Types of ROM
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to ROM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to dive into Read-Only Memory, or ROM. Can anyone tell me why ROM is critical in digital systems?

Is it because it retains data even when the power is off?

Exactly! ROM is non-volatile, meaning it preserves data without power. This makes it crucial for storing firmware. Now, can anyone list the types of ROM?

I've heard of Mask ROM and EPROM.

Great! Each type of ROM has unique characteristics. Remember the acronym MPEEF for Mask, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, and Flash. This will help you recall them!

What’s the difference between EPROM and EEPROM?

Excellent question! EPROM can be erased using UV light, while EEPROM can be erased electrically. This means EEPROM allows for easier reprogramming. Let’s explore this further.

To summarize, ROM is essential for permanent data storage, and each type serves specific needs in technology.
Types of ROM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve into the specific types of ROM: starting with Mask ROM. Can someone explain its characteristics?

Mask ROM is fixed during production, so it can't be changed afterward, right?

Exactly! Now, what about PROM?

PROM can only be written once after it’s made, can it be reused?

Correct! It's a one-time programmable memory. Now, what do you think are the main uses of EPROM?

Since it can be erased, it's probably used for things that need updates, like firmware?

Exactly right! EPROM is used when we need to periodically update the firmware. Let’s not forget about EEPROM and Flash memory, which allows for easier data rewriting. To wrap up, can anyone summarize the importance of these types?

They provide non-volatile storage to keep essential data secure and updatable.

Well done!
Applications of ROM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s talk about where we see these types of ROM in real life. Can anyone provide examples of where ROM might be used?

Flash memory is used in USB drives, right?

Exactly! And what about firmware updates?

That would be EPROM since it can be erased and rewritten.

Perfect! And Mask ROM is typically found in devices like microcontrollers that need predetermined instructions. Why is it beneficial in those devices?

Because it provides a permanent solution without power requirements!

Exactly! Let’s conclude this session. The applicability of ROM types across technology is vast and vital.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Different types of ROM, including Mask ROM, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, and Flash memory, are described, emphasizing their characteristics and applications across various technologies.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Read-Only Memory (ROM) is a crucial type of non-volatile memory used in digital systems where data needs to be stored in a permanent format. ROM retains information without the need for power, making it essential for firmware and system data storage. The section outlines several types of ROM:
- Mask ROM: Programmed during manufacturing, providing fixed data that cannot be altered later.
- PROM: Programmable ROM that can be written only once after manufacturing.
- EPROM: Erasable Programmable ROM, which can be erased using ultraviolet light, allowing for reprogramming.
- EEPROM: Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM enables data to be rewritten and retains data without power.
- Flash Memory: A faster type of EEPROM used extensively in USB drives and SSDs due to its high speed and reliability.
Understanding the types of ROM is key for selecting the appropriate memory solution in digital system design.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to ROM Types
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
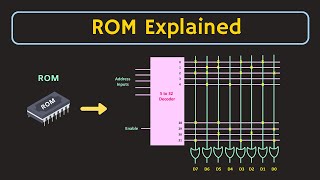
Types of ROM:
Type | Description
Mask | Programmed during manufacturing
PROM | Programmable once after manufacture
EPROM | Erasable via UV light
EEPROM | Electrically erasable and reprogrammable
Flash | Fast EEPROM variant; used in USBs, SSDs
Detailed Explanation
This chunk provides an overview of the different types of Read-Only Memory (ROM). Each type has unique characteristics and uses.
- Mask ROM: This type is programmed at the time of manufacturing, meaning the data is written into the chip during its production, and it cannot be changed afterward.
- PROM (Programmable ROM): This is a one-time programmable memory, meaning users can write data to it once, but it cannot be erased or rewritten afterward.
- EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM): Unlike PROM, EPROM can be erased by exposing it to UV light, allowing it to be reprogrammed multiple times.
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM): This memory can be erased and rewritten electrically, allowing for more flexibility compared to EPROM.
- Flash Memory: A type of EEPROM that is particularly fast and used in modern devices like USB drives and Solid State Drives (SSDs). This type can be erased and reprogrammed quickly, making it very convenient for everyday use.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the types of ROM as different kinds of books:
- Mask ROM is like a classic book printed permanently, you can’t change any words.
- PROM is like a diary where you can only write in it once; once you write, you can’t erase it.
- EPROM is similar to a dry erase board; you can write, then erase with a special method, and write again.
- EEPROM is like a regular chalkboard; you can erase and write on it as needed.
- Flash Memory is like a digital notepad, very easy to update, and convenient in your pocket!
Key Concepts
-
ROM: A non-volatile type of memory that permanently retains data without power.
-
Mask ROM: Fixed data programmed at manufacturing stage, not alterable.
-
PROM: A type of ROM that can only be programmed once after fabrication.
-
EPROM: Can be erased using ultraviolet light for reprogramming.
-
EEPROM: Allows for electrical erasure and reprogramming.
-
Flash Memory: An advanced type of EEPROM, known for speed and versatility.
Examples & Applications
Mask ROM is widely used in gaming consoles where fixed data is needed.
EEPROM is common in BIOS chips of computers where firmware needs to be updated.
Flash memory is utilized in USB drives and SSDs for portable data storage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
ROM is like a book we all can trust, keeps its tales in power, that’s a must.
Stories
Imagine a library (ROM) where some books (Mask ROM) are locked forever, while others (PROM) can only be read once, and some are rewritten easily (EEPROM). Flash memory is like the fastest librarian getting you the right book instantly.
Memory Tools
Remember MPEEF for Mask, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, Flash: Different ROM types serve distinct needs.
Acronyms
MPEEF
Mask
PROM
EPROM
EEPROM
Flash - types of ROM.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Mask ROM
Read-Only Memory programmed during manufacturing with fixed data.
- PROM
Programmable Read-Only Memory that can be written once after manufacturing.
- EPROM
Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory that can be erased using ultraviolet light.
- EEPROM
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory that can be reprogrammed without removing the chip.
- Flash Memory
A fast type of EEPROM used in various portable storage devices like USBs and SSDs.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
