Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FETs
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FETs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into Nanosheet and Nanoribbon FETs—what are they and why are they significant for future semiconductor technology? Can anyone summarize what a FET is?

A FET is a type of transistor that controls the flow of current using an electric field.

Correct! Now, Nanosheet FETs use wider channels than nanowires. Why do you think that would be beneficial?

Wider channels could allow for more current to flow, right?

Exactly! This higher drive current can significantly enhance performance. Can anyone guess what a stackable design means?

It means you can put multiple devices on top of each other, saving space!

Well said! This approach allows for more transistors in less area, which is crucial for meeting future demands.
Benefits of Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FETs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand why stackability is important, let’s talk about the advantages of using Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FETs over FinFETs. What do you think some advantages might be?

Maybe they have better control over the current?

Yes! They offer improved gate control. Plus, the higher drive current can lead to faster processing speeds. How could more drive current benefit us in real-world applications?

It would allow devices to run faster and handle more tasks at once.

Exactly! This capacity for enhanced functionality will drive the development of advanced electronics.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores Nanosheet and Nanoribbon FETs as emerging semiconductor technologies that offer advantages over traditional FinFETs. With wider channels, these devices enable higher drive currents and a stackable design that enhances device density. This adaptability is crucial for future semiconductor scaling.
Detailed
Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FETs
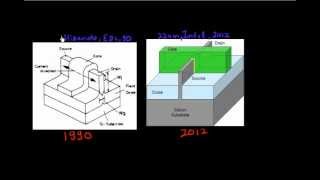
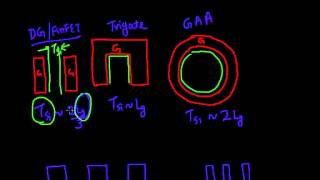
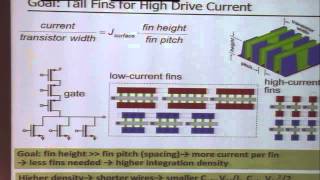
Nanosheet and Nanoribbon Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) are innovative semiconductor devices designed to address the limitations experienced with FinFET technology as scaling reaches practical limits. By utilizing wider channels compared to nanowires, these FETs can achieve higher drive current, which is essential for improved performance in high-density applications.
One of the key benefits of Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FETs is their stackable design, allowing multiple layers of these devices to be integrated vertically, leading to increased transistor count in a smaller footprint. This is particularly important as the semiconductor industry seeks to enhance performance while maintaining energy efficiency. The advancements in Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FET technology provide promising pathways to continue fulfilling the demand for more powerful and efficient devices, supporting future technology scaling.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FETs
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FETs
● Wider channels than nanowires → higher drive current.
● Stackable design improves density.
Detailed Explanation
Nanosheet and nanoribbon FETs are advanced transistor structures that overcome some limitations of traditional components like nanowires. One of their main advantages is that they have wider channels. This means they can carry more electrical current (higher drive current). A wider channel can allow for more efficient operation, which is crucial for more powerful and faster electronic devices. Additionally, the stackable design of these FETs enhances the overall density of devices, allowing for more components to fit into a smaller space.
Examples & Analogies
Think of nanosheet FETs like a wide, multi-lane highway. The wider lanes (wider channels) allow for more cars (electrical current) to travel at the same time, reducing traffic jams (performance bottlenecks). This design also acts like a layered cake, where you can stack additional layers (transistor components) vertically, increasing the amount of cake in a given area, much like increasing device density.
Performance Advantages
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Higher drive current enables superior performance in electronic applications.
Detailed Explanation
The ability to support higher drive current means that nanosheet and nanoribbon FETs can perform better than previous generations of transistors. When these transistors are used in circuits, they can enhance the speed and efficiency with which the circuits operate. This is particularly important for applications requiring fast data processing, such as in smartphones, computers, and data centers.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine if your local coffee shop decided to add more baristas during the morning rush. With more people making coffee (higher drive current), orders are fulfilled faster, resulting in a shorter wait time for customers and a more efficient service. Similarly, in electronics, higher drive current helps fulfill processing tasks more quickly and efficiently.
Density Improvements
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Stackable design improves density.
Detailed Explanation
The stackable aspect of nanosheet FETs refers to their design which allows multiple layers of these devices to be placed on top of each other. This three-dimensional approach increases the number of transistors that can be fit into a given area, known as device density. Higher density is important in modern electronics because it allows manufacturers to create smaller, more powerful devices without increasing their size.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a bookshelf: if you can stack books vertically (stackable design), you can fit more books in a single shelf space compared to laying them flat. In technology, stacking components allows for more processing power and features in devices without making them bulkier, similar to a compact bookshelf packed with books.
Key Concepts
-
Wider Channels: Nanosheet/Nanoribbon FETs feature wider channels than traditional nanowires, leading to higher drive currents.
-
Stackable Design: Ability to integrate multiple FETs vertically for increased density and performance.
Examples & Applications
In smartphone technology, Nanosheet FETs can enable faster processors, improving app performance.
In memory devices, the stackable design of Nanosheet FETs helps create denser memory chips.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Nanosheets stack high, currents that fly, performance that won’t die!
Stories
Imagine a city of skyscrapers (stackable FETs) where each building allows more people (current) to live and work, optimizing space and resources.
Memory Tools
WIDE: Wider channels Increase Drive current Efficiency.
Acronyms
SNAP
Stackable Nanosheet FETs Achieve Performance.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Nanosheet FET
A type of field-effect transistor with a channel structure that is wider than a nanowire, allowing for increased drive current.
- Nanoribbon FET
A field-effect transistor characterized by a channel in the shape of a ribbon, beneficial for tighter integration and improved performance.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
