Memory Addressing
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Memory Addresses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll delve into memory addressing. Each memory location has a unique binary address that the CPU uses to access data. Does anyone want to explain what a binary address is?

A binary address is a combination of 0s and 1s that identifies where data is stored in memory.

So, it’s like assigning a specific house number to a street, right?

Exactly, great analogy! Just as each house has a unique number, each memory location gets a unique binary address that the computer uses to find data. Now, who knows how many locations a 4-bit address can access?

I think it can access 16 locations because `2^4 = 16`.

Correct! And remember, this scales up. A 16-bit address bus can address 65,536 locations. This concept is critical as it drives how every piece of data is accessed within the computer.
Address Bus Width
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about the address bus width. How do you think the size of the address bus affects memory addressing?

I think a wider address bus means more locations can be accessed, right?

That's right! With an n-bit address bus, you can access `2^n` locations. So, why do you think computer architecture focuses on increasing address bus width?

To access more memory, especially as applications and data sizes grow!

Exactly. Upgrading the address bus can directly enhance a system's performance and capacity. Understanding this can help in designing systems with the necessary capabilities for future applications.
Real-world Application of Memory Addressing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s apply what we've learned. Can anyone think of a real-world application that relies on memory addressing?

GPS systems! They must access several locations quickly.

I read that video games also rely heavily on memory addressing to manage graphics and data.

Exactly! Whether it’s GPS systems, video games, or databases, effective memory addressing ensures that data is retrieved and processed accurately and efficiently. It's a crucial concept that underlies many technologies that we use daily.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Memory addressing involves a unique binary address assigned to each memory location, enabling the retrieval of data stored in digital systems. A memory bus width determines how many locations can be accessed, illustrated by the example of a 16-bit address bus capable of addressing 65,536 locations.
Detailed
Memory Addressing
Memory addressing is a fundamental concept in digital systems that enables the accessing of specific memory locations through unique binary addresses. Each memory location corresponds to a binary address, which is determined by the width of the address bus. For example, an n-bit address bus can access up to 2^n locations. To illustrate, a 16-bit address bus can access 2^16 = 65,536 locations, showcasing the relationship between address bus size and available memory space. This section is crucial for understanding how digital systems locate and manipulate stored data efficiently.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Memory Location Access
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
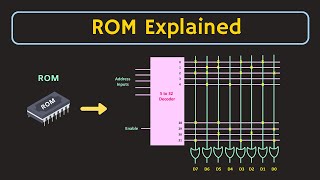
- Memory locations are accessed via a unique binary address.
Detailed Explanation
Each memory location in a computer is assigned a unique address that is represented in binary form. This binary address serves as a reference to locate and access the specific memory cell or location where data is stored. When the CPU needs to read or write data, it uses this unique address to pinpoint the correct location in memory.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a mail delivery system where each house has a unique postal address. Just like a mail carrier uses the address to deliver letters to the right home, the CPU uses the binary address to access the correct memory location for storing or retrieving data.
Address Bus and Its Capacity
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- nn-bit address bus can access 2^n locations.
- Example: 16-bit address bus → 2^16 = 65,536 locations.
Detailed Explanation
The width of the address bus is crucial in determining how many memory locations can be accessed. For an n-bit address bus, the number of addressable locations is calculated as 2 raised to the power of n (2^n). For instance, if we have a 16-bit address bus, this means we can access 2^16 locations, which equals 65,536 different memory addresses. This defines the capacity of memory that the system can effectively use.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a library where every book needs a unique number to identify it. If the library has 16 sections, each capable of holding 2^16 books, that means you can store up to 65,536 books in your library, just like a memory system can access 65,536 addresses with a 16-bit address bus.
Key Concepts
-
Memory Address: A unique binary identifier for a memory location.
-
Address Bus Width: The number of bits in the address bus determines how many memory locations can be accessed.
-
n-bit Address Bus: An address bus that can access
2^nmemory locations.
Examples & Applications
A 4-bit address bus can access 16 locations, as shown by the calculation 2^4 = 16.
A 16-bit address bus allows access to 65,536 locations, calculated by 2^16 = 65536.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To find data in your memory bank, a binary address is what you thank!
Stories
Imagine a librarian. Each book is a memory location, and every book has a specific code. Just like how the librarian uses that specific code to find the right book, a CPU uses a binary address to find data.
Memory Tools
ABCD: Address Bus Can Direct - Helps remember how address bus works.
Acronyms
B.A.D. - Binary Addresses Determine - Reminds that binary addresses are essential for determining memory access.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Memory Address
A unique binary number used to access a specific location in memory.
- Address Bus
A communication pathway that carries address signals from the CPU to the memory.
- nbit Address Bus
An address bus composed of n bits that can access
2^nmemory locations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
