RAM Organization
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
RAM as Volatile Memory
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's begin by discussing RAM, or Random Access Memory. Can anyone tell me what we mean by volatile memory?

I think volatile memory means it loses all its data when the power goes off.

Exactly right! RAM indeed loses its data when power is lost. This makes it very different from memory types like ROM. Why do you think this characteristic of RAM is important?

It allows quick access to data that's actively being used, right?

Yes! RAM is designed for speed, allowing CPU to access and manipulate data quickly. Think of it this way—like your workspace where you keep things you use often, RAM holds data temporarily.
RAM Addressable Locations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore how RAM is organized. RAM consists of addressable locations. Who can explain what that means?

Does that mean we can access any point in RAM directly?

Correct! Each location has a unique address, allowing direct access. Each of these locations can hold an n-bit word; can anyone give me an example of what n could be?

Like 8-bit or 16-bit words?

Exactly! The size affects how much information can be processed at once. Remember, larger word sizes can speed up processing for certain applications.
Importance of RAM Organization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think understanding RAM organization is important for computer system design?

I guess it helps optimize performance and ensures that applications run smoothly?

Exactly! Proper RAM organization can minimize time delays in data access. In what situations do you think this would be critical?

Like when running resource-heavy applications or when multiple applications are open?

Correct! Running multiple applications simultaneously demands efficient RAM usage to maintain speed. That's why it’s critical to design systems with the right amount of RAM.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
RAM (Random Access Memory) organization is pivotal for temporary data storage during execution, characterized by its volatile nature, where data is lost upon power loss. Each addressable location in RAM can store a specific n-bit word, necessitating an understanding of how memory is structured for efficient computer operations.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of RAM Organization
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a fundamental component of digital systems, primarily used for temporary data storage during active execution. In essence, RAM is considered volatile memory, meaning all stored data is lost when power is turned off. One of its defining characteristics is the ability to perform both read and write operations, which is essential for processing tasks on computers.
Key Concepts of RAM Organization
- Addressable Locations: RAM is organized into several addressable locations, where each location can store an n-bit word. The specific size of the word (like 8-bit or 16-bit) can impact the efficiency of the data processing tasks.
- Structure: The structure comprises rows and columns where data is stored, enabling direct access to any specific location without needing to go through other locations sequentially.
- Volatility: The volatile nature of RAM signifies that it only holds data during operational periods, which differs from non-volatile memory types that retain data without power.
Understanding the organization of RAM is crucial as it plays a significant role in the overall performance and efficiency of computer systems, particularly when it comes to executing programs and managing data flow.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
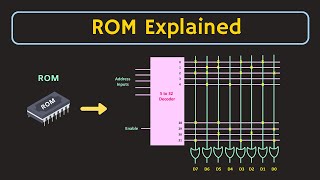
Addressable Locations
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Organized in addressable locations
Detailed Explanation
RAM (Random Access Memory) is structured in a way that each storage unit has a specific address. This organization allows the CPU to retrieve any piece of data quickly by specifying its address. This is like having a library where every book has a unique code, making it easy for anyone to find a specific book quickly.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a large library where books are organized on shelves. Each shelf has a number, and every book on that shelf has a unique title. If someone wants to find a particular book, they just look for the shelf number and then spot the title on that shelf. Similarly, in RAM, each data point has a unique address that makes it easy to access.
Storage of n-bit Words
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Each location stores n-bit word (e.g., 8-bit, 16-bit)
Detailed Explanation
Each addressable location in RAM can store a number of bits defined by 'n'. This bit size (like 8, 16, or even 32 bits) indicates how much information can be held at that location. For example, an 8-bit word can hold values from 0 to 255, while a 16-bit word can hold values from 0 to 65535. This capacity is crucial for determining how much data a RAM module can handle in a single access.
Examples & Analogies
Think of each location in RAM like a small container for holding marbles. An 8-bit container can hold up to 256 marbles, while a 16-bit container can hold many more—65536 marbles, to be exact. Just like if you had different sizes of containers, the size of the RAM word defines how much data can be held in each memory location.
Key Concepts
-
Addressable Locations: RAM is organized into several addressable locations, where each location can store an n-bit word. The specific size of the word (like 8-bit or 16-bit) can impact the efficiency of the data processing tasks.
-
Structure: The structure comprises rows and columns where data is stored, enabling direct access to any specific location without needing to go through other locations sequentially.
-
Volatility: The volatile nature of RAM signifies that it only holds data during operational periods, which differs from non-volatile memory types that retain data without power.
-
Understanding the organization of RAM is crucial as it plays a significant role in the overall performance and efficiency of computer systems, particularly when it comes to executing programs and managing data flow.
Examples & Applications
Accessing an 8-bit or 16-bit variable in a Python program involves RAM addressable locations storing the variable values temporarily during computation.
A web browser uses RAM to store information about open tabs, allowing quick access while running multiple applications.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
RAM is fast and quite essential, it makes our computing very potential!
Stories
Imagine RAM as a desk full of papers that can be quickly accessed and written upon. When the desk is cleared, everything is lost—this illustrates the volatile memory nature of RAM.
Memory Tools
Remember RAM's role: 'Rapid Access Memory' which signifies fast data retrieval.
Acronyms
Use 'VARD' for RAM characteristics
Volatile
Addressable
Read/write
Data focused.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
A type of volatile memory that allows both read and write operations for temporary data storage during execution.
- Addressable Locations
Specific memory locations in RAM where data is stored, each identified by a unique address.
- Volatile Memory
Type of memory that loses its contents when power is turned off.
- nbit Word
A unit of data size where 'n' indicates the number of bits; common sizes include 8-bit and 16-bit.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
