Bituminous Binders – Types and Selection
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition and Role of Bituminous Binders
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, everyone! Today we will discuss bituminous binders. Can anyone tell me what bitumen is?

Is it a kind of sticky black material?

Exactly! Bitumen is a viscous, black, semi-solid hydrocarbon material obtained from crude oil. Its primary role is to bind aggregates together in pavements. Can anyone list some of its key functions?

It provides flexibility and waterproofing?

And it helps prevent cracking from thermal changes!

Great points! Remember, we can think of the acronym 'BFF'—Binding, Flexibility, and Waterproofing—to remember its main functions. Let's move on to the types of binders.
Types of Bituminous Binders
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, there are various types of bituminous binders. Can anyone name a few?

I think there's conventional bitumen and modified bitumen?

Correct! We have Conventional Bitumen, which is categorized by penetration grades, Viscosity Graded Bitumen, which uses viscosity measurements, Polymer Modified Bitumen that enhances elasticity, and Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen which improves performance using recycled materials. Could you give examples of these types?

For PMB, we can say PMB-40 and PMB-70!

Yes! And each type is designed to meet specific performance requirements. An easy way to remember them is the mnemonic 'C-V-P-C': Conventional, Viscosity, Polymer, Crumb.
Criteria for Selection of Bituminous Binders
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Selection of a bituminous binder is crucial. What factors do you think influence this selection?

Climatic conditions, like hot or cold weather, right?

And the traffic volume and types! Like heavy trucks need stronger binders.

Exactly! Additionally, the type of pavement layer and construction techniques also matter. If we consider the mnemonic 'C-T-L-T'—Climatic, Traffic, Layer, Technique—it can help us recall these factors. Can anyone give a specific example of a binder choice based on these conditions?

Using PMB for high-speed traffic areas in warm climates would be ideal.

That’s absolutely right! Well done, everyone.
Performance-Based Bitumen Selection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about performance-based bitumen selection. What is the Superpave grading system?

Is it about choosing binders for specific temperature ranges?

Correct! Superpave PG grading considers expected pavement temperature ranges such as PG 64-22. This approach is based on expected climate and load, offering better field performance correlation. Remember the acronym 'S-P-G'—Superpave Performance Grade. What benefits does this method offer?

It makes binder selection more scientific and reliable for real-world conditions!

Exactly! It ensures that our pavements can withstand the demands of traffic and environment effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Bituminous binders are vital components in flexible pavements, affecting the durability and performance under traffic loads. The section discusses various types, their properties, and the selection criteria based on climatic and traffic conditions.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Bituminous binders are hydrocarbon materials essential in road construction, primarily used to bind aggregates in flexible pavements, providing waterproofing and enhancing performance under varying conditions. This section outlines their types, including conventional bitumen, viscosity-graded bitumen, polymer-modified bitumen (PMB), crumb rubber modified bitumen (CRMB), and emulsions.
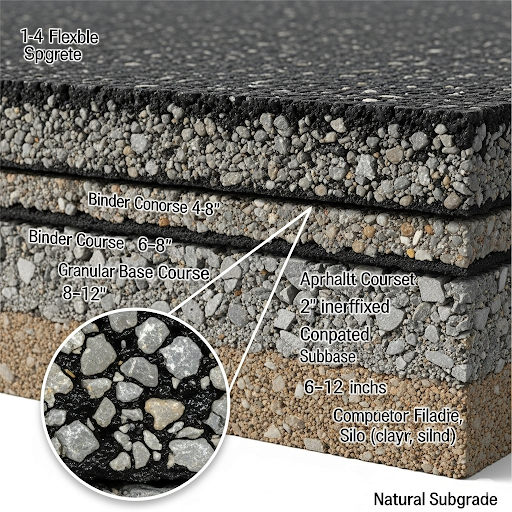

