Nature of Matter
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition and Importance of Matter
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start our lesson by defining what we mean by 'matter.' Can anyone tell me what matter is?

Isn't matter anything that has mass and takes up space?

Great answer! That's correct. Matter is everything around us that has mass and occupies space. Now, why do you think it's important to study matter in chemistry?

Because chemistry is all about substances and how they interact, right?

Exactly! Chemistry is fundamentally about matter—the composition, properties, and changes it undergoes in various reactions.

So, understanding matter helps us understand chemical reactions?

Exactly! Understanding matter forms the basis for exploring chemical transformations and interactions.

What other properties of matter are important?

Excellent question! Let's explore the states of matter next. Remember, matter exists primarily in three forms: solid, liquid, and gas.

To help remember, think **S-L-G** for **Solid, Liquid, Gas**.

So, to summarize, matter is defined as anything that has mass and occupies space. This understanding is crucial for our exploration of chemistry.
States of Matter
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss the three states of matter. Who can share what they remember about solids?

Solids have a definite shape and volume. The particles are tightly packed.

Spot on! And what about liquids?

Liquids have a definite volume but not a definite shape—they take the shape of their container.

Correct! And gases?

Gases have neither a definite shape nor a volume. They completely fill their container.

Exactly! To remember the properties: Solids are **rigid**, Liquids are **fluid**, and Gases are **expansive**. Can you think of examples for each?

Solid would be ice, liquid is water, and gas could be steam.

Correct! Now, remember that states of matter can change through heating or cooling, like how ice melts into water.
Classification of Matter
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, who can tell me about how we classify matter?

Matter can be classified as pure substances or mixtures?

Correct! A pure substance has a uniform and definite composition, while a mixture contains two or more pure substances. Can anyone give an example of each?

Water is a pure substance, and air is a mixture.

Excellent examples! Pure substances can be further divided into elements and compounds. Can anyone tell me the difference?

Elements are made of one type of atom, while compounds are made of two or more types of atoms chemically bonded.

