ROM Cell
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to ROM Cells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to discuss ROM cells. Can anyone tell me what ROM stands for?

Read-Only Memory!

Correct! Now, how is ROM different from RAM?

ROM is non-volatile and retains data without power, while RAM is volatile and loses data when off.

Exactly right! Because of this, ROM is essential for storing firmware. Can anyone think of an example of firmware that uses ROM?

The BIOS in computers stores important boot instructions!

Great example! Remember, ROM cells have fixed states which differentiate them from RAM. Let's move to the types of ROM next.
Types of ROM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

There are several types of ROM. Who can name one of them?

Mask ROM is one type!

That's right! Mask ROM is programmed during manufacturing. Can anyone explain why this is beneficial?

Because it ensures the data is fixed and reliable!

Exactly! But what happens if we need to change that data?

We could use PROM! It can be programmed once after it's made.

Great! Now what about EPROM? What's special about it?

EPROMS can be erased using UV light!

Exactly! And EEPROMs can be erased electrically, making them versatile for repeated use.
Applications of ROM Cells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about the applications of ROM cells. Where do we often find them?

In embedded systems like microwaves or washing machines!

Right! They hold the control software. What about storage solutions like USBs?

USB drives use Flash memory, which is a type of EEPROM!

Nice connection! So, since ROM retains data permanently, why is that important for devices?

It allows devices to boot up correctly and maintain settings!

Yeah, like remembering my microwave's cooking times even when it's unplugged!

Exactly, that's the essence of why ROM cells are crucial in tech!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section focuses on Read-Only Memory (ROM) cells, emphasizing their role in non-volatile data retention in digital devices. These cells have fixed logic states, making them essential for applications requiring permanent data storage.
Detailed
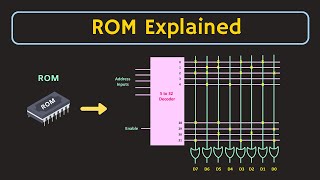
ROM Cells
ROM (Read-Only Memory) cells are a fundamental part of non-volatile memory in digital systems. Unlike volatile memory types like RAM, which lose their content when powered off, ROM cells retain their stored data without requiring continuous power. This characteristic makes them essential for applications such as firmware storage, boot loaders, and embedded systems.
Structure and Functioning
ROM cells are designed to hold data in a fixed state. The logical state of these cells can be hardwired or programmed during manufacturing processes. This non-volatility ensures that the data remains intact even when the device is turned off, which is crucial for system start-up and configuration.
Types of ROM
ROM includes various types, such as:
- Mask ROM: Programmed during manufacturing and cannot be altered later.
- PROM: Programmable once after manufacturing.
- EPROM: Can be erased using UV light and reprogrammed.
- EEPROM: Electrically erasable and can be rewritten multiple times.
- Flash Memory: A quicker variant of EEPROM used in USB drives and SSDs.
By understanding the design and operational principles of ROM cells, one can appreciate their pivotal role in digital memory architecture.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is a ROM Cell?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ROM Cell:
● Logic state is fixed (hardwired or programmed once)
Detailed Explanation
A ROM (Read-Only Memory) cell is a type of memory cell where the logic state is set and remains fixed. This means that once data is written to it, it cannot be changed or erased during normal operation. The ROM cell is designed to retain its information without needing power, making it non-volatile.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a ROM cell like a printed book. Once the book is printed, the words and information in it cannot be changed. Even if you take the book out of a library (representing power), the content remains the same, just like how a ROM cell retains its data without power.
Fixed Logic States
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Logic state is fixed (hardwired or programmed once)
Detailed Explanation
The term 'fixed logic state' refers to the fact that the data contained within a ROM cell is permanently established, either during manufacturing (hardwired) or programmed at a later point (such as with PROM). Once this state is set, it cannot be altered, providing a stable and reliable form of storage for essential data and instructions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a movie that has been recorded and distributed on a DVD. Once the DVD is created, it cannot be edited or changed. You can watch it as many times as you want, but the content remains the same, just like data stored in a ROM cell.
Applications of ROM Cells
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Used in various applications to store firmware and permanent data.
Detailed Explanation
ROM cells are crucial for applications where firmware (the software that is written to hardware) needs to be stored permanently. This includes the basic instructions required to boot up computers and embedded systems, allowing them to function correctly without needing to load any additional software every time they are powered on.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the BIOS in your computer. It's like the foundational knowledge of the system. It helps start your computer and gets it ready for use. The information stored in the BIOS is in ROM, ensuring it is always available and unchanged, similar to how your favorite family recipe book is kept safe and unchanged for years.
Key Concepts
-
Non-Volatility: ROM retains data without power.
-
Types of ROM: Includes Mask ROM, PROM, EPROM, and EEPROM.
-
Applications: Used in firmware, boot loaders, and various digital devices.
Examples & Applications
The BIOS of a computer is stored in ROM to ensure it initializes correctly on boot.
A washing machine uses ROM to store its control programs.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If you need to store a lot, and not forget a jot, use ROM in your tech, it holds memories that connect!
Stories
Once in the land of digital devices, there was a wise old ROM who never forgot. It knew all the boot instructions and firmware secrets while the forgetful RAM lost its memories every time the power went out.
Memory Tools
To remember the types of ROM: 'Mighty People Erase Everything' - Mask, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM.
Acronyms
Remember 'P.E.F.F.' for the types of ROM
PROM
EPROM
Flash Memory
and Mask.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ROM
Read-Only Memory; a type of non-volatile memory that retains data without power.
- Mask ROM
A type of ROM that is programmed during manufacturing and cannot be altered.
- PROM
Programmable Read-Only Memory; can be programmed once post-manufacturing.
- EPROM
Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory; can be erased using UV light.
- EEPROM
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory; can be reused multiple times.
- Flash Memory
A quick variant of EEPROM common in USB drives and SSDs.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
