Properties of Ethanoic Acid
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Ethanoic Acid
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're diving into ethanoic acid, also known as acetic acid. Can anyone tell me where we might find this acid in our daily lives?

Isn't that the stuff in vinegar?

Exactly! Vinegar is a 5-8% solution of acetic acid. It serves many purposes from food preservation to flavoring. Now, can anyone guess what happens when we cool pure acetic acid?

Does it freeze? I've heard it called glacial acetic acid.

Yes, that’s correct! At 290 K, it can freeze, earning it that name. It's fascinating how its properties change under varying conditions. Remember the phrase 'Glacial Acetic Acid' to recall this unique property!
Reactions Involving Ethanoic Acid
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's explore some important reactions involving ethanoic acid. Who can tell me what happens when we mix it with ethanol?

Isn’t that how we make esters?

Precisely! When ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, it forms an ester. This reaction is known as esterification. Esters are used in perfumes due to their fruity scents.

What about acid-base reactions? Does it react like regular acids?

Yes, it does! Ethanoic acid can react with sodium hydroxide to form sodium acetate and water. However, remember it's a weak acid unlike strong acids that completely ionize.

Let's take a quick quiz: what products are formed when ethanoic acid reacts with carbonates?
Properties of Ethanoic Acid
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Ethanoic acid is considered a weak acid. Who can remind me why it doesn’t fully ionize?

Uh, because it’s a carboxylic acid and does not dissociate completely like HCl?

Exactly! This means its reactions can differ significantly from stronger acids. Remember, weak acids partly dissociate, influencing their behavior in different chemical reactions.

Does that mean we can use it safely in all contexts?

That’s a good point! While it's safe in small quantities for food use, too much can be harmful. We need to always be cautious when handling concentrated forms.

