Joints in Cement Concrete Pavement
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Types of Joints
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the types of joints found in cement concrete pavements. Can anyone tell me what expansion joints are used for?

Are they to allow for thermal expansion?

Exactly! Expansion joints help accommodate the changes in size that occur due to temperature fluctuations. That's essential for preventing cracks. Now, what about contraction joints?

I think they control cracking too, right?

Correct! They create predetermined weak points for cracks to form, instead of them appearing randomly in the pavement. This is a crucial aspect of joint placement in pavements. Let's not forget construction joints—Student_3, what do you think they do?

They connect different sections of the concrete, right?

Yes, you got it! Construction joints are essential when you're placing concrete in separate pours. Lastly, can anyone share what warpage joints are for?

They help to manage uneven warping of the slab due to conditions like curing?

Great insight! Always remember the acronym 'ECCA' for the types of joints we discussed: **E**xpansion, **C**ontraction, **C**onstruction, and **A**warp. Let’s summarize: We discussed expansion and contraction joints for temperature and cracking management, construction joints for joining, and warpage joints for handling deformations.
Joint Sealants
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've reviewed the joint types, let's talk about joint sealants. Who can explain why they are necessary?

To keep water and debris out of the joints, right?

Absolutely! Preventing water infiltration is crucial to protect the pavement's integrity. What kinds of sealants do you think we can use?

I remember hot-poured rubber is one type.

Correct! Hot-poured rubber is flexible and good for sealants. What about others?

Are polysulphide and silicone options as well?

Yes, both are excellent choices! They all ensure that joints stay functional without being compromised. To remember sealant types, think: 'HPS'—Hot-poured, Polysulphide, Silicone. Can anyone summarize their main role?

They prevent water and debris from entering the joints.

Perfect! Learning about sealants helps highlight their pivotal role in joint longevity.
Load Transfer Devices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's discuss load transfer devices. Can anyone explain what they do?

I think they help brace the slabs against loads at the joints?

Exactly right! They ensure loads are distributed effectively across the slabs. What about dowel bars and tie bars? Who can differentiate between them?

Dowel bars are for expansion and contraction joints, while tie bars keep the slabs together?

Perfectly summarized! Dowel bars facilitate horizontal movement while allowing load transfer, whereas tie bars maintain alignment. Think of the acronym 'DT' for **D**owel and **T**ie to remember their uses. Why do you think these devices are crucial?

They help prevent pavement failure!

