Bituminous Emulsions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Bituminous Emulsions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to explore bituminous emulsions. Can anyone describe what a bituminous emulsion is?

Is it a type of material used in road construction?

Exactly! Bituminous emulsions are dispersions of bitumen in water, stabilized by emulsifying agents. They are important because they allow us to apply bitumen in various forms more easily.

Why do we need emulsions instead of just using liquid bitumen?

Great question! Emulsions enhance the application process, allowing for easier handling and improved adhesion with aggregates.
Types of Bituminous Emulsions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move on to the types of emulsions. Cationic and anionic emulsions are the most common. Who can tell me the difference?

Is it about how they interact with aggregates?

Right! Cationic emulsions have better adhesion with aggregates compared to anionic emulsions, which are limited due to their interaction with acidic aggregates.

So, cationic is preferred?

Yes, they are most often used in practice due to their effective performance with a wide range of aggregates.
Setting Time Classification
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Setting time is another critical factor for emulsions. Can someone recap the classifications?

We have rapid setting, medium setting, and slow setting?

Correct! Rapid-setting emulsions cure quickly, ideal for urgent applications, while slow-setting emulsions allow for extended working time. Each has its unique advantages depending on the job.

When would we use medium-setting emulsions?

Medium-setting emulsions strike a balance between curing speed and workability, making them versatile for various situations.
Applications of Bituminous Emulsions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s look at the applications of bituminous emulsions. What are some uses?

Like tack coats and surface dressing?

Exactly! They're also used in prime coats, slurry seals, and cold mix asphalt. Each application takes advantage of the unique properties of emulsions.

So, why not use them everywhere?

