Properties of Matter and Their Measurement
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Physical and Chemical Properties
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to dive into the properties of matter. Can anyone tell me what we mean by physical properties?

Are those the characteristics we can see or measure without changing the substance?

Exactly! Physical properties include attributes like color, melting point, and density. Now, who can give me an example of a chemical property?

How about reactivity with acids? That changes the substance.

Great example! Chemical properties require a change in composition. Let’s remember this as - 'Chemical changes create new situations.'
Measurement in Chemistry
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about properties, let's discuss measurement. Why is it important in chemistry?

So we can quantify our observations and experiments?

Exactly! Measurement allows us to communicate results clearly. Can someone tell me what the SI system includes?

Isn't it the standardized system used for scientific measurements?

Yes! The SI system includes units like meter for length, kilogram for mass, and mole for the amount of substance. Remember: 'SI is the path to precision!'
Mass, Weight, and Density
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s clarify mass and weight. Who can summarize the difference?

Mass is the amount of matter, and it remains constant, but weight changes with gravity.

Right! Mass is measured in kilograms while weight is a force measured in newtons. Now, what about density?

Density is mass per unit volume, right? Like how tightly the particles are packed.

Exactly! Dense materials pack particles tightly, while less dense materials have more space. Let's create a rhyme: 'Density's the essence, packed tight, gives matter its might!'
Significant Figures and Uncertainty
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we need to talk about uncertainty in measurements. Can anyone explain what significant figures are?

They’re the digits in a number that are known with certainty plus one estimated digit?

