & Analogies
Think of PMT as your monthly salary. If you receive ₹20,000 every month (PMT) and plan to calculate your salary over the next year (n=12), you’d use the interest rate (r) to determine how much that monthly salary will be worth today if you invest that money rather than spending it. For example, if the annual interest rate is 6%, using the PVA formula will clarify how much that total future salary is valued at today.
Key Concepts
-
Present Value: The worth of future cash flows in today's terms.
-
Annuity: A series of equal payments over time.
-
Cash Flow: Money spent or received.
-
Discounting: The process of determining present value from future amounts.
Examples & Applications
Example: If PMT = ₹2,000, r = 6% (0.06), and n = 10 years, calculate PVA using the formula.
Example: Understanding how changing the interest rate affects the PVA of a fixed annuity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To find today's worth of future cheer, discount those payments, keep them near!
Stories
Imagine you are planning for a future vacation. You save an amount each month, and the interest your savings earn means that your present savings will accumulate and grow over time, making your future vacation more attainable.
Memory Tools
PVA: Present Value Annuity - just remember to think about today's value and future payments.
Acronyms
PVA - Remember
*P*resent
*V*alue
*A*nnuity to keep the formula in mind.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Annuity
A series of equal payments made at regular intervals.
- PVA
Present Value of an Annuity, the current worth of a series of future annuity payments.
- PMT
The periodic payment made in an annuity.
- Interest Rate (r)
The percentage at which money grows in a specific period.
- Number of Periods (n)
The total duration over which payments will be made.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
