Percentage Composition
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Percentage Composition
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will learn about percentage composition. Percentage composition helps us understand how much of each element is in a compound. Can anyone tell me what they think percentage means?

Is it about how much of something is part of the whole?

Exactly! To calculate the percentage composition, we use this formula: Mass % of an element equals the mass of that element in the compound divided by the molar mass of the compound, all multiplied by 100. Let's try it with water. What is the molar mass of water, H2O?

It's about 18 grams per mole!

Right! Now, hydrogen contributes 2 grams, and oxygen contributes 16 grams to that total. Therefore, the percentage of hydrogen in water is...

Would it be (2/18) × 100, which is about 11.1%?

Perfect! That’s how we calculate it. And for oxygen?

Is it (16/18) × 100? That gives us about 88.9%!

Well done! So remember the key formula for calculating percentage composition. It's essential for understanding the make-up of compounds.
Examples of Percentage Composition
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s take another example. What about glucose, C6H12O6? Who can calculate its molar mass first?

I can! For glucose, it's 6(12.01) + 12(1.008) + 6(16.00). That gives us 180.16 grams per mole.

Great work! Now, how do we find the percentages of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen?

For carbon, it's (72.06 / 180.16) × 100, which is about 40%.

Correct! And what about hydrogen and oxygen?

For hydrogen, it's (12.096 / 180.16) × 100, around 6.7% and for oxygen, (96.00 / 180.16) × 100, which gives roughly 53.3%.

Fantastic calculations everyone! Now we can use these percentages to assess how pure glucose samples are.
Applications of Percentage Composition
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Has anyone heard how percentage composition is useful in the real world?

I think it's important for checking the purity of substances in medicine.

That's one example! In pharmaceuticals, knowing the percentage composition ensures proper dosages. Can someone else give an example?

In cooking, knowing the percentages can help with recipes.

Exactly! In recipes, consistency in composition can lead to better results. Finally, let’s just sum up what we’ve learned today about percentage composition.

It helps us understand elements in compounds and their roles in different fields.