Let’s summarize: Ethanoic acid is a versatile compound, weakly acidic, and is significant in food preservation and the production of esters.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Ethanoic acid or acetic acid is primarily known for its role as a food preservative in the form of vinegar. It has unique properties, such as a low freezing point and weak acidity compared to mineral acids. Its reactions with bases, alcohols, and carbonates are significant, showcasing its importance in both organic chemistry and everyday applications.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Ethanoic Acid
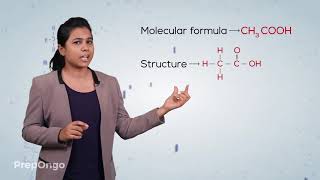
Ethanoic acid (CH₃COOH), often referred to as acetic acid, is a pivotal compound in chemistry and daily life. It's a member of the carboxylic acid family, which implies it possesses a -COOH functional group. A dilute solution (5-8%) of this acid in water is commonly used as vinegar, an effective food preservative.
Physical Properties
- Melting Point: Pure ethanoic acid has a melting point of 290 K, leading to its freezing in cold climates, where it is then referred to as glacial acetic acid.
Chemical Properties
Despite being an acid, ethanoic acid is classified as a weak acid, as it does not completely ionize in water like stronger mineral acids (e.g., hydrochloric acid). This characteristic often requires different approaches for experimentation and comparison with stronger acids.
Key Reactions:
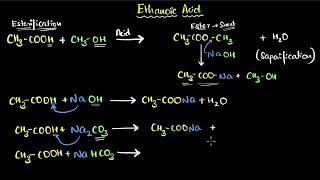
- Esterification: Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, producing an ester. This process highlights the acid's organic chemistry applications in creating sweet-smelling perfumes and flavorings.
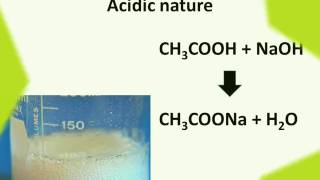
- Acid-Base Reactions: It reacts with bases such as sodium hydroxide to yield sodium acetate (a salt) and water, showcasing its acidic nature.
- Reactions with Carbonates: Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate, resulting in carbon dioxide, water, and salts, emphasizing its role in producing gas during culinary uses.
Significance
The properties and reactions of ethanoic acid exemplify the versatility of carbon compounds in organic chemistry, contributing to food preservation, synthetic processes in organic chemistry, and industrial applications.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Ethanoic Acid
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
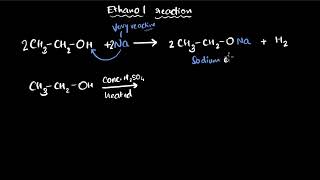
Ethanoic acid is commonly called acetic acid and belongs to a group of acids called carboxylic acids. A 5-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar and is used widely as a preservative in pickles. The melting point of pure ethanoic acid is 290 K and hence it often freezes during winter in cold climates. This gave rise to its name glacial acetic acid.
Detailed Explanation
Ethanoic acid, known as acetic acid, is part of a class of acids known as carboxylic acids, which generally contain the -COOH group. When diluted (5-8%), it is referred to as vinegar, a common ingredient in food preservation and cooking. At low temperatures, pure ethanoic acid can solidify into a crystalline form, hence its nickname 'glacial acetic acid.'
Examples & Analogies
Consider how you might store food in your refrigerator. Just as vinegar (acetic acid) prevents spoilage when added to pickles, the cold temperature of the fridge slows down bacteria growth. Similarly, glacial acetic acid solidifies at low temperatures, illustrating how temperature can affect the state and properties of substances.
Acidity Comparison
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The group of organic compounds called carboxylic acids are obviously characterised by their acidic nature. However, unlike mineral acids like HCl, which are completely ionised, carboxylic acids are weak acids.
Detailed Explanation
Carboxylic acids, including ethanoic acid, exhibit acidic behavior, meaning they can donate protons (H+ ions) when dissolved in water. However, they do not completely dissociate as strong acids like hydrochloric acid (HCl) do; instead, they partially ionize in solution, which characterizes them as weak acids. This distinction affects how they react in different chemical environments and their overall strength as acids.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a crowded party. A strong acid like HCl is like a party-goer who instantly mingles and spreads out among everyone—fully participating right away. On the other hand, a weak acid like ethanoic acid is like someone who takes their time to socialize—participating, but gradually and not with everyone at once. This illustrates how weak acids work by partially ionizing in solution.
Reactions of Ethanoic Acid
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
(i) Esterification reaction: Esters are most commonly formed by reaction of an acid and an alcohol. Ethanoic acid reacts with absolute ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst to give an ester.
CH₃COOH + CH₃CH₂OH -- (Acid) --> CH₃COOC₂H₅ + H₂O
(ii) Reaction with a base: Like mineral acids, ethanoic acid reacts with a base such as sodium hydroxide to give a salt (sodium ethanoate or commonly called sodium acetate) and water:
CH₃COOH + NaOH → CH₃COONa + H₂O
(iii) Reaction with carbonates and hydrogencarbonates: Ethanoic acid reacts with carbonates and hydrogencarbonates to give rise to a salt, carbon dioxide, and water.
Detailed Explanation
Ethanoic acid can undergo several types of reactions:
1. Esterification, where it reacts with an alcohol (like ethanol) in the presence of an acid catalyst to form an ester and water. Esters are commonly used in flavorings and fragrances due to their pleasant scents.
2. It can react with bases (like sodium hydroxide) to form a salt and water, a neutralization reaction resulting in sodium acetate.
3. Ethanoic acid reacts with carbonates (like sodium carbonate) and bicarbonates (sodium bicarbonate) to produce a salt (sodium acetate), water, and carbon dioxide gas. This reaction can produce fizzing or bubbling due to the release of carbon dioxide, evident in fizzy drinks.
Examples & Analogies
Think of baking a cake. The combination of ethanoic acid (like vinegar) with baking soda (a bicarbonate) causes bubbling, similar to fizzy drinks. This reaction can help leaven the cake, making it fluffy. Additionally, when you mix vinegar with oil in salad dressing, you're drawing upon the esterification process when flavors blend harmoniously as they interact.
Reactions with Carbonates and Bicarbonates
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Ethanoic acid reacts with carbonates and hydrogencarbonates to give rise to a salt, carbon dioxide, and water. The salt produced is commonly called sodium acetate.
2CH₃COOH + Na₂CO₃ → 2CH₃COONa + H₂O + CO₂
CH₃COOH + NaHCO₃ → CH₃COONa + H₂O + CO₂
Detailed Explanation
This section highlights the interaction of ethanoic acid with carbonates and bicarbonates. When ethanoic acid interacts with sodium carbonate (a common base), the reaction produces sodium acetate (the salt), water, and carbon dioxide, which can be observed as fizzy bubbles. Similarly, when interacting with sodium bicarbonate, similar products are formed, with the evolution of carbon dioxide gas noticeable in both reactions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a science experiment where you add vinegar to baking soda; you see a frothy explosion of bubbles. This is the same reaction highlighted here, where carbon dioxide is released, demonstrating how ethanoic acid interacts with carbonates to create effervescence.
Key Concepts
-
Carboxylic Acid: A type of organic compound characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH).
-
Weak Acid: An acid that does not completely ionize in solution.
-
Esterification: Reaction between an acid and an alcohol to form an ester and water.
-
Glacial Acetic Acid: The solid form of acetic acid at low temperatures.
Examples & Applications
Example of ethanoic acid in vinegar, used for food preservation.
Example of esterification: Ethanoic acid reacting with ethanol to form an ester.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For the acid that's weak, vinegar's what you seek; Acetic's the name, in cooking it claims fame.
Stories
Imagine a chef using glacial acetic acid in winter to preserve his last summer harvest. He creates delicious pickles from fresh vegetables, ensuring the taste lasts through the cold months.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Esterification = Ethanoic + Ethanol = Ester' to recall the reaction.
Acronyms
A.C.I.D. - Acetic, Carboxylic, Ionization, Dissociation. This helps remember the properties of acetic acid.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ethanoic Acid
Commonly known as acetic acid, a carboxylic acid used in food preservation and organic reactions.
- Esterification
A chemical reaction that forms an ester from an acid and an alcohol.
- Weak Acid
An acid that only partially ionizes in solution.
- Glacial Acetic Acid
Pure form of acetic acid which solidifies at low temperatures.
- Sodium Acetate
The salt formed when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
