Modifiers and Additives in Bituminous Binders
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Modifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we’re diving into the role of modifiers in bituminous binders. What do you think modifiers might do?

Maybe they make the binder stronger or more flexible?

Exactly! Modifiers enhance the performance characteristics of bituminous binders, improving their strength and flexibility. We categorize these into several types, such as polymers. Can anyone tell me what kinds of polymer modifications we see?

Are those like SBS or SBR?

Yes! Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene (SBS) and Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) are prominent examples. Remember the acronym P.R.A.W., it stands for Polymer, Rubber, Anti-stripping, Wax, which are key modifiers. Any questions about that?

What about the effects of using these modifiers? Do they really help a lot?

Great question! The modifiers significantly improve the binder's resistance to rutting and low-temperature cracking, leading to longer-lasting pavements.

To summarize, modifiers like polymers and rubber increase flexibility and adhesion, which are crucial for road durability.
Effects of Modifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've discussed what modifiers are, let's talk about their effects. Can someone explain why we might want to use adhesion improvers?

They help the bitumen stick to the aggregates better, right?

Exactly! Adhesion improvers enhance the bond, especially in wet conditions, which is critical. And what do you think is the overall outcome of using additives?

Longer service life for roads?

Yes! In addition to lasting longer, they improve overall performance in varying conditions. Any further insights on this aspect?

Could that mean less maintenance needed over time?

Absolutely right! Reduced maintenance leads to cost savings. So remember, the implementation of modifiers enhances performance dramatically.

To wrap up, using modifiers leads to better performance under stress and environmental conditions, improving roadway longevity.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Modifiers and additives play a crucial role in improving the performance characteristics of bituminous binders, including resistance to rutting, fatigue, and low-temperature cracking. The types of modifiers discussed include polymers, rubber powder, anti-stripping agents, and others, each contributing to increased service life of pavements.
Detailed
Modifiers and Additives in Bituminous Binders
This section focuses on the various modifiers and additives utilized in bituminous binders to enhance their overall performance. These substances are essential in improving how bituminous binders handle stress, temperature variations, and aging, ultimately leading to increased durability and longevity of road surfaces.
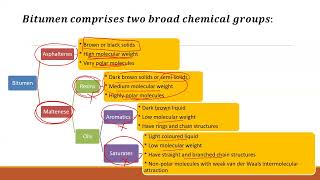
10.9.1 Types of Modifiers
Modifiers can be broadly classified into:
- Polymers (Elastomers and Plastomers): Enhance elasticity and temperature susceptibility of bituminous binders.
- Rubber Powder: Increases flexibility and resistance to cracking.
- Anti-stripping Agents: Improve the adhesion of bitumen to aggregates, promoting better performance in wet conditions.
- Adhesion Improvers: Further enhance the bond between the binder and aggregates.
- Waxes and Resins: Help improve handling properties and performance at different temperatures.
10.9.2 Effects of Modifiers
Using these modifiers results in significant benefits, including:
- Improved resistance to rutting and fatigue, leading to longer-lasting pavements.
- Enhanced performance in varying climatic conditions, particularly in extreme temperatures or heavy rainfall.
- Greater overall service life of the pavement structures, reducing the need for maintenance and repairs.

Understanding and selecting the appropriate modifiers and additives is crucial for transportation and highway engineers, ensuring that the materials used in construction will meet performance expectations and regulatory standards.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Types of Modifiers
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Polymers (Elastomers and Plastomers)
- Rubber Powder
- Anti-stripping Agents
- Adhesion Improvers
- Waxes and Resins
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines the different types of modifiers used to enhance bituminous binders. Modifiers can be classified into several categories such as polymers, which include elastomers and plastomers; rubber powder, which is derived from recycled tires; anti-stripping agents that help prevent the separation of aggregates from the binder; adhesion improvers that enhance the bond between the binder and aggregates; and waxes and resins that can affect the viscosity and physical properties of the binder. Each of these components is crucial in increasing the durability and performance of asphalt mixtures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these modifiers like ingredients in a recipe. Just as you might add spices or herbs to enhance the flavor of a dish, modifiers are added to bituminous binders to improve their properties. For example, adding rubber powder to the mix is similar to tossing in some chili to make a dish spicy—both not only change the character of the mix but also help achieve a specific outcome, such as increased flexibility or durability.
Effects of Modifiers
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Improve resistance to rutting, fatigue, low-temperature cracking.
• Increase service life of the pavement.
Detailed Explanation
Modifiers play a significant role in enhancing the performance of bituminous binders. They help improve resistance to rutting, which is the deformation caused by heavy traffic loads. Additionally, modifiers help the binder withstand fatigue, minimizing cracks that develop from repeated stress over time. Low-temperature cracking is another issue that modifiers address, ensuring that the pavement remains intact during cold weather. Lastly, by improving the overall quality of the binder, these modifiers can extend the service life of a pavement, making it more cost-effective in the long run.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a pair of shoes that are designed for running. If they include special cushioning (like the modifiers in binders), they will support your feet better, reducing blisters (fatigue) and keeping the shoes intact even when it rains (low-temperature cracking). That's much like how modifiers protect asphalt pavements, enabling them to perform well under various conditions and increasing their lifespan.
Key Concepts
-
Modifiers: Substances like polymers and rubber that enhance the performance of bituminous binders.
-
Adhesion Improvers: Enhancements that promote better bonding between binder and aggregates.
-
Service Life: The duration a pavement can effectively function without significant maintenance.
Examples & Applications
The use of SBS polymers in hot climates improves temperature resistance and reduces cracking.
Rubber powder from recycled tires is used to enhance flexibility and durability in bituminous mixtures.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Modifiers make binders strong, they help pavements last long!
Stories
Imagine a road that can withstand the toughest rains and heavy trucks; modifiers like polymers are the unseen heroes behind its endurance.
Memory Tools
Remember M.A.R.W.: Modifiers are Rubber and Wax substances that improve binder performance.
Acronyms
P.R.A.W. stands for Polymer, Rubber, Anti-stripping, and Wax which enhance binder quality.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Polymers
Large molecules composed of repeating structural units, used for enhancing the elasticity and temperature resistance of bituminous binders.
- Rubber Powder
Particles derived from recycled tires that improve the flexibility and durability of bituminous mixtures.
- Antistripping Agents
Additives that promote adhesion between bitumen and aggregate, overcoming moisture-related loss.
- Waxes and Resins
Substances added to improve the performance of bituminous binders at various temperatures.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
