Concept of Time Value of Money
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition and Core Concept of TVM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome everyone! Today, we're diving into the Time Value of Money, or TVM. Can anyone tell me what TVM means?

Is it about how money can grow over time?

Exactly! TVM explains that money available today is more valuable than the same amount in the future because of its capacity to earn. Can anyone name one reason why this is the case?

Inflation affects the purchasing power of money, right?

Great point! Inflation is indeed one reason. It reduces the value of money over time. Now, let's connect that to opportunity cost. Who can explain the idea of opportunity cost?

It’s when you lose the potential return from what you could have invested the money in!

Very well said! Opportunity cost means that money today could be invested for returns, making it worth more over time. To summarize this session: TVM emphasizes that present money has more value due to inflation, opportunity cost, and risk.
Importance of Understanding TVM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss why understanding TVM is critical for finance and tech. Can anyone think of a decision influenced by TVM?

Investor funding decisions!

True! Understanding the value of potential investments compared to their future cash flows is vital. What else?

Loan repayment plans?

Correct again! With loans, the time value affects repayment schedules and interest calculations. Let's quickly review: TVM is essential for assessing investments, budgeting, and loan decisions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
TVM is a foundational concept in finance, emphasizing that money today has more value due to factors like inflation, opportunity cost, and risk. Understanding TVM is crucial for making informed financial decisions in areas like investments and budgeting.
Detailed
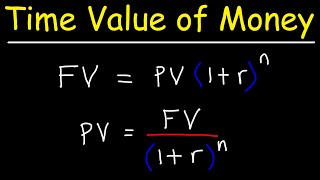
Concept of Time Value of Money (TVM)
The Time Value of Money (TVM) embodies the principle that money received now holds greater value than the same amount received in the future. This is attributed to its potential earning capacity. TVM serves as the foundation for numerous financial decisions, impacting investment appraisals, project evaluations, loan computations, and retirement planning. Students, particularly those in tech fields, are encouraged to grasp this concept for effective budgeting and profitability assessments.
Key Reasons for TVM:
- Inflation diminishes the purchasing power of money over time, indicating that a fixed amount will buy less in the future.
- Opportunity Cost states that money available today can be invested to yield returns, enhancing its value over time.
- Risk and Uncertainty highlight that while future cash flows are uncertain, present money is guaranteed, making it more valuable.
Grasping these concepts is essential for both personal and professional financial management.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Time Value of Money
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The idea that money received today has more value than money received in the future due to its ability to earn returns (interest or investment income).
Detailed Explanation
The Time Value of Money (TVM) is a core financial principle that asserts that a specific amount of money today is worth more than the same amount in the future. This is mainly because money available today can earn interest or be invested, thereby increasing its value over time. Understanding this concept is critical for making informed financial decisions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider you have ₹1,000 today. If you place it in a savings account that earns an interest rate of 5% annually, in one year, you would have ₹1,050. However, if you were to receive that ₹1,000 a year from now, you would not have that additional ₹50. Thus, receiving money now is better than receiving the same amount later.
Reasons for Time Value of Money
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Reasons for TVM:
- Inflation: Reduces the purchasing power of money over time.
- Opportunity cost: Money today can be invested to earn returns.
- Risk and uncertainty: Future money is uncertain; present money is guaranteed.
Detailed Explanation
There are several factors that contribute to the Time Value of Money. First, inflation deteriorates the purchasing power of currency over time, meaning that a certain amount of money buys fewer goods and services in the future. Second, the opportunity cost of not investing money today leads to missed earning potential, as invested money can generate returns. Lastly, future cash flows come with inherent risks and uncertainties; whereas the money you possess today is secure and guaranteed.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have ₹10,000 today. If there's an inflation rate of 3%, that ₹10,000 next year would only be able to buy what ₹9,700 can today. Thus, not only does your money decrease in purchasing power, but if you invest this money instead, it could grow, increasing your wealth over time.
Key Concepts
-
Present Value: Money today is worth more than the same amount in the future.
-
Inflation: Affects purchasing power and reduces future money value.
-
Opportunity Cost: Potential earnings from investing current money.
Examples & Applications
If you have ₹1,000 today and you invest it at 5% interest, in one year, you will have ₹1,050. In contrast, if you receive ₹1,000 a year from now, you miss the interest gain available now.
Imagine a scenario where a person decides not to invest ₹10,000 today, which could yield a return of 6%. Over 5 years, this decision results in a loss of potential earnings.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Money now, oh what a deal, future's value, not as real.
Stories
Imagine a traveler who chooses to invest their money today. Years later, their investment grows, showing how today's decision shapes future fortunes.
Memory Tools
I O R - Inflation, Opportunity Cost, Risk.
Acronyms
TVM - Today’s Value Matters.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Time Value of Money (TVM)
The principle that money available now is worth more than the same sum in the future due to its earning potential.
- Inflation
The decrease in purchasing power of money over time, leading to higher prices.
- Opportunity Cost
The potential returns lost by not investing money which could create measurable value.
- Risk
The uncertainty associated with future cash flows that can affect financial decisions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
