Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Combustion of Carbon Compounds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll start with the concept of combustion. When carbon compounds burn in oxygen, what do you think they produce?

I think they produce carbon dioxide and release heat.

Exactly! This reaction can be represented as C + O₂ → CO₂ + heat and light. What can you tell me about incomplete combustion?

That happens when there's not enough oxygen and it produces carbon monoxide and soot.

Great observation! So, remember, complete combustion leads to carbon dioxide, while incomplete combustion results in harmful emissions like carbon monoxide. Let's remember to connect 'C' for carbon with our combustion equation!

That's a good way to remember it, 'C for CO₂'.

Exactly! So, what's significant about the products of combustion?

It affects our environment due to CO₂ emissions contributing to global warming.

Yes, a crucial takeaway!
Oxidation Reactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

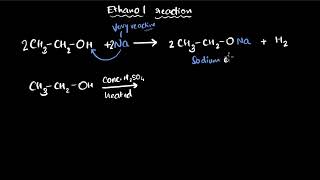
Next, let's look at oxidation. What is an oxidizing agent, and can anyone give me an example?

Potassium permanganate is one, right?

Yes, it shows color change when it oxidizes ethanol.

Correct! When we add potassium permanganate to ethanol, it turns clear, indicating oxidation. What does this produce?

It produces ethanoic acid!

Great! So remember, oxidation reactions are significant in converting alcohols to acids.
Addition and Substitution Reactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss addition reactions. When unsaturated hydrocarbons are combined with hydrogen, what do we call that?

Hydrogenation!

Correct! Hydrogenation transforms unsaturated compounds into saturated ones. Can anyone think of a practical application?

In food industry, they hydrogenate oils to make them solid.

Exactly! Now let's connect this to substitution reactions. What occurs when we expose hydrocarbons to chlorine in sunlight?

Chlorine replaces hydrogen atoms to form haloalkanes.

That's right! Substitution reactions show how versatile carbon compounds can react. So, who can summarize today's key learning?

We learned about combustion, oxidation, addition, and substitution reactions!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the chemical properties of carbon compounds are explored, including the processes of combustion and oxidation, the concepts of addition and substitution reactions, and the environmental implications of fuel combustion. Examples are provided to illustrate the oxidation of ethanol and the characteristics of combustion reactions for different types of carbon compounds.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section delves into the various chemical properties exhibited by carbon compounds. The discussion opens with the combustion of carbon in its allotropic forms, where carbon burns in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, releasing significant heat and light.
- Combustion: This process emphasizes that many carbon compounds ignite in the presence of oxygen to produce energy. For example:
- Complete Combustion:
C + O₂ → CO₂ + heat and lightCH₄ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O + heat and light
- Incompletion: When there isn't enough oxygen, incomplete combustion occurs, producing carbon monoxide (CO) and soot.
- Oxidation: The oxidation reactions of carbon compounds, particularly alcohols like ethanol, are shown through experiments involving potassium permanganate as an oxidizing agent. This highlights carbon’s ability to undergo oxidation to form carboxylic acids.
- Addition Reactions: Unsaturated hydrocarbons can undergo addition reactions where they add hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst, transforming into saturated hydrocarbons. This is significant in food processing, as the hydrogenation of vegetable oils is common.
- Substitution Reactions: In the presence of chlorine and sunlight, saturated hydrocarbons can substitute one or more hydrogen atoms. This reaction leads to the formation of haloalkanes, illustrating the reactivity of carbon compounds with halogens.
Through these points, the section illustrates the nature and significance of electrical bonds in carbon compounds and their broader environmental and industrial implications.
Youtube Videos







Key Concepts
-
Combustion: The process of burning in oxygen.
-
Oxidation Reactions: Reactions where substances lose electrons.
-
Addition Reactions: Unsaturated hydrocarbons adding hydrogen.
-
Substitution Reactions: Replacing hydrogen with other elements.
Examples & Applications
The combustion of methane (CH₄) produces carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
Oxidation of ethanol (C₂H₅OH) to acetic acid (CH₃COOH) using potassium permanganate.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To remember what burns with a glow, carbon and oxygen start the show.
Stories
Once upon a time, carbon sat next to oxygen at a campfire. Together they created warmth and light. But sometimes, they didn’t have enough oxygen, and it turned smoky.
Memory Tools
C.O.A.T. - Combustion, Oxidation, Addition, and Substitution denote reactions of carbon.
Acronyms
CAOS - Combustion, Addition, Oxidation, Substitution reactions are vital for carbon chemistry.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Combustion
A chemical reaction that occurs when a substance combines with oxygen, producing heat and light.
- Oxidation
A chemical reaction in which a substance loses electrons or gains oxygen.
- Addition Reaction
A reaction where unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen to form saturated hydrocarbons.
- Substitution Reaction
A reaction where one atom or a group of atoms in a molecule is replaced with another atom or group.
- Oxidizing Agent
A substance that facilitates oxidation by accepting electrons.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