Understanding binder properties (such as adhesive, cohesive, and water-resistant characteristics) and selection criteria (such as climatic conditions, traffic types, and construction techniques) is essential. Performance-based selection methods like the Superpave PG grading system are also discussed, emphasizing their correlation with field performance. The section highlights the importance of modifiers and additives to improve the characteristics of binders and concludes with storage, handling, and safety measures to be observed during the application.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Bituminous Binders
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bituminous binders are the core binding agents used in road construction, especially in flexible pavements. Their role is crucial in holding together the aggregates, providing waterproofing, and ensuring the road’s overall performance under varying traffic loads and climatic conditions.
Detailed Explanation
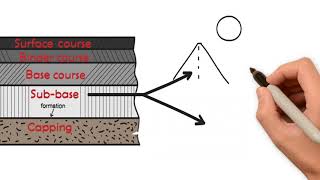
Bituminous binders are essential materials in constructing roads. They function by binding together aggregates, which are the various materials used to create the surface of the road. This binding is necessary because it ensures that the road can withstand various factors such as the weight of vehicles (traffic loads) and different weather conditions (climatic conditions). Essentially, without bituminous binders, the road would lack stability, leading to various issues such as cracking or degradation over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a road like a cake. The aggregates are like the bits of fruit or nuts in a cake, while the bituminous binders act like the icing that holds everything together. Just as icing keeps the ingredients from falling apart and gives the cake its structure, bituminous binders keep the areas together to form a smooth, long-lasting road.
Definition and Key Functions of Bituminous Binders
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
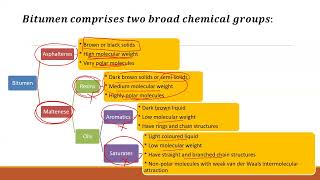
Bitumen is a hydrocarbon material that is soluble in carbon disulfide and composed mainly of asphaltenes and maltenes. It is a viscous, black, semi-solid material obtained as a residual product in the distillation of crude oil. Bituminous binders are used to bind aggregate particles together, provide waterproofing, and enhance load distribution properties of flexible pavements.
Detailed Explanation
Bitumen is primarily a thick liquid or semi-solid that is derived from refining crude oil. It contains complex molecules called asphaltenes and maltenes. The chief functionalities of bituminous binders include binding the aggregate particles—important for structural integrity—protecting the road from water through waterproofing, and improving how the load from vehicles is distributed across the pavement. This ensures that the road can effectively cater to both heavy and light traffic.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine bitumen as the glue used in craft. When you apply glue to pieces of paper (the aggregates), it holds them together, allowing you to create a solid art project (the road). If the glue isn't strong or waterproof, the project would fall apart or get ruined when exposed to moisture, which is similar to how roads can suffer without effective bituminous binders.
Types of Bituminous Binders
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bituminous binders can be broadly classified into various types:
10.2.1 Conventional Bitumen (Penetration Grade Bitumen)
- These are straight-run bitumen categorized based on penetration values (e.g., 30/40, 60/70, 80/100).
- Penetration value indicates the hardness or softness of the binder.
10.2.2 Viscosity Graded Bitumen
- Classified based on viscosity measurements at standard temperatures (VG-10, VG-20, VG-30, VG-40).
- Replaces penetration grading in many countries due to better performance correlations.
10.2.3 Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB)
- Bitumen modified with polymers like SBS, SBR, EVA, etc.
- Improves elasticity, temperature susceptibility, and fatigue resistance.
- Types include PMB-40, PMB-70, etc.
10.2.4 Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen (CRMB)
- Bitumen modified with recycled rubber from tires.
- Enhances elasticity, resistance to rutting and cracking.
Detailed Explanation
There are different types of bituminous binders, each suited for specific applications. Conventional bitumen is categorized by penetration values; lower numbers indicate harder materials, while higher numbers signify softer ones. Viscosity graded bitumen measures the fluidity of the binder at certain temperatures, and it's preferred in many regions for its performance. Polymer modified bitumen incorporates polymers to enhance its properties, while crumb rubber modified bitumen uses recycled tires to create a more elastic product that can withstand wear and tear better than standard binders.
Examples & Analogies
Consider bituminous binders like different types of flour used in baking. Just as you might choose cake flour for lightness or bread flour for strength based on what you're making, engineers select specific types of binders based on the expected performance and conditions of the road.
Key Concepts
-
Bituminous Binders: Essential binders in road construction providing waterproofing and binding properties.
-
Types of Binders: Includes Conventional Bitumen, Viscosity Graded Bitumen, PMB, CRMB, and Emulsions.
-
Selection Criteria: Factors like climate, traffic volume, layer type, and construction methods influence the choice of binders.
-
Performance-Based Selection: Methods like Superpave ensure better correlation with field performance.
Examples & Applications
In a hot climate, PMB might be chosen for its elasticity.
For cold regions, softer grades of conventional bitumen could be appropriate.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Binders keep roads strong and neat, keeping asphalt a safe place for feet.
Stories
Imagine a chef using different spices (binder types) to make a delicious dish (road); each spice enhances the flavor based on ingredients (traffic conditions) used.
Memory Tools
Use 'BFF'—Binding, Flexibility, Waterproofing—to remember the roles of bituminous binders.
Acronyms
Remember 'C-T-L-T'—Climatic, Traffic, Layer, Technique for the binder selection criteria.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bitumen
A viscous, black, semi-solid hydrocarbon material used as a binding agent in road construction.
- Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB)
Bitumen modified with polymers to enhance elasticity, temperature susceptibility, and fatigue resistance.
- Viscosity Graded Bitumen
Bitumen classified based on viscosity measurements at standard temperatures, replacing penetration grading in many countries.
- Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen (CRMB)
Bitumen modified with recycled rubber from tires, improving its performance characteristics.
- Bituminous Emulsions
Dispersions of bitumen in water, stabilized by emulsifying agents, used in various pavement applications.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