Good point! While they are versatile, the right emulsion type depends on project specifications and environmental conditions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section highlights the significance of bituminous emulsions, detailing their types, setting classifications, and applications. It explains the differences between cationic and anionic emulsions, the implications of their setting times, and their practical usage in various road applications.
Detailed
Bituminous Emulsions
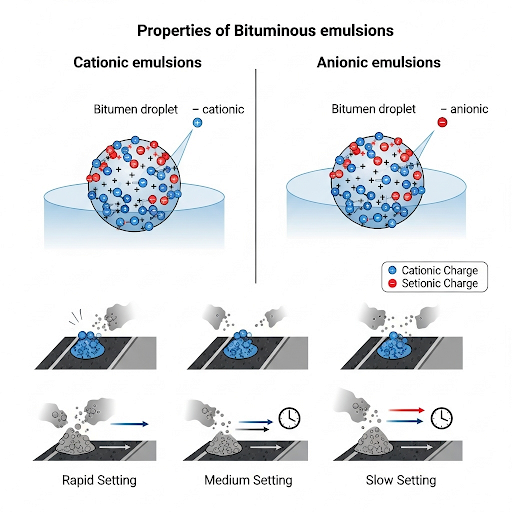
Bituminous emulsions are defined as dispersions of bitumen in water, stabilized by emulsifying agents. They play a vital role in modern road construction by allowing for a variety of applications and enhancing the effectiveness of bituminous binders. This section differentiates between the main types of emulsions, namely cationic and anionic emulsions. Cationic emulsions are favored for their superior adhesion properties with aggregate materials, while anionic emulsions see limited use primarily due to their poor adhesion with acidic aggregates.
Furthermore, emulsions are classified based on their setting times:
- Rapid Setting (RS) emulsions cure quickly, making them ideal for quick applications.
- Medium Setting (MS) emulsions provide a balance of setting time and application versatility.
- Slow Setting (SS) emulsions are beneficial for situations requiring extended workability.
The diverse applications of bituminous emulsions include prime coats, tack coats, surface dressing, slurry seals, and cold mix asphalt. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective pavement design and construction, ensuring that the right materials are selected for specific project requirements.
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What are Bituminous Emulsions?
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bituminous emulsions are dispersions of bitumen in water, stabilized by emulsifying agents.
Detailed Explanation
Bituminous emulsions consist of tiny droplets of bitumen suspended in water. The 'emulsifying agents' help to keep these droplets from separating back out of the water, effectively creating a stable mixture. This stability allows the emulsion to be spread on surfaces without the bitumen settling, making it easier to apply during road construction.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a salad dressing made with oil and vinegar. Without the emulsifier (like mustard), the oil and vinegar would simply separate after a short time. Just like that dressing, bituminous emulsions require emulsifying agents to remain mixed and usable.
Types of Emulsions
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
10.3.1 Types of Emulsions:
• Cationic Emulsions: Most commonly used due to better adhesion with aggregates.
• Anionic Emulsions: Limited use due to poor adhesion with acidic aggregates.
Detailed Explanation
There are two main types of bituminous emulsions based on the charge of the droplets: cationic and anionic. Cationic emulsions have positively charged droplets, which bond well with negatively charged aggregates commonly used in road construction. This quality makes them the more widely employed choice. In contrast, anionic emulsions, with negatively charged droplets, don’t adhere as effectively to certain aggregates, limiting their use.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine glue. Cationic emulsions are like super glue that sticks firmly to surfaces, ensuring solid bonds, while anionic emulsions are more like a weak adhesive tape that doesn’t hold things together as well, leading to potential issues in the construction process.
Setting Time Classification
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
10.3.2 Setting Time Classification:
• Rapid Setting (RS)
• Medium Setting (MS)
• Slow Setting (SS)
Detailed Explanation
Bituminous emulsions are classified by their setting times, which describe how quickly they harden after application. Rapid Setting (RS) emulsions are designed to set quickly, making them ideal for situations where time is of the essence. Medium Setting (MS) emulsions have moderate setting times, while Slow Setting (SS) emulsions take longer to set, allowing for more flexibility in application and adjustments during the early stages.
Examples & Analogies
Consider preparing a pancake. If you use a quick-cooking mix, the pancakes are ready to flip in no time – this is like Rapid Setting emulsion. If you use a traditional recipe that takes longer to set, you can take your time pouring and adjusting; this parallels the Slow Setting emulsions.
Applications of Bituminous Emulsions
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
10.3.3 Applications:
• Primecoats, tackcoats, surface dressing, slurry seals, and cold mix asphalt.
Detailed Explanation
Bituminous emulsions serve various purposes in road construction. They are used as primecoats to prepare surfaces for further layers of asphalt, tackcoats to bond new layers to existing pavements, and for surface dressing to enhance durability and prevent water infiltration. Slurry seals combine emulsions with aggregate to create a protective layer, while cold mix asphalt utilizes these emulsions to provide flexible repair options.
Examples & Analogies
Think of bituminous emulsions like different types of adhesives in crafting. Some are great for basic bonding (like primecoats), while others are meant for creating a water-resistant seal (like slurry seals), helping projects to last longer and perform better.
Key Concepts
-
Bituminous Emulsions: These are dispersions of bitumen in water, allowing for various applications in road construction.
-
Cationic vs. Anionic: Cationic emulsions have better adhesion properties with aggregates compared to anionic emulsions.
-
Setting Time: Bituminous emulsions can be classified into rapid, medium, and slow setting types based on curing time.
Examples & Applications
Cationic emulsions are commonly used in surface treatments due to their excellent adhesion to aggregate materials.
An example of rapid setting emulsion is used in road repairs requiring quick curing times to minimize disruption.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Emulsions in the mix, the bitumen fix, sticky and wet, the road will perfect.
Stories
Imagine a clever engineer named Emma who uses cationic emulsions to coat the new road. The traffic flows smoothly because they stick better to the aggregates compared to the other type.
Memory Tools
Think 'CMS' for the three types of setting: C for Cationic, M for Medium, S for Slow.
Acronyms
CARS = Cationic Adhesion Road Strength, highlighting what cationic emulsions do.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bituminous Emulsions
Dispersions of bitumen in water, stabilized by emulsifying agents.
- Cationic Emulsions
Emulsions with positive charge, providing better adhesion with aggregates.
- Anionic Emulsions
Emulsions with negative charge, less effective with acidic aggregates.
- Rapid Setting (RS)
Emulsions that cure quickly for fast applications.
- Medium Setting (MS)
Emulsions that allow a balance of working and setting time.
- Slow Setting (SS)
Emulsions that provide extended working time before curing.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