Correct! In 0.0045, there are two significant figures. Always consider the precision of tools used for measuring. Remember, 'Count the known, but estimate the uncertain!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section explores how properties of matter are categorized as physical or chemical, emphasizing how these properties can be measured without altering the material's identity. It introduces the International System of Units (SI) and the importance of measurement in chemical experimentation.
Detailed
Properties of Matter and Their Measurement
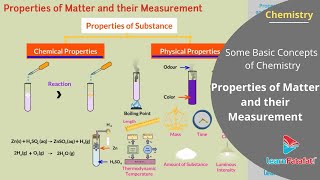
Understanding matter is fundamental to chemistry. Every substance has specific properties, which can be classified into two categories:
- Physical properties - These are observable without changing the substance's identity, including color, boiling point, and melting point.
- Chemical properties - These involve the composition and behavior of a substance during a chemical reaction, such as acidity or reactivity.
Measurement is crucial in chemistry, as it provides quantitative data necessary for experimental analysis. The SI (International System of Units) establishes a standardized system for measurement, offering seven base units including the meter (length), kilogram (mass), second (time), and mole (amount of substance).
Additionally, the concepts of mass vs. weight, volume, density, and uncertainty in measurement are discussed. Understanding how to accurately measure and describe these properties is essential for scientists to conduct precise experiments and validate outcomes.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Every substance has unique or characteristic properties. These properties can be classified into two categories — physical properties, such as colour, odour, melting point, boiling point, density, etc., and chemical properties, like composition, combustibility, reactivity with acids and bases, etc.
Physical properties can be measured or observed without changing the identity or the composition of the substance. The measurement or observation of chemical properties requires a chemical change to occur. Measurement of physical properties does not require occurrence of a chemical change.
Detailed Explanation
Properties of matter are vital in identifying and understanding different substances.
- Physical properties are those attributes that can be assessed without altering the substance's chemical identity. For example, if you measure the melting point of ice, it still remains water even after melting.
- Chemical properties, however, require a substance to undergo a chemical reaction to be observed. For instance, if you burn wood, the smoke and ash that result demonstrate its combustibility, which is a chemical property.
Understanding these properties helps chemists predict how substances will behave in various situations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of physical properties like the characteristics of a soda drink. The fizz (carbonation) and the sweetness can be assessed without changing the drink itself. On the other hand, if you mix soda with baking soda (a chemical reaction), it fizzes and changes its composition, showing how reactivity (a chemical property) can alter the substance.
Measurement of Physical Properties
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Quantitative measurement of properties is required for scientific investigation. Many properties of matter, such as length, area, volume, etc., are quantitative in nature. Any quantitative observation or measurement is represented by a number followed by units in which it is measured. For example, length of a room can be represented as 6 m; here, 6 is the number and m denotes metre, the unit in which the length is measured.
Detailed Explanation
Understanding how to measure physical properties is crucial in chemistry. For example, measurements often use standard units for clarity:
- Quantitative measurements involve both a number and a unit (like meters or grams) to provide context.
- Using a consistent measurement system ensures that scientists can accurately replicate experiments and compare results.
If you say a table is 2 meters long, both the number and the unit give clear information on the length.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to measure ingredients for a cake. If you say 'add flour until it feels right,' it's subjective. Instead, you measure it accurately in grams or cups, which gives consistent results every time you bake.
The International System of Units (SI)
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The International System of Units (in French Le Systeme International d’Unités — abbreviated as SI) was established by the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM from Conference Generale des Poids et Measures). The CGPM is an inter-governmental treaty organisation created by a diplomatic treaty known as the Metre Convention, which was signed in Paris in 1875. The SI system has seven base units.
Detailed Explanation
The SI system provides a common framework for measurement to ensure consistency worldwide. Each base unit corresponds to fundamental physical quantities, including length (meter), mass (kilogram), time (second), and others. This system evolved from various historical measurement practices to standardize scientific communication globally. By having a universal system, researchers can share their findings without confusion over measurement interpretations.
Examples & Analogies
Consider traveling to another country; if you measure distances in miles and everyone else uses kilometers, you'll be confused. Similarly, in science, having a common measurement system prevents misunderstandings and allows for clear communication regardless of where the research is conducted.
Mass and Weight
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The mass of a substance is the amount of matter present in it, while weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object. The mass of a substance is constant, whereas, its weight may vary from one place to another due to change in gravity.
Detailed Explanation
Mass and weight are often confused but are fundamentally different. The mass remains the same regardless of where you are, measuring how much matter something contains. Weight, however, depends on gravitational pull and can change – for instance, your weight on Earth is greater than on the Moon due to differing gravitational forces.
Knowing this distinction is essential in scientific contexts, especially when calculating forces or understanding how objects interact.
Examples & Analogies
When you go to the doctor, they measure your weight on a scale, but if you could take that scale to the Moon, it would show much less weight due to weaker gravity. However, your mass would still be the same, no matter where in the universe you weigh yourself.
Volume Measurement
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Volume is the amount of space occupied by a substance. It has the units of (length)³. For instance, in SI system, volume has units of m³. However, in chemistry laboratories, smaller volumes are often denoted in cm³ or dm³ units. A common unit, litre (L) which is not an SI unit, is used for measurement of volume of liquids.
Detailed Explanation
Volume is a fundamental property that defines how much space a substance occupies. The SI unit for volume is cubic meters (m³), but in labs, more practical units like liters (L), which is equivalent to cubic decimeters (dm³), and cubic centimeters (cm³) are often used for liquids. This flexibility allows chemists to work accurately with various substances without confusion.
Understanding volume is important for mixing chemicals, preparing solutions, and conducting experiments.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how you pour a drink. When you fill a cup, you're measuring its volume in milliliters (mL) or liters (L). In cooking, measuring cups often use liters or cups to describe volume, ensuring that recipes are followed accurately for perfect results.
Density
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The two properties — mass and volume discussed above are related as follows:
Density of a substance is its amount of mass per unit volume. So, SI units of density can be obtained as follows:
Density = Mass/Volume
Thus, the SI unit of density is kg/m³, but in laboratory settings, it's often expressed in g/cm³.
Detailed Explanation
Density is a crucial property in understanding materials. It tells us how tightly packed the matter in a substance is. The formula for density, Density = Mass/Volume, helps us understand how to distinguish between materials:
- A high density means the material is packed tightly (like lead), while a low density indicates a more spread out structure (like cork). Therefore, with the density, we can classify substances, identify materials, and predict interactions.
Examples & Analogies
Think about floating and sinking - an object like a stone sinks in water because it has a higher density compared to water. Conversely, a piece of wood floats because its density is lower than that of water. This fundamental principle of density explains not just buoyancy, but also why different materials behave the way they do when mixed.
Temperature Measurements
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
There are three common scales to measure temperature — °C (degree celsius), °F (degree Fahrenheit) and K (kelvin). The kelvin scale is the SI unit. It is interesting to note that temperature below 0 °C (i.e., negative values) are possible in Celsius scale but in Kelvin scale, negative temperature is not possible.
Detailed Explanation
Temperature is a critical measurement in chemistry that affects reactions, states of matter, and various physical properties. The three scales are:
- Celsius (°C): Used widely in everyday life. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C.
- Fahrenheit (°F): Primarily used in the U.S., where water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F.
- Kelvin (K): The SI unit where 0 K is absolute zero, the theoretical temperature where molecular motion stops.
Familiarizing oneself with temperature scales is essential in scientific work where accuracy determines the outcome.
Examples & Analogies
When cooking, you might read recipes that specify temperatures in Fahrenheit or Celsius, like baking cookies at 350°F or boiling water at 100°C. However, scientists often use Kelvin for precise calculations, especially in physics, where understanding the behavior of gases at varying temperatures is crucial.
Key Concepts
-
Physical Properties: Observable characteristics of substances.
-
Chemical Properties: Attributes that define a substance's behavior in chemical reactions.
-
SI Units: Standardized units for measurement in science.
-
Density: Mass per unit volume of a substance reflecting particle proximity.
-
Significant Figures: Clarity in measurement and precision.
Examples & Applications
The melting point of ice is a physical property because it can be measured without changing the substance's nature.
The ability of iron to rust is a chemical property since it involves a reaction with oxygen.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When measuring things, don't miss, Density's mass over volume's bliss!
Acronyms
P.C.S.D. - Properties, Chemical, SI, Density, Significant figures.
Stories
Imagine a scientist measuring the color of a rose (physical property) and later testing it to see if it reacts with vinegar (chemical property).
Memory Tools
To remember SI units, think: M.K.S. (Meter, Kilogram, Second).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Physical Properties
Characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the substance's identity.
- Chemical Properties
Attributes that describe a substance's potential to undergo chemical change.
- International System of Units (SI)
A standardized system used for scientific measurements, comprising seven base units like meter and kilogram.
- Density
Mass of a substance divided by its volume, indicating how closely the particles are packed.
- Significant Figures
The digits in a number that are known with certainty plus one estimated digit.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
