Classification of Matter
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Matter
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to delve into the classification of matter. What do we think matter is?

Isn’t matter anything that has mass and takes up space?

Exactly! Matter is vital in chemistry. Now, can someone tell me the two main categories of matter?

Pure substances and mixtures!

Correct! Pure substances can either be elements or compounds. What’s the difference between these?

Elements consist of only one type of atom, while compounds are made of two or more different atoms.

Great explanation! For remember, think of the acronym 'E.C.' for Elements and Compounds. Now, where do mixtures fit in?

Mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous!

Right on! Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition, while heterogeneous mixtures do not. Who can provide examples of both?

Saltwater is a homogeneous mixture and a salad is a heterogeneous mixture.

Perfect examples! Remember, mixtures allow us to separate substances by physical means. Can anyone think of a mixture that we encounter in daily life?

Air! It's made up of different gases.

Exactly! Let’s summarize what we discussed. We have defined matter, identified two main categories, and understood the basic distinction between elements, compounds, and mixtures.
Deep Dive into Mixtures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into mixtures. What does it mean to say a mixture is homogeneous?

It means the components are evenly mixed and you can't see the different parts!

Good! And what about heterogeneous mixtures?

In heterogeneous mixtures, you can see and pick out different substances!

Correct again! Can we link these characteristics back to real-life examples?

Sure! Cream in coffee is an example of a homogeneous mixture while a fruit salad represents a heterogeneous mixture.

Perfect choices! Recall the memory aid for mixtures: 'Homogeneous is like harmony' where everything blends together, while 'Heterogeneous is a mix of parts you can see.' Great job class, let’s summarize what we learned today.
Classification Significance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do we need to classify matter in chemistry?

So we can understand how different substances will behave in reactions!

Exactly! By classifying elements and compounds, chemists can predict how substances interact. Can anyone give me an example of how this is significant?

If you know something is a compound, you can determine it has a specific ratio of elements, like water always being H₂O.

That's an excellent example! Think of the acronym 'E.C.M.' for Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures. Who can summarize what these classifications help us understand?

They help us understand properties, reactions, and how to separate substances.

