Types of Cutbacks
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Cutback Bitumen
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into cutback bitumen. Can anyone tell me what cutback bitumen is?

Is it just regular bitumen diluted with something?

Exactly! Cutback bitumen is bitumen mixed with volatile solvents to reduce its viscosity, making it easier to work with, especially in cooler temperatures. Now, who can name the main types of cutbacks?

There are Rapid Curing, Medium Curing, and Slow Curing cutbacks, right?

Correct! Let's explore these types in detail and their unique applications.
Types of Cutbacks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's begin with Rapid Curing cutbacks. Who can describe what solvent it uses?

It uses petrol or naphtha!

Great! Rapid Curing is typically used for quick applications like patch repairs. How about Medium Curing?

It uses kerosene and is used for the prime coat of asphalt.

Exactly! And finally, Slow Curing cutbacks use diesel. Can someone tell me why we use them?

For preparing cold mixes!

Right again! Let’s summarize these details before moving on.
Environmental Considerations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about environmental considerations with cutbacks. What do you all think happens when we use solvents?

They can release harmful VOCs?

Spot on! This has led to regulations against their use. How might these regulations change our construction choices?

We might use alternative materials or more environmentally-friendly binders.

Exactly! Excellent discussion guys, let's summarize what we learned today.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
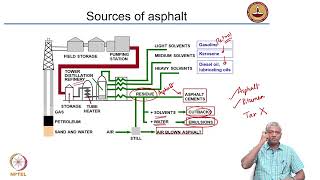
Type of cutbacks in bituminous binders are categorized based on the curing rates – Rapid Curing, Medium Curing, and Slow Curing – determined by their solvent types. Each type has specific applications and considerations, especially concerning environmental impacts.
Detailed
Types of Cutbacks
Cutback bitumen consists of bitumen diluted with volatile solvents to reduce viscosity, facilitating easier application at lower temperatures. The three primary types of cutbacks include:
- Rapid Curing (RC): Utilizes petrol or naphtha as a solvent. Commonly used for patch repairs and surface dressing projects due to its quick drying time.
- Medium Curing (MC): Employs kerosene as a solvent and is typically used for prime coat applications, allowing for moderate curing times.
- Slow Curing (SC): Incorporates diesel or heavy oils. This type is suitable for preparing cold mixes, allowing a more prolonged workability period.
Environmental Considerations
Although cutbacks were prevalent in road construction, they have become less favored due to the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which pose environmental risks. Regulatory measures are now in place to limit their use in favor of more environmentally-friendly alternatives.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Rapid Curing (RC) Cutbacks
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Rapid Curing (RC): Uses petrol or naphtha as solvent.
Detailed Explanation
Rapid Curing cutbacks (RC) use solvents like petrol or naphtha to dilute bitumen, making it less viscous. This modification allows the bitumen to be applied at lower temperatures, which is especially useful during colder weather conditions. The rapid curing process means that the solvent evaporates quickly after application, allowing the material to set and cure swiftly, leading to a faster return to service for the road surface.
Examples & Analogies
Think of rapid curing cutbacks like a quick-drying paint; it allows homeowners to finish a room and start using it again without waiting long. Similarly, RC cutbacks enable quicker road repairs.
Medium Curing (MC) Cutbacks
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Medium Curing (MC): Uses kerosene.
Detailed Explanation
Medium Curing cutbacks (MC) utilize kerosene as the solvent for diluting bitumen. The medium curing process strikes a balance between the rapid and slow curing types. It allows for a moderate evaporation rate, which means that the application can be used for tasks that require a bit more working time before it sets, such as prime coats on roads.
Examples & Analogies
Consider this like a medium-baking cake, which is neither too quick nor too slow to bake. Medium curing cutbacks provide just the right amount of time to ensure proper application without rushing the process.
Slow Curing (SC) Cutbacks
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Slow Curing (SC): Uses diesel or heavy oils.
Detailed Explanation
Slow Curing cutbacks (SC) are blended with diesel or heavy oils. The slow curing process allows these cutbacks to remain workable for an extended period due to a slower evaporation of the solvent. This is particularly beneficial when preparing cold mix asphalt, as it gives contractors more time to work with the material before it hardens.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a slow-cooked stew, where the ingredients have time to blend flavors over an extended period. Slow curing cutbacks allow more time for the bitumen to mix effectively with aggregates before it sets.
Key Concepts
-
Types of Cutbacks: Rapid, Medium, and Slow Curing, each with unique solvents and applications.
-
Environmental Considerations: The impact of using VOCs from cutback bitumen.
Examples & Applications
An example of Rapid Curing (RC) is using petrol for surface dressing on a road to ensure quick curing and adherence.
Medium Curing (MC) cutback is often used as a prime coat before applying asphalt layers in road construction.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cutbacks come in three types, RC, MC, SC, get them right or application might not be tight!
Stories
Imagine a construction crew preparing for paving in the cold. They choose Slow Curing cutback, ensuring a workable mix to keep the road strong despite the winter chill.
Memory Tools
Remember 'RMS' for 'Rapid', 'Medium', 'Slow' when discussing cutback types.
Acronyms
Use 'PDS' for 'Petrol, Diesel, Solvent' to remember solvents used in cutbacks.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cutback Bitumen
Bitumen diluted with volatile solvents to lower viscosity for easier application.
- Rapid Curing (RC)
A type of cutback that uses petrol or naphtha, used for quick applications like patch repairs.
- Medium Curing (MC)
A type of cutback that uses kerosene, commonly applied as a prime coat.
- Slow Curing (SC)
A type of cutback that uses diesel or heavy oils, suitable for cold mix preparation.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic chemicals that have high vapor pressures at room temperature and can cause environmental harm.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
