Maintenance of Concrete Pavements
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're focusing on preventive maintenance for concrete pavements. It's vital because it prevents larger issues down the line.

What are some specific preventive measures we can take?

Great question! Common preventive measures include sealing joints and conducting regular surface cleanings. Who can tell me why sealing joints is essential?

Is it to prevent water from getting into the pavement?

Exactly! When water penetrates, it can cause significant damage. Remember the acronym J.O.I.N.T. to recall the importance of Joints: 'Just Offer Increased Normal Tension.'

So, if we can keep water out, the pavement lasts longer, right?

Yes! Regular checks and maintenance can ultimately extend the pavement's life. To summarize, preventive maintenance is proactive and essential for durability.
Corrective Maintenance Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss corrective maintenance techniques, which are necessary when we encounter issues.

What kinds of issues would need corrective maintenance?

Common examples include cracks and localized failures. Crack filling is a popular method. Does anyone know why it's important?

Because if we don't fill cracks, they might become bigger?

Precisely! Filling cracks prevents further water damage. Let’s create a mnemonic: F.I.L.L. for 'Fixing Imperfections Leads to Longevity.'

That’s a good way to remember it!

Exactly! And remember, once repairs are made, monitoring the pavement is crucial. So, what did we learn about corrective maintenance?

It’s about addressing problems to prevent them from growing.
Overlays for Concrete Pavements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's explore overlays. They play a significant role in concrete pavement maintenance.

What is an overlay, and when do we need it?

An overlay is a new layer of concrete placed on the existing surface. It’s often used when the pavement is deteriorating but structurally sound.

How does it help?

Overlays can restore surface integrity and improve ride quality. Remember: O.V.E.R.L.A.Y. - 'Offering Very Essential Repairs Leading to a New layer.'

So it's like giving the pavement a fresh coat?

Exactly! And it’s a cost-effective way to extend the pavement lifespan. So, the key points for today: preventive maintenance is proactive, corrective addresses existing issues, and overlays restore effectiveness.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Concrete pavement maintenance is essential for extending pavement life and ensuring safety. It includes preventive measures like sealing joints and surface cleaning, corrective actions such as crack filling and partial depth patching, and may involve overlays to improve the pavement's surface.
Detailed
Maintenance of Concrete Pavements
The maintenance of concrete pavements is a crucial aspect that addresses the longevity and serviceability of these infrastructures. It involves a combination of preventive and corrective measures:
- Preventive Maintenance: This includes strategies to proactively preserve the pavement, such as sealing joints to prevent water ingress and surface cleaning to remove debris and contaminants.
- Corrective Maintenance: When issues arise, corrective actions become necessary. This can involve crack filling to repair damages and partial depth patching to address localized failures in the pavement surface.
- Overlays: In some cases, bonded or unbonded concrete overlays may be applied to restore the pavement's surface, extending its life further.
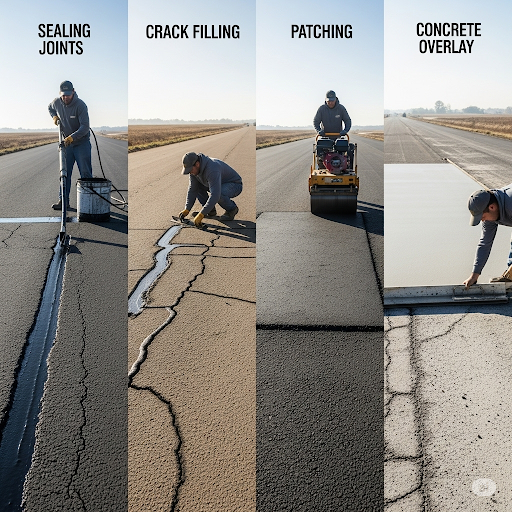

Through these strategies, maintenance not only helps enhance the durability of concrete pavements but also ensures safety and operational efficiency on road networks, underscoring the importance of regular maintenance practices.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Preventive Maintenance
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Preventive Maintenance: Sealing joints, surface cleaning
Detailed Explanation
Preventive maintenance involves actions taken to stop issues before they arise. This includes sealing joints, which are gaps between concrete slabs that can allow water to enter and potentially damage the pavement. By sealing these joints, we can protect the internal structure of the pavement. Additionally, regular cleaning of the pavement surface helps to remove debris and contaminants that could lead to deterioration.
Examples & Analogies
Think of preventive maintenance like regular check-ups at a doctor's office. Just as a doctor checks your health before problems occur, preventive maintenance checks and takes care of pavement conditions before they develop into serious issues.
Corrective Maintenance
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Corrective Maintenance: Crack filling, partial depth patching
Detailed Explanation
Corrective maintenance is performed after damage has occurred. Crack filling involves applying a sealant in cracks that have formed in the concrete. This prevents water from entering and causing further damage. Partial depth patching is used to repair localized areas of spalling or deterioration by removing the damaged concrete and replacing it with new material, which restores the integrity of the pavement.
Examples & Analogies
Consider corrective maintenance like fixing a tire on a bike that has a flat. You have to patch or replace the tire after it gets damaged, just like filling cracks in concrete after they've already appeared.
Overlays
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Overlays: Bonded or unbonded concrete overlays
Detailed Explanation
Overlays are additional layers of concrete applied on top of existing pavements. They can be bonded, where the new concrete adheres to the old surface, or unbonded, where they are laid without bonding to the existing pavement. Overlays are used to extend the life of the pavement, improve surface smoothness, and enhance resistance to weathering.
Examples & Analogies
Think of overlays like putting a new layer of paint on a wall. Just as adding a fresh coat of paint can cover imperfections and protect the wall underneath, a concrete overlay rejuvenates and repairs the pavement surface.
Key Concepts
-
Preventive Maintenance: Involves proactive measures like joint sealing and surface cleaning.
-
Corrective Maintenance: Actions taken to fix existing issues such as cracks.
-
Overlays: New concrete layer applied to restore the existing surface.
Examples & Applications
Sealing joints regularly to prevent water infiltration into the pavement.
Using crack filling materials to repair hairline fractures before they worsen.
Applying a bonded overlay to improve surface smoothness and longevity of the pavement.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For pavement to last and endure, preventive measures are the cure.
Stories
Imagine a road that gets a fresh coat of paint each summer; it shines and lasts longer, just like overlays help restore old concrete pavements.
Memory Tools
Use P.C.O. to remember: Preventive, Corrective, Overlays are key maintenance types.
Acronyms
J.O.I.N.T. (Just Offer Increased Normal Tension) helps you recall the importance of sealing joints.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Preventive Maintenance
Actions taken to preserve the condition of concrete pavements and prevent future deterioration.
- Corrective Maintenance
Repair actions taken to address existing damages in concrete pavements.
- Overlays
A new layer of concrete applied over existing pavement to restore surface integrity.
- Joint Sealing
The process of filling joints to prevent water ingress and associated damages.
- Crack Filling
A corrective maintenance technique to repair and prevent the extension of cracks in pavements.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
