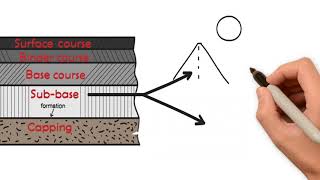
Sub-base
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of the Sub-base
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the role of the sub-base in cement concrete pavements. Can anyone tell me what material is typically used for the sub-base?

I think it's made from granular materials or sometimes lean concrete.

Correct! Granular materials provide excellent drainage and stability. Now, why do you think the thickness of the sub-base is crucial?

Is it to ensure that it can handle the load and distribute it properly?

Exactly! A thickness of 100 mm to 150 mm helps in load distribution. Remember this acronym: STABLE—Sub-base Thickness Affects Building Load Efficiency.

That's a handy way to remember!

Good to hear! To summarize, the sub-base not only supports the pavement but also protects it from moisture damage.
Construction Techniques of Sub-base
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss how we prepare the sub-base. What do you think is the first step in preparing the sub-base?

I guess it would be selecting the right material?

Great point! Selecting quality granular materials or lean concrete is essential. What comes after that?

Do we need to compact the sub-base?

Exactly! Compaction ensures stability. We aim for a compaction level of around 95% of Modified Proctor Density. If we don’t compact enough, what could be the consequences?

The pavement might crack or settle unevenly.

Exactly! Well done! To sum up, preparation, material selection, and compaction are key components for a stable sub-base.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The sub-base is typically made from granular materials or lean concrete, with a thickness of 100 mm to 150 mm. It is crucial for providing stability to the pavement structure and ensuring effective load distribution.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The sub-base layer is essential in the construction of cement concrete pavements, commonly known as rigid pavements. This layer is typically composed of granular materials or lean concrete, and it serves multiple purposes including acting as a working platform during construction and facilitating load transfer from the pavement surface to the underlying ground. The standard thickness for the sub-base ranges from 100 mm to 150 mm, which impacts the overall performance and durability of the pavement system. Proper preparation and compaction of the sub-base ensure that it provides adequate support while maintaining drainage to prevent moisture issues that could compromise the integrity of the pavement.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Sub-base
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Often made from granular material or lean concrete
Detailed Explanation
The sub-base is a foundational layer used in road construction, typically composed of either granular materials like sand or gravel, or lean concrete which is a mix with lower cement content. Its primary purpose is to provide stability and support for the pavement structure that is laid above it.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the sub-base as the bed on which a mattress rests. Just as a good bed provides comfort and support for a good night's sleep, a solid sub-base ensures that the pavement above can support traffic loads effectively without sinking or cracking.
Thickness of the Sub-base
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Thickness: 100 mm to 150 mm
Detailed Explanation
The thickness of the sub-base typically ranges from 100 mm to 150 mm (approximately 4 to 6 inches). This thickness is crucial as it affects the overall strength and stability of the pavement above. A properly thickened sub-base distributes loads evenly and reduces the risk of failure under heavy traffic.
Examples & Analogies
Consider building a tall bookshelf; if you don't have a strong base or if it's too thin, the bookshelf might wobble or even fall over when you place books on it. Similarly, having the right thickness for the sub-base is necessary to support the weight of vehicles without causing damage.
Role of the Sub-base
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Acts as a working platform and load transfer medium
Detailed Explanation
The sub-base plays a dual role: it serves as a working platform during the construction of the pavement, allowing heavy machinery to operate without damaging the underlying layers, and it also acts as a medium for transferring loads from the pavement to the underlying soil. This ensures that the stresses are spread over a larger area, reducing the potential for failure.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine laying a large, heavy tabletop over a flimsy set of chairs; if the base is not strong enough, the table will collapse under weight. The sub-base is like the stable, strong foundation that prevents this from happening, ensuring the table (or pavement) can safely bear the load placed on it.
Key Concepts
-
Sub-base: The layer supporting the pavement, crucial for load distribution.
-
Lean concrete: A lower cement content mixture used in sub-bases.
Examples & Applications
An example of a well-prepared sub-base might be a layer of granular stone that allows moisture drainage while supporting heavy traffic loads.
Using lean concrete as a sub-base can be cost-effective, especially for lighter traffic roads where high-strength materials are not necessary.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Sub-base thick, not too thick, keeps pavements straight and slick.
Stories
Once upon a time, a builder named Sam used just the right sub-base thickness for his road. Too thick, and the road would crack; too thin, and it would fail. He learned that 100 to 150 mm was the magic number!
Memory Tools
Remember SUB for Sub-base: Stability, Uniformity, and Bearing capacity.
Acronyms
STABLE - Sub-base Thickness Affects Building Load Efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Subbase
The layer beneath the pavement, usually made of granular material or lean concrete, providing support and load distribution.
- Lean Concrete
A mixture with a lower cement content than regular concrete, primarily used as a base layer.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