Fantastic! Remember, classification is key to mastering chemistry.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
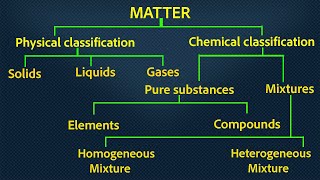
Matter is classified based on its composition and properties. Pure substances, which have fixed compositions, can be classified into elements and compounds, while mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. Understanding these classifications is essential for studying chemistry and its applications in everyday life.
Detailed
Classification of Matter
Matter is defined as anything that has mass and occupies space. It can be broadly categorized into two main types: pure substances and mixtures. The pure substances can be further split into elements and compounds, while mixtures can be either homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Types of Matter:
- Pure Substances:
- Elements: Consist of only one type of atom. Examples include oxygen (O₂), gold (Au), and iron (Fe).
- Compounds: Formed when two or more different types of atoms bond together in fixed proportions, resulting in new properties. Examples include water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
- Mixtures:
- Homogeneous Mixtures: Possess a uniform composition throughout; individual components are not distinguishable. Examples include saltwater and air.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: Consist of visibly different substances or phases. Examples include salad and granite.
Importance of Classification:
The classification of matter aids in understanding its behavior and interactions in different chemical environments. Scientists and chemists utilize these classifications to predict reactions, properties, and applications of various substances, thereby establishing a strong foundation for further studies in chemistry.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Pure Substances and Mixtures
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In Class IX (Chapter 2), you have learnt that at the macroscopic or bulk level, matter can be classified as mixture or pure substance. These can be further sub-divided as shown in Fig. 1.2. When all constituent particles of a substance are same in chemical nature, it is said to be a pure substance. A mixture contains many types of particles.
Detailed Explanation
Matter is categorized into two main types: pure substances and mixtures. A pure substance is made up of only one type of particle and has a consistent composition throughout. This could be elements like gold or compounds-like water, where the ratio of ingredients is always the same. On the other hand, a mixture consists of multiple types of particles that can be present in any ratio, meaning its composition can vary, like air or a salad where you can have different proportions of ingredients.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a glass of pure orange juice versus a fruit salad. The juice is a pure substance because it comes from oranges and has the same consistent taste, while the fruit salad is a mixture because it contains different types of fruits mixed together, and you can have different amounts of each fruit.
Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Mixtures
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A mixture may be homogeneous or heterogeneous. In a homogeneous mixture, the components completely mix with each other. This means particles of components of the mixture are uniformly distributed throughout the bulk of the mixture and its composition is uniform throughout. Sugar solution and air are the examples of homogeneous mixtures. In contrast to this, in a heterogeneous mixture, the composition is not uniform throughout and sometimes different components are visible.
Detailed Explanation
Mixtures can be further classified into homogeneous and heterogeneous types. A homogeneous mixture looks the same throughout, and you cannot distinguish the different components. Examples include solutions like sugar water. In contrast, a heterogeneous mixture consists of visibly different substances or phases, like a bowl of cereal where you can see the flakes and the milk separately, or a salad with distinct pieces of vegetables.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making a smoothie: if you blend fruits into a homogenous drink, it looks the same and you can’t see the individual fruits. In comparison, a chunky vegetable soup contains visible pieces of vegetables, making it a heterogeneous mixture.
Separation of Mixtures
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It is worthwhile to mention here that the components of a mixture can be separated by using physical methods, such as simple hand-picking, filtration, crystallisation, distillation, etc.
Detailed Explanation
One of the key characteristics of mixtures is that their components can often be separated through physical methods rather than chemical reactions. For example, if you have a mixture of sand and salt, you can dissolve the salt in water, and after filtration, the sand can be separated from the saltwater. Once the water is evaporated, salt can be recovered from the solution. Physical separation techniques do not alter the chemical identities of the substances.
Examples & Analogies
Think of making a salad with lettuce, tomatoes, and cucumber. If someone prefers just the tomatoes, they simply pick them out; no chemical change occurs on the remaining ingredients. Similarly, in the case of sand and salt, you can separate them without changing their inherent properties.
Characteristics of Pure Substances
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Pure substances have characteristics different from mixtures. Constituent particles of pure substances have fixed composition. Copper, silver, gold, water and glucose are some examples of pure substances. Glucose contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a fixed ratio and its particles are of same composition. Hence, like all other pure substances, glucose has a fixed composition.
Detailed Explanation
Pure substances distinctively have a constant and definite composition, meaning they are made up of the same type of particles consistently throughout. For example, glucose (C6H12O6) always consists of 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 6 oxygen atoms in that specific ratio, regardless of the quantity you have. This is in contrast to mixtures, which can have varying proportions of different components.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a bag of sugar and how it consistently tastes sweet regardless of how much you pour; it remains pure sugar. However, if you mix sugar with coffee, the sweetness will depend on how much sugar you add and how strong the coffee is; hence, the coffee is a mixture with variable composition.
Elements and Compounds
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Pure substances can further be classified into elements and compounds. Particles of an element consist of only one type of atoms. These particles may exist as atoms or molecules. You may be familiar with atoms and molecules from the previous classes; however, you will be studying about them in detail in Unit 2.
Detailed Explanation
Pure substances can be broken down into two categories: elements and compounds. An element is a pure substance that cannot be made simpler through chemical means and is made up of one kind of atom. Examples include gold (Au), oxygen (O2), and hydrogen (H2). Compounds, on the other hand, are pure substances formed when two or more different elements combine chemically in fixed proportions, such as water (H2O), which is made of oxygen and hydrogen atoms bonded together.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a LEGO set: each different shaped piece represents an element. If you connect these pieces together in a specific arrangement, you create a new structure, just like combining different atoms creates a compound.
Properties of Compounds vs. Elements
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Elements are present in a compound in a fixed and definite ratio and this ratio is characteristic of a particular compound. Also, the properties of a compound are different from those of its constituent elements. For example, hydrogen and oxygen are gases, whereas, the compound formed by their combination i.e., water is a liquid.
Detailed Explanation
When elements form a compound, they do so in specific ratios, which gives compounds unique characteristics that are often very different from the properties of the individual elements. This is known as emergent properties—as seen with water. Hydrogen is flammable, and oxygen supports burning, yet when these gases combine, they form water which extinguishes fire.
Examples & Analogies
It's like cooking: if you mix flour (element) and water (element), they form dough (compound) that behaves entirely different than flour or water alone—dough can be shaped and baked, whereas the separate ingredients cannot.
Key Concepts
-
Matter: Anything with mass and volume; it's the foundation of chemistry.
-
Pure Substances: Includes elements and compounds with fixed composition.
-
Mixtures: Combinations of two or more pure substances, classified as homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Examples & Applications
Water (H₂O) is a compound with a fixed ratio of hydrogen to oxygen.
Saltwater is a homogeneous mixture, while a salad represents a heterogeneous mixture.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Matter is everything you can see, Pure substances are what they should be; Elements sing, compounds create, Mixtures mix, and don't discriminate.
Stories
Once in a kingdom, there were pure lakes (elements) and a famed compound fountain that never changed. The village mixed soups (homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures), with some being clear and some chunky, reflecting life's diversity.
Memory Tools
Remember P.E.M. for the classifications: Pure substances consist of Elements and Compounds; Mixtures have Homogeneous and Heterogeneous forms.
Acronyms
To recall types of mixtures
HM for Harmonious Mixes (homogeneous) and HD for Hodgepodge Dishes (heterogeneous).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Matter
Anything that has mass and occupies space.
- Pure Substance
Matter that has a uniform and definite composition.
- Mixture
A combination of two or more pure substances where each retains its individual properties.
- Element
A pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
- Compound
A pure substance formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together.
- Homogeneous Mixture
A mixture that has a uniform composition throughout.
- Heterogeneous Mixture
A mixture in which the components are not evenly distributed and individual substances are visible.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