Absolutely! Proper load transfer devices greatly enhance a pavement's resilience and longevity.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore four primary types of joints in cement concrete pavements: expansion joints, contraction joints, construction joints, and warpage joints. Additionally, we discuss the types of sealants used to protect joints and the load transfer devices that enhance the structural performance of these pavements.
Detailed
Joints in Cement Concrete Pavement
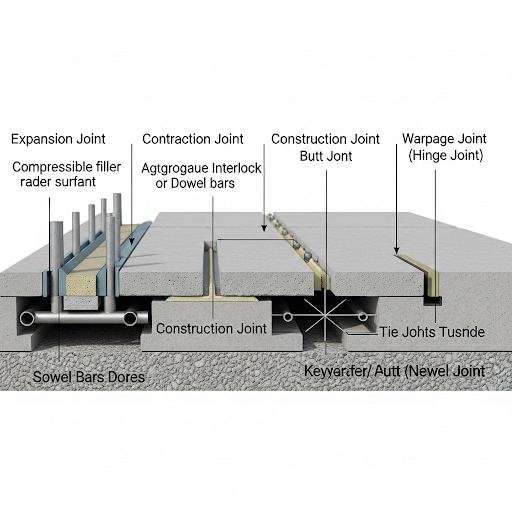
Cement concrete pavements require specific joints to manage environmental stresses and loads effectively. This section delineates the four main types of joints employed:
1. Types of Joints
- Expansion Joints: Designed to accommodate thermal expansion of the pavement material, which prevents cracking due to pressure from heat-induced expansion.
- Contraction Joints: Intended to control cracking by creating predefined weak points. When concrete shrinks, it will crack at these joints instead of randomly.
- Construction Joints: Utilized when there's a discontinuity in concrete placement, ensuring structural integrity between successive placements.
- Warpage Joints: Address slab warping, which can occur due to uneven curing or environmental factors.
2. Joint Sealants
Sealants play a crucial role in protecting the joints from water and debris infiltration. Commonly used materials include:
- Hot-poured rubber
- Polysulphide
- Silicone sealants
3. Load Transfer Devices
To ensure effective load distribution across joints, devices are used:
- Dowel Bars: Employed at expansion and contraction joints to allow for horizontal movement while transferring loads.
- Tie Bars: Used in longitudinal joints to keep slabs aligned and prevent their separation.
This thorough understanding of joint types, sealants, and load transfer systems is integral in the construction of durable and efficient cement concrete pavements.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Types of Joints
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Expansion Joints – Accommodate thermal expansion
- Contraction Joints – Control cracking
- Construction Joints – Between successive placements
- Warpage Joints – Address slab warping
Detailed Explanation
In cement concrete pavements, different types of joints are necessary to maintain the integrity of the pavement as it reacts to temperature changes and loading. Here's a breakdown:
- Expansion Joints: These joints allow the concrete slabs to expand when heated. Without these joints, the concrete can buckle due to the increased size from heat.
- Contraction Joints: These are intentionally created cracks that control where the concrete will crack due to contraction as it cools. This helps to prevent random cracking.
- Construction Joints: These joints are placed between different pours of concrete, allowing for separate concrete placements without compromising the structure.
- Warpage Joints: These address situations where slabs might warp under pressure or uneven loading conditions, helping to maintain an even surface.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a long, continuous chain that expands as it gets warmer. If there are no gaps in the chain, it will become tense and might break. Similarly, the expansion joints in concrete act as the gaps that prevent the material from breaking under heat. The contraction joints work like perforations on packaging that aid in controlled tearing, ensuring it breaks at specific points rather than randomly.
Joint Sealants
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Hot-poured rubber, polysulphide, or silicone sealants
• Prevent ingress of water and debris
Detailed Explanation
Joint sealants are crucial in cement concrete pavements. They fill the joints and act as a barrier to protect them from water and debris. Here's why they're important:
- Materials: Common types include hot-poured rubber and polysulphide sealants. These materials are flexible and can expand or contract with the joint movement, providing a durable solution.
- Function: By preventing water and debris from entering the joints, sealants help maintain the pavement's integrity. Water can lead to damage like freezing and thawing cycles, which can cause cracks.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the seal around a bathroom tub. If the seal is broken, water can leak underneath, causing damage over time. Similarly, joint sealants in concrete pavements stop water from seeping in, protecting the structure and extending its life.
Load Transfer Devices
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Dowel Bars: For expansion and contraction joints
• Tie Bars: For longitudinal joints
Detailed Explanation
Load transfer devices are crucial in maintaining the stability of joints in cement concrete pavements. They work as follows:
- Dowel Bars: These are cylindrical bars inserted in expansion and contraction joints. They help transfer loads across joints, ensuring that the slabs remain aligned and that no significant displacement occurs.
- Tie Bars: These are used in longitudinal joints to hold adjacent slabs together. They prevent the slabs from separating under load, maintaining overall structural integrity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a bridge where beams are tied using metal rods to keep them from swaying or separating during strong winds. Dowel bars and tie bars in concrete pavements play a similar role, ensuring that the slabs stay connected and stable under various loads.
Key Concepts
-
Expansion Joints: Essential for absorbing thermal expansion and preventing pavement cracking.
-
Contraction Joints: Created to manage cracking through controlled weak points.
-
Construction Joints: Facilitate successive concrete placements for structural continuity.
-
Warpage Joints: Help correct slab deformations due to uneven curing.
-
Sealants: Protect joints from environmental threats such as water ingress.
-
Load Transfer Devices: Essential components for distributing loads and enhancing pavement durability.
Examples & Applications
A road in a high-temperature area utilizes expansion joints extensively to prevent damage during heat waves.
A newly constructed highway features contraction joints that are strategically spaced to minimize cracking.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Joints expand and contract, so make them exact, seal with care, keep water rare!
Stories
Imagine a bustling highway under the sun. The concrete expands, but thanks to the expansion joints, it remains intact and strong. The rain can’t penetrate, thanks to the tight sealants holding the pavement guard. Thus, the highway endures the test of time.
Memory Tools
Remember 'ECCA' for joints: Expansion, Contraction, Construction, Awarpage.
Acronyms
Use 'HPS' to recall joint sealants
**H**ot-poured
**P**olysulphide
**S**ilicone.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Expansion Joints
Joints in concrete that allow for thermal expansion of the material, preventing cracking.
- Contraction Joints
Joints designed to control cracking by creating planned weak points in the concrete.
- Construction Joints
Joints that occur between successive concrete placements to ensure structural integrity.
- Warpage Joints
Joints that address warping of the concrete slab, commonly occurring due to uneven curing.
- Sealants
Materials used to protect joints from water and debris infiltration.
- Dowel Bars
Steel bars used at expansion and contraction joints to transfer loads while allowing movement.
- Tie Bars
Steel bars used in longitudinal joints to keep slabs aligned and minimize displacement.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
