Memory Parameters
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Memory Capacity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's begin with memory capacity. It is vital for determining how much data a memory device can hold. Can anyone tell me how memory capacity is calculated?

Is it the number of words multiplied by the word size?

Exactly! So, if a memory device has 1024 words and each word is 8 bits, what would be its total capacity?

That would be 1024 times 8, which is 8192 bits, or 1024 bytes.

Correct! Remember that the unit of measurement for memory capacity is crucial. Let’s continue with access time.
Access Time Explained
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Access time is essential for performance. It defines how quickly memory can respond to queries. What factors do you think influence access time?

Maybe the type of memory, like RAM versus ROM?

Absolutely! RAM typically has faster access times compared to ROM. Now, can anyone give me an example of an application where access time is crucial?

In gaming, fast access times are critical for loading textures and assets quickly.

Great example! Access time plays a critical role in performance-intensive applications.
Word Size and Address Bus Width
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss word size. It determines how much data can be processed in a single operation. What happens if a system has a larger word size?

It can handle more data at once, right?

Exactly! Now, what about address bus width? How does it affect memory?

It determines how many memory locations can be accessed. So, a larger width means we can address more locations?

Spot on! A 16-bit address bus can access 65,536 locations, while a 32-bit can access over 4 billion. That’s significant!
Cycle Time Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Cycle time is the interval between successive accesses. Why do you think this is crucial for memory devices?

If the cycle time is long, it could slow down the entire system, especially if multiple memory accesses are required.

Precisely! Faster cycle times can enhance overall system throughput. Make sure to remember these concepts!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Memory parameters such as capacity, access time, cycle time, word size, and address bus width all play crucial roles in the functioning and efficiency of memory devices in digital systems. Understanding these parameters helps in optimizing memory usage and system design.
Detailed
Memory Parameters Overview
In digital systems, memory is characterized by several critical parameters that determine its efficiency and functionality. This section dives into the main memory parameters:
- Capacity: Refers to the total storage, which is calculated as the number of words multiplied by the word size (in bits). This defines how much data can be stored.
- Access Time: The time it takes to read from or write to memory. It reflects how quickly the memory can respond to read or write requests.
- Cycle Time: This is the interval between successive accesses to the memory. A shorter cycle time indicates faster memory usage overall.
- Word Size: The number of bits stored in each memory location. This can vary across different memory types and affects the overall processing capabilities.
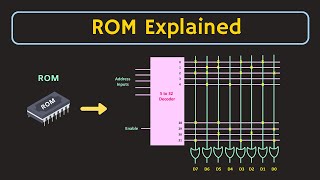
- Address Bus Width: Determines the maximum number of unique memory locations that can be accessed, calculated as 2^n for an n-bit address bus. This directly impacts the capacity of the memory system.
Understanding these parameters is essential in selecting and designing memory for optimized performance in digital systems.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Capacity
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Total storage = number of words × word size
Detailed Explanation
Capacity refers to how much data a memory device can hold. It is calculated by multiplying the number of words the memory can store by the size of each word in bits. For example, if a memory chip can store 1,024 words and each word is 16 bits, then the capacity is 1,024 multiplied by 16, giving a total capacity of 16,384 bits, or 2,048 bytes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of capacity like a bookshelf. If each shelf can hold a certain number of books (words) and each book has a specific number of pages (word size), the total number of pages on the bookshelf would represent the capacity of that storage space.
Access Time
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Time to read/write a word
Detailed Explanation
Access time refers to the duration it takes to retrieve (read) or store (write) a single word of data in memory. This time can vary significantly between different types of memories, with SRAM typically having faster access times compared to DRAM, which is slower due to the need for refresh cycles.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a library where some sections are highly organized and allow you to quickly find a book (like SRAM), while others are a bit disorganized and require you to search through shelves for longer (like DRAM). The time taken to locate a book in these two libraries illustrates the concept of access time.
Cycle Time
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Time between successive accesses
Detailed Explanation
Cycle time is the interval required between two access operations. It indicates how quickly a memory can respond to successive read or write requests. For instance, if it takes 10 nanoseconds to perform a read operation, the cycle time might also be around 10 nanoseconds, and this time defines how closely together the memory can handle multiple operations.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a vending machine that can only accept one coin at a time. If it takes a certain amount of time to process one coin before accepting another, that waiting time corresponds to the cycle time for the memory. You can't put in another coin until the first transaction is completed.
Word Size
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bits in one memory location
Detailed Explanation
Word size refers to the number of bits stored in a single addressable memory location. Common word sizes include 8 bits, 16 bits, 32 bits, and 64 bits. The larger the word size, the more data can be processed at once, which can enhance performance in certain applications (like processing multimedia).
Examples & Analogies
Think of word size as the size of a block of ice cream in an ice cream shop. A larger scoop (larger word size) means you get more ice cream (data) in one serving, which can be particularly enjoyable when having a big dessert (processing large amounts of data simultaneously).
Address Bus Width
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Determines how many locations can be accessed (2^n)
Detailed Explanation
The address bus width indicates the number of unique addresses the memory can have, and is determined by the number of lines in the address bus. For an n-bit address bus, the number of accessible locations is 2 raised to the power of n. For instance, a 16-bit address bus can access 2^16 locations, which equals 65,536 different addressable memory locations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a parking lot with each parking spot assigned a unique number (address). If there are 16 spots, you can have 2^4 = 16 different numbers. The width of the address bus is like the total number of spots available: more spots (a wider bus width) means more cars (data) can find their own space (address).
Key Concepts
-
Capacity: The total storage of memory devices, crucial for data handling.
-
Access Time: The speed at which data can be read from or written to memory.
-
Cycle Time: The delay between successive memory accesses; crucial for performance.
-
Word Size: Determines how much data can be processed at once.
-
Address Bus Width: Influences how many unique memory locations can be accessed.
Examples & Applications
A computer with 4 GB RAM (capacity) where each word is 32 bits.
A system with a 32-bit address bus can access up to 4 GB of memory, as 2^32 = 4,294,967,296.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Memory's capacity is quite vast; read and write with speed is a blast.
Stories
Imagine a library (memory) with shelves (capacity) holding books. The time it takes to find or return a book is like access time, and the more shelves (bus width) you have, the more books you can hold.
Memory Tools
CABC War: Capacity - Access - Bus Width - Cycle Time.
Acronyms
MAC
Memory Access Capacity.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Capacity
Total storage size determined by the number of words multiplied by the word size.
- Access Time
Time taken to read or write a word from memory.
- Cycle Time
Interval between successive memory accesses.
- Word Size
Number of bits in one memory location.
- Address Bus Width
Number of unique memory locations that can be accessed, calculated as 2^n.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
