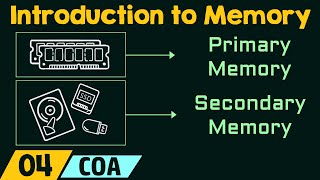
Classification of Memory
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Primary Memory
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about primary memory. Can anyone tell me what primary memory includes?

Is it just RAM?

Great start! Primary memory includes RAM and ROM. RAM is fast and can be accessed directly by the CPU, while ROM is used to store firmware. Can anyone remind me why the speed of RAM is crucial?

Because it needs to be fast for applications to run smoothly!

Exactly! Remember the mnemonic 'RAM Runs All Memory!' Let's summarize: primary memory is essential for quick data access.
Secondary Memory
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move on to secondary memory. Who can tell me what makes it different from primary memory?

It's larger but slower, right?

Correct! Secondary memory devices like HDDs and SSDs provide larger storage but with slower access times. Reflecting on our earlier lesson, how does that impact system performance?

The system might be slower accessing data compared to primary memory.

Exactly! Remember, 'Secondary Stores Safety' - it's about keeping data safe, even if access is slower. Always consider the balance of speed and capacity when designing systems.
Volatile vs Non-Volatile Memory
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss volatile and non-volatile memory. Who can explain what volatile memory means?

Volatile memory loses its data when power is lost, like RAM.

Correct! And what about non-volatile memory?

It keeps the data even when the power is turned off, like ROM or Flash.

Exactly! Here's a mnemonic to remember that: 'Non-volatile Never Needs Power!' This is crucial when determining what type of memory to use for storing important data.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section covers the different types of classification of memory, including primary and secondary memory, along with volatile and non-volatile categories. Each type serves distinct purposes, with primary memory providing fast access and secondary memory offering larger storage capacity.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Memory classification is essential to understanding how digital systems function efficiently. The classification scheme helps in the categorization of memory types based on several criteria, including speed, size, cost, and volatility.
Types of Memory
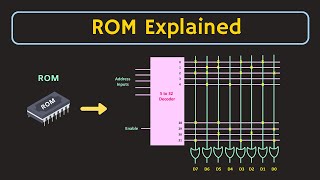
- Primary Memory: Fast and directly accessible, primarily consisting of RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read-Only Memory).
- Examples: RAM, ROM
- Secondary Memory: Larger storage capacity but slower access speeds than primary memory, including storage devices such as HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and SSD (Solid State Drive).
- Examples: HDD, SSD
- Volatile Memory: Loses its data when the power is turned off. It is primarily used for temporary data storage during execution.
- Examples: RAM, Cache
- Non-Volatile Memory: Retains data even when powered off, making it suitable for permanent data storage.
- Examples: ROM, Flash
Understanding these classifications helps in selecting appropriate memory devices for various applications, ultimately impacting the performance and efficiency of digital systems.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Volatile vs Non-Volatile Memory
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Volatile | Loses data when power is off | RAM, cache
Non-Volatile | Retains data without power | ROM, Flash
Detailed Explanation
Memory can also be categorized based on its behavior when power is lost:
- Volatile Memory: This type of memory loses its content when the power is turned off. Examples include:
- RAM: Used for temporary data storage when a device is on. If the device shuts down, all data in RAM disappears.
- Cache: A smaller, faster type of volatile memory that provides high-speed data access to the processor.
- Non-Volatile Memory: This memory retains its data even when power is off. Examples include:
- ROM: Used to store firmware and essential instructions that are needed for a device to boot up.
- Flash Memory: Common in USB drives and SSDs, it keeps data safe without needing power.
Examples & Analogies
Consider volatile memory like a whiteboard where you can quickly write and erase notes while studying. Once you wipe it clean (turn off the power), all info is lost. Non-volatile memory, however, is like a notebook that keeps everything you’ve written down, even when you close it and put it away.
Key Concepts
-
Primary Memory: Fast access memory, includes RAM and ROM.
-
Secondary Memory: Larger but slower memory storage options.
-
Volatile Memory: Loses data when powered off, used for temporary tasks.
-
Non-Volatile Memory: Retains data without power, used for permanent storage.
Examples & Applications
RAM is often used as primary memory for running applications, while SSDs serve as secondary storage for data files.
An example of volatile memory is cache memory, which is lost on power failure.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
'Volatile vanishes when power's gone, Non-volatile stays all day long.'
Stories
Imagine a computer as a busy office. Primary memory is like the desk where workers find files quickly, while secondary memory is a storage room where they keep those files for future use.
Memory Tools
For volatile memory, think 'Vanishes with Voltage!'
Acronyms
PRIM means Primary RAM Is Memory, highlighting the key components of primary memory.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Primary Memory
Fast, directly accessible memory used by the CPU, including RAM and ROM.
- Secondary Memory
Larger memory that is not directly accessible by the CPU, such as HDDs and SSDs.
- Volatile Memory
Memory that loses its data when power is turned off, typically used for temporary storage.
- NonVolatile Memory
Memory that retains its data without power, used for permanent storage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