Exactly right! Think of elements as building blocks, and compounds as structures built from those blocks. Good job everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section delves into the concept of matter, detailing its definition as substances that possess mass and volume. It highlights the three fundamental states of matter—solids, liquids, and gases—along with their unique characteristics and classifications into pure substances and mixtures.
Detailed
Nature of Matter
Matter is defined as anything that has mass and occupies space, comprising everything from everyday objects to the substances around us, such as air and water. This section discusses the classifications and characteristics of matter, breaking it down into three primary states—solid, liquid, and gas. Each state exhibits distinct physical properties:
- Solid: Has a definite shape and volume, with particles closely packed in an orderly fashion, resulting in minimal movement.
- Liquid: Has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container with particles that are close together but can move around.
- Gas: Neither has a definite shape nor volume, with particles far apart, allowing for rapid and free movement.
Furthermore, matter can be classified into pure substances, which consist of uniform composition (e.g., elements and compounds), and mixtures, which contain two or more different substances that retain their individual properties. This foundational understanding of matter is critical for studying chemistry as it forms the basis for exploring chemical reactions, states, and transformations.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Matter
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
You are already familiar with the term matter from your earlier classes. Anything which has mass and occupies space is called matter. Everything around us, for example, book, pen, pencil, water, air, all living beings, etc., are composed of matter. You know that they have mass and they occupy space.
Detailed Explanation
Matter is a fundamental concept in science. It refers to anything that has mass (how much 'stuff' something has) and takes up space (volume) in the universe around us. This definition encompasses a wide range of entities, including solids, liquids, gases, and even living organisms. In practical terms, you can think of matter as everything you can see, touch, or interact with, like the air you breathe, the water you drink, and the objects you use every day.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a crowded room filled with people. Each person occupying space represents matter. Likewise, a glass of water holds not just a liquid but a collection of water molecules that also occupy space and have mass.
States of Matter
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
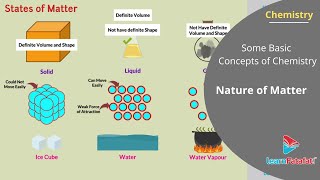
You are aware that matter can exist in three physical states viz. solid, liquid and gas. The constituent particles of matter in these three states can be represented as shown in Fig. 1.1. Particles are held very close to each other in solids in an orderly fashion and there is not much freedom of movement. In liquids, the particles are close to each other but they can move around. However, in gases, the particles are far apart as compared to those present in solid or liquid states and their movement is easy and fast.
Detailed Explanation
Matter exists primarily in three distinct forms known as states: solid, liquid, and gas. In solids, particles are tightly packed in a structured arrangement, leading to a definite shape and volume. In liquids, particles are still close together but can move past one another, resulting in a definite volume but no fixed shape (they take the shape of their container). In gases, particles are widely spaced and move freely, which means gases have neither a definite volume nor a fixed shape—they fill any container they are in. Understanding these states helps explain the physical properties of the materials around us.
Examples & Analogies
Think of ice (solid), water (liquid), and steam (gas) as three forms of H2O. Ice holds its shape in a cube, water flows in any direction, and steam expands to fill any space. This analogy illustrates how different states of matter behave according to the arrangement and movement of their particles.
Characteristics of Matter
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Because of such arrangement of particles, different states of matter exhibit the following characteristics: (i) Solids have definite volume and definite shape. (ii) Liquids have definite volume but do not have definite shape. They take the shape of the container in which they are placed. (iii) Gases have neither definite volume nor definite shape. They completely occupy the space in the container in which they are placed.
Detailed Explanation
The arrangement of particles in solids, liquids, and gases defines their distinct properties. Solids maintain their shape and volume, which means a block of wood will not change form unless physically altered. Liquids, such as juice or oil, will occupy a certain volume but will conform to the shape of the container they are in, meaning a glass of water takes a cylindrical shape inside its glass but remains a certain volume. Gases, like air or helium, will expand to fill the entire volume of their container, regardless of its shape or size, which is why the air in a balloon takes on its shape.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the difference between a sauce pan filled with soup (liquid) that stands at a certain level, versus a balloon (gas) filled with air that shapes itself to the balloon's confines. A rock (solid) will rest in any position without spilling or spilling into the surrounding area.
Interconversion of States
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These three states of matter are interconvertible by changing the conditions of temperature and pressure. On heating, a solid usually changes to a liquid, and the liquid on further heating changes to gas (or vapour). In the reverse process, a gas on cooling liquifies to the liquid and the liquid on further cooling freezes to the solid.
Detailed Explanation
By adjusting temperature and pressure, one can change the state of matter. For example, when you heat ice (solid), it melts into water (liquid). If you continue to heat the water, it eventually boils and converts to steam (gas). Conversely, when steam is cooled, it condenses back into water, and if you cool that water sufficiently, it freezes back into ice. This ability to swap states is critical in various scientific and practical processes, such as cooking or in natural weather patterns.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an ice cream cone on a hot day. The ice cream, when heated by the warmth of the environment, melts into the liquid form, risking a slip from your cone! Similarly, when conditions of temperature drop, that same liquid can freeze into a solid again, maintaining the original ice cream shape.
Classification of Matter
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In Class IX (Chapter 2), you have learnt that at the macroscopic or bulk level, matter can be classified as mixture or pure substance. These can be further sub-divided.
Detailed Explanation
Matter can be broadly categorized into two main types: mixtures and pure substances. A pure substance consists of only one type of particle and has a fixed composition, such as water (H2O) or pure gold. In contrast, a mixture contains two or more different particles that are not chemically bonded, such as air, which is a mixture of gases. Pure substances maintain consistent properties, while mixtures can vary in composition and characteristics. This classification aids in understanding the chemical behavior and properties of materials in various contexts.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making a fruit salad (mixture). The fruits retain their individual flavors, colors, and shapes. Now, consider distilled water (pure substance); it has a consistent chemical composition and completely different characteristics from any fruit, illustrating the fundamental differences between mixtures and pure substances.
Key Concepts
-
Matter: Defined as anything with mass and volume.
-
States of Matter: Includes solids, liquids, and gases with distinct properties.
-
Classification of Matter: Divided into pure substances and mixtures.
Examples & Applications
Ice is an example of a solid, which maintains a definite shape and volume.
Water represents a liquid, which has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container.
Air is a mixture, consisting of various gases including oxygen and nitrogen.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Matter is where mass can be found, filling the space that’s all around.
Stories
Imagine a party where ice cubes in cups melt into water and evaporate into fog, illustrating how states of matter change at a gathering!
Memory Tools
Remember S-L-G for Solid, Liquid, Gas.
Acronyms
P-M for Pure Matter which refers to substances with uniform composition.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Matter
Anything that has mass and occupies space.
- Solid
A state of matter with a definite shape and volume.
- Liquid
A state of matter with a definite volume but takes the shape of its container.
- Gas
A state of matter with neither definite shape nor volume.
- Pure Substance
Matter with a uniform and definite composition.
- Mixture
Matter containing two or more substances that retain their individual properties.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
