Law of Multiple Proportions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Law of Multiple Proportions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're focusing on a crucial concept in chemistry known as the Law of Multiple Proportions, proposed by John Dalton. Can anyone tell me what this law signifies?

Does it have to do with how different elements can combine in various ways?

Exactly! This law states that when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the mass ratios of one element that combines with a fixed mass of the other element will be small whole numbers. This is an essential part of understanding chemical compositions.

Could you give us an example?

Sure! Let's consider hydrogen and oxygen. They combine to form water and hydrogen peroxide. In these compounds, the mass ratio of oxygen combined with a fixed mass of hydrogen gives us a clear demonstration of this law.

So, the mass of oxygen in water versus hydrogen peroxide is a perfect example?

Exactly, those ratios reveal how elements interact based on their proportions, reinforcing the concept of atomic theory as well.

This helps in understanding how to predict compounds formed during chemical reactions!

Absolutely! This law underpins many chemical reactions and contributes to our understanding of empirical and molecular formulas. Great discussion!
Applications of the Law of Multiple Proportions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into how the Law of Multiple Proportions applies beyond theoretical concepts. Can anyone think of a practical application of this law?

Maybe in pharmaceuticals, where specific compounds are created?

Very good point! In drug formulation, understanding the precise ratios of elements in compounds is crucial for efficacy and safety.

So, if we can predict the ratios, we could tailor medication effectively, right?

Exactly! Moreover, this law also aids in developing materials and understanding their properties based on their compositions. It plays a huge role in material science.

And it helps chemists avoid unwanted reactions by knowing how elements combine!

Great observations! Understanding the ratios at which elements combine allows chemists to predict product formation accurately, ensuring that they can design safer and more efficient reactions.

So, the implications extend to multiple fields, making chemistry very interdisciplinary!

Absolutely! Chemistry connects to many realms of science and technology through principles like the Law of Multiple Proportions. Excellent contributions today!
Understanding the Ratios in Compounds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s work on calculating the mass ratios based on Dalton's examples. Who can recall the masses of hydrogen and oxygen in water and hydrogen peroxide?

Water has 2 grams of hydrogen and 16 grams of oxygen, while hydrogen peroxide has the same 2 grams of hydrogen but 32 grams of oxygen.

Correct! Now, if we compare the oxygen mass ratios from both compounds, what do we observe?

We can simplify those mass values into a whole number ratio. It is 16 grams for water and 32 grams for hydrogen peroxide!

That's right. What is the simplified ratio?

It's 1:2!

Exactly! That means for every fixed mass of hydrogen, the mass of oxygen that combines varies in a predictable and simplifiable way. This is the beauty of the Law of Multiple Proportions.

It's amazing how such simple ratios can lead to complex chemical understandings!

Very true! This understanding helps in many fields, from pharmaceuticals to environmental science. A fine discussion everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the Law of Multiple Proportions as proposed by Dalton in 1803, highlighting how elements can combine in various ways to form different compounds. It emphasizes the concept that the ratios of the masses of elements involved can be expressed in simple whole numbers, illustrated through the examples of water and hydrogen peroxide.
Detailed
Law of Multiple Proportions
The Law of Multiple Proportions is a fundamental principle in chemistry introduced by John Dalton in 1803. It states that when two elements form more than one compound, the ratios of the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are always in the ratio of small whole numbers.
For instance, consider the elements hydrogen and oxygen, which combine to form two different compounds: water (H₂O) and hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂). When we analyze their compositions, we find that:
- In water (H₂O), 2 grams of hydrogen combine with 16 grams of oxygen.
- In hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), 2 grams of hydrogen combine with 32 grams of oxygen.
The mass ratios of oxygen in these compounds can be compared:
- Water: 16 g O
- Hydrogen Peroxide: 32 g O
This gives us a ratio of 16:32, which simplifies to 1:2, illustrating the essence of the law. This principle is crucial for understanding chemical reactions and compound formations, contributing to the basis for Dalton’s atomic theory.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Law of Multiple Proportions
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This law was proposed by Dalton in 1803. According to this law, if two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element, are in the ratio of small whole numbers.
Detailed Explanation
The Law of Multiple Proportions explains that when two elements can form different compounds, the different masses of one element that combine with a set mass of another can be expressed as whole number ratios. For example, if you can form different compounds from hydrogen and oxygen, the mass of oxygen that combines with the same mass of hydrogen can be expressed in simple ratios.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it this way: imagine you are making different recipes for fruit salads and you have bananas and apples. If you use a fixed weight of apples (let’s say 100 grams), you might use 50 grams of bananas for one type of salad, but for another type, you use 100 grams of bananas. The ratio of bananas in both salads compared to apples is 1:2, showing how different combinations can create distinct outcomes while keeping the same amount of the other ingredient constant.
Example of Water and Hydrogen Peroxide
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For example, hydrogen combines with oxygen to form two compounds, namely, water and hydrogen peroxide.
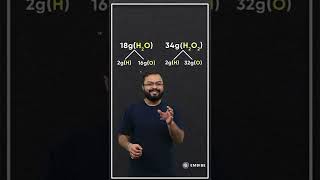
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water
2g 16g 18g
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Hydrogen Peroxide
2g 32g 34g
Here, the masses of oxygen (i.e., 16 g and 32 g), which combine with a fixed mass of hydrogen (2g) bear a simple ratio, i.e., 16:32 or 1:2.
Detailed Explanation
In this example, hydrogen and oxygen combine to create two different compounds: water (H2O) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). In both instances, we look at how much oxygen combines with a fixed amount of hydrogen (2 grams). For water, 16 grams of oxygen is used, whereas for hydrogen peroxide, 32 grams of oxygen is used. When we take the masses of oxygen used (16 g and 32 g) and compare them for the same mass of hydrogen (2 g), we find they are in a 1:2 ratio, which reinforces the Law of Multiple Proportions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are building structures with blocks. If you decide to use 2 red blocks as your constant base, you have the option to stack either 1 green block to create one type of structure or 2 green blocks to create a different structure. The ratio of blocks used when you change your structure still follows a simple whole number ratio, just like the elements in the compounds.
Key Concepts
-
Law of Multiple Proportions: Describes how elements combine in fixed ratios to form different compounds.
-
Mass Ratios: Essential for predicting and understanding chemical compounds' compositions.
Examples & Applications
Example of the Law of Multiple Proportions: Water (H2O) versus Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) showcases ratios of oxygen in simple whole numbers.
In both compounds, hydrogen remains constant at 2 grams, but oxygen varies greatly.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When elements do combine, the ratios align, in small whole numbers they always shine.
Stories
In a chemist's lab, two elements find themselves combining various ways to create compounds, like the friendship of hydrogen and oxygen that leads to water or hydrogen peroxide. The mass ratios dance in harmony, always in small whole numbers.
Memory Tools
Remember the HBO - Hydrogen, Bonding, Oxygen forming compounds and the ratios help in forming so many compounds.
Acronyms
MORAL - Mass of one Ratio of another Law which helps us remember the Law of Multiple Proportions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Law of Multiple Proportions
A principle that states when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other are in the ratio of small whole numbers.
- Compound
A substance formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together.
- Mass Ratio
The ratio of the mass of one substance to the mass of another substance within a compound.
- Hydrogen Peroxide
A chemical compound (H2O2) consisting of hydrogen and oxygen used primarily as a bleaching or antiseptic agent.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