Well said! Keep working with these calculations, and you'll find they come in handy all throughout chemistry.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, students learn to calculate the percentage composition of elements in a compound, aiming to derive information about the constituents in a compound. The significance of percentage composition in understanding chemical formulas and the purity of samples is also discussed.
Detailed
Percentage Composition
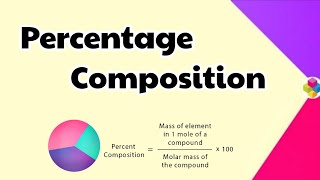
Percentage composition refers to the calculation of the mass percentage of each element present in a compound. It provides crucial information about the makeup of the compound, aiding in the determination of its chemical formula and purity. To find the percentage composition of an element in a compound, the following formula is used:
Formula for Percentage Composition
Mass % of an element = (mass of the element in the compound / molar mass of the compound) × 100%
This section covers:
- Examples demonstrating the calculation of percentage composition for water, glucose, and sodium sulfate, alongside the processes involved in each calculation.
- Importance of percentage composition in chemical analysis, such as verifying whether a sample meets its expected elemental makeup in purity tests.
- How to utilize percentage composition to deduce empirical and molecular formulas from experimental data.
Understanding percentage composition is fundamental in fields such as chemistry, environmental science, and nutrition, where the composition of compounds influences functionality and effectiveness.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Percentage Composition
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
So far, we were dealing with the number of entities present in a given sample. But many a time, information regarding the percentage of a particular element present in a compound is required.
Detailed Explanation
In chemistry, understanding how much of each element is present in a compound can tell us a lot about that compound. This concept is referred to as 'percentage composition.' It helps us determine the makeup of substances and assess their purity, which can be crucial in various applications, whether in laboratories or industries.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a cake recipe. If you were to bake a cake made of flour, sugar, and eggs, knowing the percentage of flour, sugar, and eggs will help you understand how the cake will taste and its texture. Similarly, knowing the percentages of elements in a compound helps chemists predict its behavior and applications.
Calculating Percentage Composition - Method
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Mass % of an element = (mass of that element in the compound / molar mass of the compound) × 100.
Detailed Explanation
To find the percentage of an element in a compound, you use the formula:
1. First, determine the mass of the element in the compound.
2. Then, divide this mass by the total molar mass of the compound.
3. Finally, multiply by 100 to convert the value into a percentage. This gives us the mass percentage of that element within the compound.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a bottle of soda that contains water, sugar, and carbon dioxide. If you want to find out how sweet your soda is, you could calculate the percentage of sugar it contains relative to the total mass of the soda. The same concept applies here when we determine the percentage of an element in a compound.
Example: Water (H2O) Composition
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For known compounds also, such information provides a check whether the given sample contains the same percentage of elements as present in a pure sample. In other words, one can check the purity of a given sample by analysing this data.
Detailed Explanation
Using water as an example, its molar mass is about 18.02 grams per mole. The mass percentage of hydrogen and oxygen can be calculated as follows:
- For hydrogen:
Mass % of hydrogen = (2.016 g / 18.02 g) × 100 = 11.18%.
- For oxygen:
Mass % of oxygen = (16.00 g / 18.02 g) × 100 = 88.79%. This shows that water is primarily composed of oxygen, with hydrogen making up a smaller percentage.
Examples & Analogies
If you have a bottle of pure water and another bottle that contains some impurities, by calculating the percentage composition of water (the percentage of H2O), you can assess how pure your sample is compared to what is expected. This is similar to tasting a dish that should have a certain flavor; if it tastes off, you can check the ingredients and their proportions.
Example: Ethanol Composition
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Let us take one more example. What is the percentage of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in ethanol? Molecular formula of ethanol is: C2H5OH. Molar mass of ethanol is: (2×12.01 + 6×1.008 + 16.00) g = 46.068 g.
Detailed Explanation
To find the percentage composition in ethanol, you start by calculating the molar mass, which is 46.068 g. Then, determine the mass percentages of each element:
- Mass of carbon in ethanol = (2 × 12.01 g = 24.02 g),
- Mass of hydrogen = (6 × 1.008 g = 6.048 g),
- Mass of oxygen = 16.00 g.
The mass percentages would then be calculated as follows:
- % of Carbon = (24.02 g / 46.068 g) × 100 = 52.14%
- % of Hydrogen = (6.048 g / 46.068 g) × 100 = 13.13%
- % of Oxygen = (16.00 g / 46.068 g) × 100 = 34.73%.
Examples & Analogies
When you analyze your favorite drink like a fruit juice or soda, knowing the percentage of sugar, water, and other ingredients helps you understand the taste. For ethanol, knowing the percentages of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen can reveal insights into its properties and applications, similar to how you might want to know how much sugar is in your beverage.
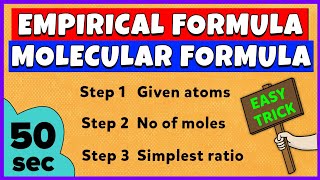
Empirical vs. Molecular Formula
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole number ratio of various atoms present in a compound, whereas the molecular formula shows the exact number of different types of atoms present in a molecule of a compound.
Detailed Explanation
The empirical formula simplifies a compound to its most basic ratio. For instance, for glucose (C6H12O6), the empirical formula is CH2O, which shows the simplest ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. In contrast, the molecular formula provides the exact count, which in this case reflects the actual number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in each molecule of glucose.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a recipe. The molecular formula is like a detailed recipe that tells you exactly how many of each ingredient you need, while the empirical formula is like saying you only need 'two parts of sugar for every one part of flour.' Both serve different purposes, much like how understanding both formulas helps in chemical analysis.
Key Concepts
-
Percentage Composition: Refers to the mass percent of each element in a compound, crucial for understanding chemical content.
-
Molar Mass: The total mass of a compound calculated from the atomic masses of its constituent elements.
-
Empirical vs. Molecular Formula: Empirical shows the simplest ratio, while Molecular shows the actual number of atoms.
Examples & Applications
Calculating the percentage of hydrogen in water (H2O) as approximately 11.1%.
Determining the percentage composition of glucose (C6H12O6) where carbon is about 40%, hydrogen is 6.7%, and oxygen is 53.3%.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To find the mass percent, take the part, divide by the whole, and then set it apart.
Stories
Imagine you’re baking. You have 100 grams of cake. 30 grams of chocolate means 30% chocolate in your cake.
Memory Tools
To remember mass percentages, think: 'Count the part, divide by the total, multiply by 100'.
Acronyms
P.O.E. - Part Over Entirety to get the percentage composition.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Percentage Composition
The mass percentage of each element in a compound calculated based on the total molar mass.
- Molar Mass
The mass of one mole of a substance, typically expressed in grams per mole.
- Empirical Formula
The simplest whole number ratio of elements in a compound.
- Molecular Formula
A formula that shows the exact number of atoms of each element in a molecule.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
